Abstract
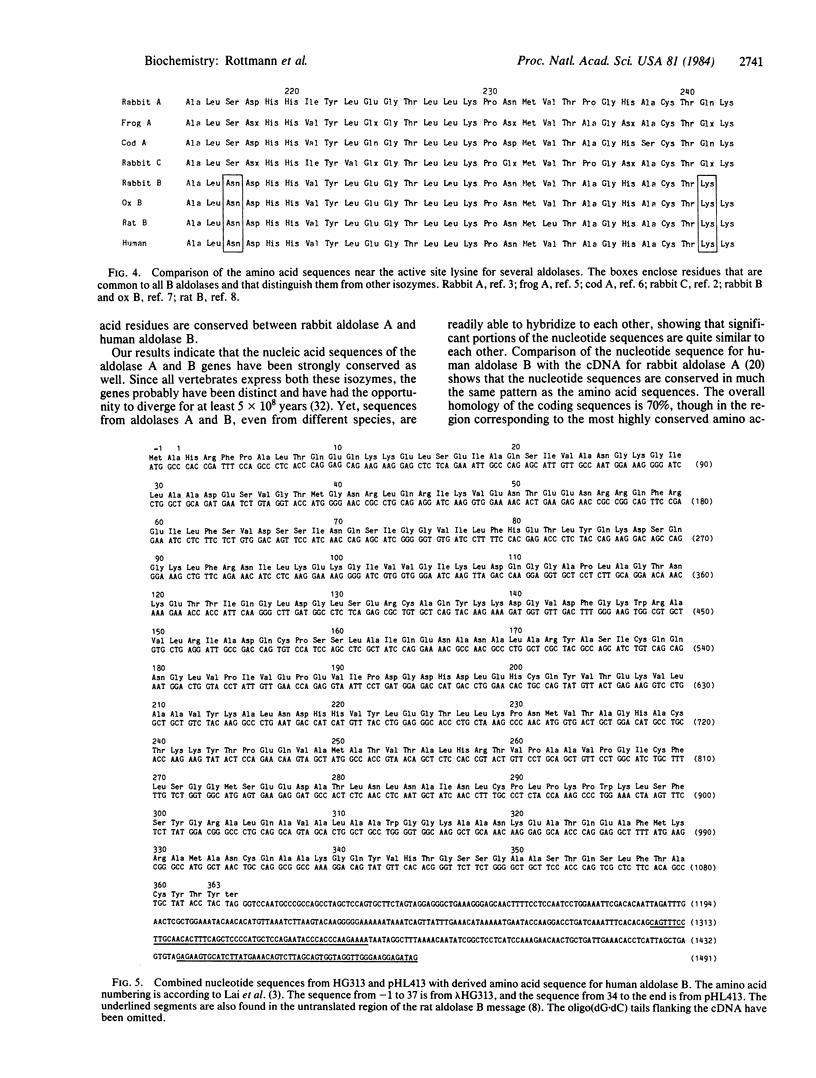
Several aldolase B clones from a human liver cDNA library have been identified by using a rabbit aldolase A cDNA as a hybridization probe. The most complete of these, pHL413, is 1389 base pairs long and covers approximately equal to 80% of the length of the mRNA, including 90% of the translated region. The cDNA, pHL413, was used to identify a genomic clone, lambda HG313, which encoded the remaining amino acids of human aldolase B. We demonstrate that the amino acid and nucleotide sequences of aldolase are strongly conserved even between different isozymes. Furthermore, in the 3'-untranslated regions of the mRNAs for the B isozyme of human and rat there is an extensive stretch of homology. Aldolase B lacks a cysteine at positions 72 and 338 and lacks a histidine at position 361. These residues, which are present in rabbit aldolase A, have previously been proposed to take part in catalysis. Our findings suggest that this may not be the case.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelman R. C., Morris H. P., Weinhouse S. Fructokinase, triokinase, and aldolases in liver tumors of the rat. Cancer Res. 1967 Dec;27(12):2408–2413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P. J. The number, location, and reactivity of the cysteine residues of sturgeon muscle aldolase. Can J Biochem. 1972 Feb;50(2):111–119. doi: 10.1139/o72-014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benfield P. A., Forcina B. G., Gibbons I., Perham R. N. Extended amino acid sequences around the active-site lysine residue of class-I fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolases from rabbit muscle, sturgeon muscle, trout muscle and ox liver. Biochem J. 1979 Nov 1;183(2):429–444. doi: 10.1042/bj1830429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costanzo F., Castagnoli L., Dente L., Arcari P., Smith M., Costanzo P., Raugei G., Izzo P., Pietropaolo T. C., Bougueleret L. Cloning of several cDNA segments coding for human liver proteins. EMBO J. 1983;2(1):57–61. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01380.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagert M., Ehrlich S. D. Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells. Gene. 1979 May;6(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FROESCH E. R., WOLF H. P., BAITSCH H., PRADER A., LABHART A. Hereditary fructose intolerance. An inborn defect of hepatic fructose-1-phosphate splitting aldolase. Am J Med. 1963 Feb;34:151–167. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(63)90050-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gliksman R., Ghosh N. K., Cox R. P. Comparison of aldolase isozymes in placenta, HeLa cells, and human fibroblast cultures. Enzyme. 1977;22(6):416–419. doi: 10.1159/000458828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godson G. N., Vapnek D. A simple method of preparing large amounts of phiX174 RF 1 supercoiled DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 11;299(4):516–520. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90223-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman F. C., Brown J. P. Affinity labeling of a previously undetected essential lysyl residue in class I fructose bisphosphate aldolase. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 25;251(10):3057–3062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman F. C., Welch M. H. Identification of the histidyl residue of rabbit muscle aldolase alkylated by N-bromoacetylethanolamine phosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Mar 15;57(1):85–92. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80360-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffee P., Lai C. Y., Pugh E. L., Horecker B. L. The function of histidine residues in rabbit muscle aldolase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jan;57(1):107–113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. Y., Chen C. Codfish muscle aldolase: purification, properties, and primary structure around the substrate-binding site. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Jun;144(2):467–475. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90350-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. Y., Nakai N., Chang D. Amino acid sequence of rabbit muscle aldolase and the structure of the active center. Science. 