Abstract
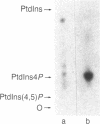
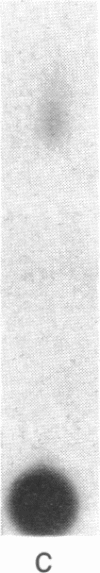
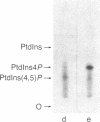
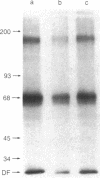
The transforming protein of avian sarcoma virus UR2, p68v-ros, has an associated tyrosine-specific protein kinase activity similar to that of p60v-src and several other oncogene products. However, this activity has not been linked unequivocally to transformation, and the physiological action of these proteins remains in doubt. We now have found that immunoprecipitated p68v-ros also is associated with phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns) kinase (ATP:PtdIns 4-phosphotransferase, EC 2.7.1.67) activity. PtdIns 4,5-bisphosphate [PtdIns(4,5)P2] specifically inhibits both this activity and the autophosphorylation of p68v-ros. Moreover, cells transformed by UR2 showed significant increases in 32P-labeling of PtdIns 4-phosphate (PtdIns4P) and PtdIns(4,5)P2 and in the formation of their catabolites, inositol 1,4-bisphosphate and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate, as compared to uninfected cells. These results suggest that a physiologically relevant function of oncogene kinases might be the phosphorylation of PtdIns and that increased turnover of PtdIns4P and PtdIns(4,5)P2 might play a role in transformation by increasing the formation of diacylglycerol, a catabolite of polyphosphoinositides that activates kinase C. This protein copurifies with the phorbol ester receptor, and its activation is likely to be intimately linked with mitogenesis. This hypothesis suggests a mechanism whereby certain oncogene proteins might cause the unrestricted growth typical of transformed cells and could explain why tumor promoters mimic many of the effects of transformation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balduzzi P. C., Notter M. F., Morgan H. R., Shibuya M. Some biological properties of two new avian sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):268–275. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.268-275.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. L., Majerus P. W. Thrombin-induced hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):1790–1792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Dawson R. M., Downes C. P., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F. Changes in the levels of inositol phosphates after agonist-dependent hydrolysis of membrane phosphoinositides. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):473–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2120473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostwick J. R., Eichberg J. Detergent solubilization and hydrophobic chromatography of rat brain phosphatidylinositol kinase. Neurochem Res. 1981 Oct;6(10):1053–1065. doi: 10.1007/BF00964412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley J. T. Properties of human erythrocyte phosphatidylinositol kinase and inhibition by adenosine, ADP and related compounds. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jun 23;498(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90081-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Carpenter G., King L., Jr Epidermal growth factor-receptor-protein kinase interactions. Co-purification of receptor and epidermal growth factor-enhanced phosphorylation activity. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4834–4842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Hunter T. Identification and characterization of cellular targets for tyrosine protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1108–1115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Reiss N. A., Schwartz R. J., Hunter T. Three glycolytic enzymes are phosphorylated at tyrosine in cells transformed by Rous sarcoma virus. Nature. 1983 Mar 17;302(5905):218–223. doi: 10.1038/302218a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J., Nakamura K. D., Hunter T., Weber M. J. Phosphotyrosine-containing proteins and expression of transformation parameters in cells infected with partial transformation mutants of Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):15–28. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.15-28.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diringer H., Friis R. R. Changes in phosphatidylinositol metabolism correlated to growth state of normal and Rous sarcoma virus-transformed Japanese quail cells. Cancer Res. 1977 Sep;37(9):2979–2984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Michell R. H. The polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase of erythrocyte membranes. Biochem J. 1981 Jul 15;198(1):133–140. doi: 10.1042/bj1980133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Larson R. E., Sabir M. A. Insulin acutely increases phospholipids in the phosphatidate-inositide cycle in rat adipose tissue. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4042–4045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman R. A., Hanafusa T., Hanafusa H. Characterization of protein kinase activity associated with the transforming gene product of Fujinami sarcoma virus. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):757–765. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90552-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman R. A., Wang L. H., Hanafusa H., Balduzzi P. C. Avian sarcoma virus UR2 encodes a transforming protein which is associated with a unique protein kinase activity. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):228–236. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.228-236.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziani Y., Erikson E., Erikson R. L. Evidence that the Rous sarcoma virus transforming gene product is associated with glycerol kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2126–2129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habenicht A. J., Glomset J. A., King W. C., Nist C., Mitchell C. D., Ross R. Early changes in phosphatidylinositol and arachidonic acid metabolism in quiescent swiss 3T3 cells stimulated to divide by platelet-derived growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12329–12335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Ek B., Rönnstrand L. Characterization of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor on human fibroblasts. Demonstration of an intimate relationship with a 185,000-Dalton substrate for the platelet-derived growth factor-stimulated kinase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):10054–10061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. Protein phosphorylated by the RSV transforming function. