Abstract
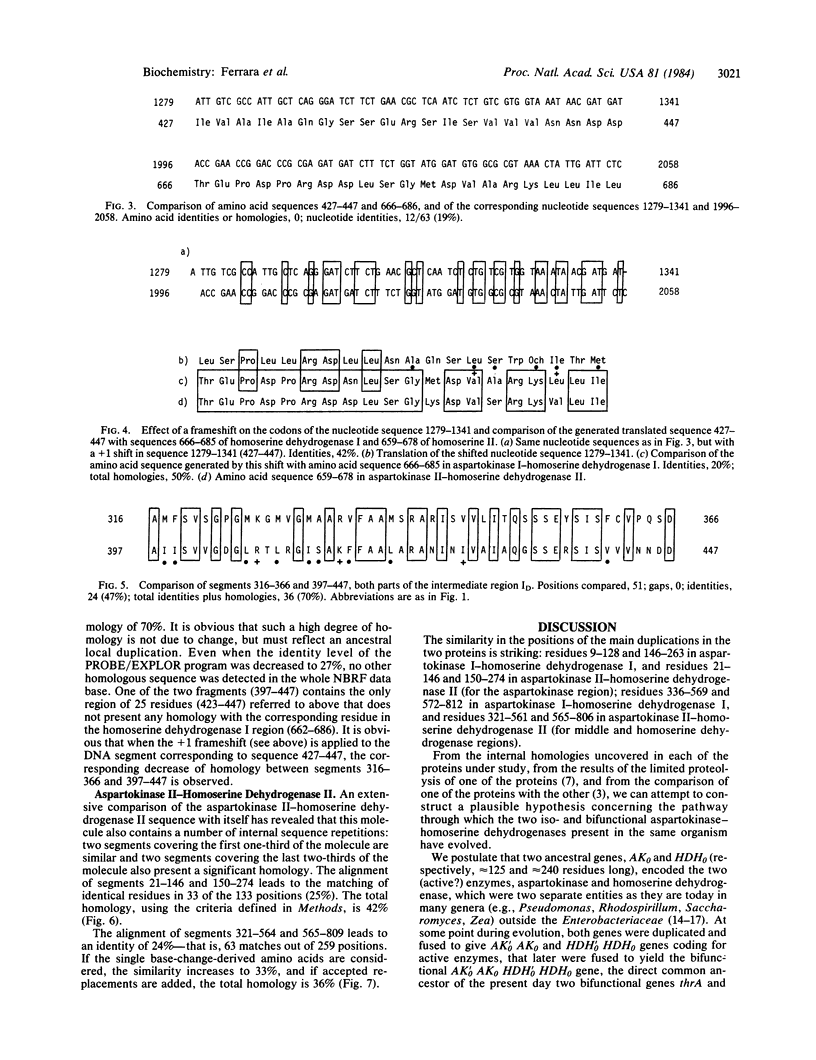
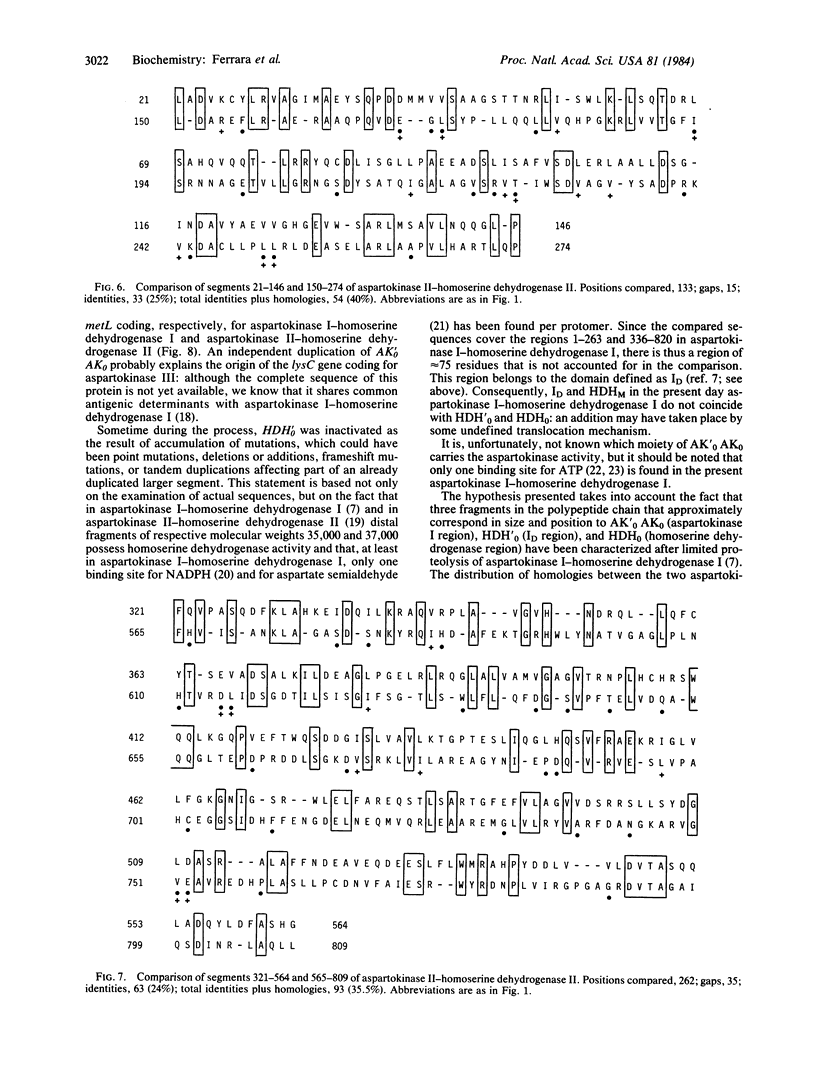
In Escherichia coli, AK I- HDH I and AK II- HDH II are two bifunctional proteins, derived from a common ancestor, that catalyze the first and third reactions of the common pathway leading to threonine and methionine. An extensive amino acid sequence comparison of both molecules reveals two main features on each of them: (i) two segments, each of about 130 amino acids, covering the first one-third of the polypeptide chain, are similar to each other and (ii) two segments, each of about 250 amino acids and covering the COOH-terminal 500 amino acids also present a significant homology. These findings suggest that these two regions may have evolved independently of each other by a process of gene duplication and fusion previous to the appearance of an ancestral aspartokinase-homoserine dehydrogenase molecule.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bryan J. K. Studies on the catalytic and regulatory properties of homoserine dehydrogenase of Zea mays roots. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Feb 11;171(2):205–216. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90154-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claverie J. M. A common philosophy and FORTRAN 77 software package for implementing and searching sequence databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):397–407. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen N., Burkart W., Lo Sasso T., Parkinson W. W., Jr, Henley L. C. Curium excretion studies in man and baboon: a predictive animal model. Health Phys. 1983;44 (Suppl 1):403–409. doi: 10.1097/00004032-198306001-00038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dautry-Varsat A., Cohen G. N. Proteolysis of the bifunctional methionine-repressible aspartokinase II-homoserine dehydrogenase II of Escherichia coli K12. Production of an active homoserine dehydrogenase fragment. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7685–7689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich R. S., Takahashi M. Threonine-sensitive aspartokinase from Escherichia coli. Magnetic resonance and binding studies. Biochemistry. 1973 Oct 23;12(22):4309–4315. doi: 10.1021/bi00746a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazel A., Müller K., Le Bras G., Garel J. R., Véron M., Cohen G. N. A triglobular model for the polypeptide chain of aspartokinase I-homoserine dehydrogenase I of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 4;22(1):158–165. doi: 10.1021/bi00270a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirth C. G., Véron M., Villar-Palasi C., Hurion N., Cohen G. N. The threonine-sensitive homoserine dehydrogenase and aspartokinase activities of Escherichia coli K12. Specific inactivation of the homoserine dehydrogenase activity by the affinity label, 2-amino-4-oxo-5-chloropentanoic acid