1974 Mar;183(130):1204–1206. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4130.1204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn R. M., Fritsch E. F., Parker R. C., Blake G., Maniatis T. The isolation and characterization of linked delta- and beta-globin genes from a cloned library of human DNA. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1157–1174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebherz H. G., Rutter W. J. Distribution of fructose diphosphate aldolase variants in biological systems. Biochemistry. 1969 Jan;8(1):109–121. doi: 10.1021/bi00829a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mainwaring W. I., Mangan F. R., Irving R. A., Jones D. A. Specific changes in the messenger ribonucleic acid content of the rat ventral prostate gland after androgenic stimulation. Evidence from the synthesis of aldolase messenger ribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1974 Nov;144(2):413–426. doi: 10.1042/bj1440413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patthy L., Váradi A., Thész J., Kovács K. Identification of the C-1-phosphate-binding arginine residue of rabbit-muscle aldolase. Isolation of 1,2-cyclohexanedione-labeled peptide by chemisorption chromatography. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Sep;99(2):309–313. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penhoet E. E., Kochman M., Rutter W. J. Molecular and catalytic properties of aldolase C. Biochemistry. 1969 Nov;8(11):4396–4402. doi: 10.1021/bi00839a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penhoet E., Kochman M., Valentine R., Rutter W. J. The subunit structure of mammalian fructose diphosphate aldolase. Biochemistry. 1967 Sep;6(9):2940–2949. doi: 10.1021/bi00861a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAPIRA F., DREYFUS J. C., SCHAPIRA G. ANOMALY OF ALDOLASE IN PRIMARY LIVER CANCER. Nature. 1963 Dec 7;200:995–997. doi: 10.1038/200995a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAPIRA F., SCHAPIRA G., DREYFUS J. C. [The enzymatic defect of benign fructosuria]. Enzymol Biol Clin (Basel) 1961;1:170–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman B. M., Green H. Control of specific protein biosynthesis during the adipose conversion of 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8811–8818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman H. M., Richards F. M. Participation of cysteinyl residues in the structure and function of muscle aldolase. Characterization of mixed disulfide derivatives. Biochemistry. 1970 Oct 27;9(22):4360–4372. doi: 10.1021/bi00824a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ting S. M., Lai C. Y., Horecker B. L. Primary structure at the active sites of beef and rabbit liver aldolases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Jun;144(2):476–484. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90351-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ting S. M., Sia C. L., Lai C. Y., Horecker B. L. Frog muscle aldolase: purification of the enzyme and structure of the active site. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Jun;144(2):485–490. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90352-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolan D. R., Amsden A. B., Putney S. D., Urdea M. S., Penhoet E. E. The complete nucleotide sequence for rabbit muscle aldolase A messenger RNA. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):1127–1131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsutsumi K., Mukai T., Hidaka S., Miyahara H., Tsutsumi R., Tanaka T., Hori K., Ishikawa K. Rat aldolase isozyme gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6537–6542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villa-Komaroff L., Efstratiadis A., Broome S., Lomedico P., Tizard R., Naber S. P., Chick W. L., Gilbert W. A bacterial clone synthesizing proinsulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3727–3731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R., Alberts B. M., Benzinger R., Lawhorne L., Treiber G. Rapid bacteriophage sedimentation in the presence of polyethylene glycol and its application to large-scale virus purification. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):734–744. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90218-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]