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):647–648. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90539-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1311–1315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwashita S., Kitamura N., Yoshida M. Molecular events leading to fusiform morphological transformation by partial src deletion mutant of Rous sarcoma virus. Virology. 1983 Mar;125(2):419–431. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90213-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Zick Y., Blithe D. L., Crettaz M., Kahn C. R. Insulin stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of the insulin receptor in a cell-free system. Nature. 1982 Aug 12;298(5875):667–669. doi: 10.1038/298667a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto A., Takai Y., Mori T., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Activation of calcium and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by diacylglycerol, its possible relation to phosphatidylinositol turnover. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2273–2276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft A. S., Anderson W. B. Characterization of cytosolic calcium-activated phospholipid-dependent protein kinase activity in embryonal carcinoma cells. Effect of retinoc acid-induced differentiation of F9 cells to parietal endoderm. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9178–9183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft A. S., Anderson W. B. Phorbol esters increase the amount of Ca2+, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase associated with plasma membrane. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):621–623. doi: 10.1038/301621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Inositol phospholipids and cell surface receptor function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):81–47. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedel J. E., Kuhn L. J., Vandenbark G. R. Phorbol diester receptor copurifies with protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):36–40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richert N. D., Blithe D. L., Pastan I. Properties of the src kinase purified from Rous sarcoma virus-induced rat tumors. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):7143–7150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E. Stimulation of Na influx, Na-K pump activity and DNA synthesis in quiescent cultured cells. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1980;19:61–85. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(81)90009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sando J. J., Young M. C. Identification of high-affinity phorbol ester receptor in cytosol of EL4 thymoma cells: requirement for calcium, magnesium, and phospholipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2642–2646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer S. T., Cohen S. Enhancement of calcium uptake and phosphatidylinositol turnover by epidermal growth factor in A-431 cells. Biochemistry. 1981 Oct 13;20(21):6280–6286. doi: 10.1021/bi00524a057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schartl M., Barnekow A. The expression in eukaryotes of a tyrosine kinase which is reactive with pp60v-src antibodies. Differentiation. 1982;23(2):109–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1982.tb01273.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatzman R. C., Grifo J. A., Merrick W. C., Kuo J. F. Phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates the beta subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 (eIF-2). FEBS Lett. 1983 Aug 8;159(1-2):167–170. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80439-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serhan C. N., Broekman M. J., Korchak H. M., Smolen J. E., Marcus A. J., Weissmann G. Changes in phosphatidylinositol and phosphatidic acid in stimulated human neutrophils. Relationship to calcium mobilization, aggregation and superoxide radical generation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jun 2;762(3):420–428. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(83)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya M., Hanafusa H., Balduzzi P. C. Cellular sequences related to three new onc genes of avian sarcoma virus (fps, yes, and ros) and their expression in normal and transformed cells. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):143–152. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.143-152.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streb H., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., Schulz I. Release of Ca2+ from a nonmitochondrial intracellular store in pancreatic acinar cells by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1983 Nov 3;306(5938):67–69. doi: 10.1038/306067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Kishimoto A., Iwasa Y., Kawahara Y., Mori T., Nishizuka Y. Calcium-dependent activation of a multifunctional protein kinase by membrane phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):3692–3695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Kishimoto A., Kikkawa U., Mori T., Nishizuka Y. Unsaturated diacylglycerol as a possible messenger for the activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Dec 28;91(4):1218–1224. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91197-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuy F. P., Henry J., Rosenfeld C., Kahn A. High tyrosine kinase activity in normal nonproliferating cells. 1983 Sep 29-Oct 5Nature. 305(5933):435–438. doi: 10.1038/305435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]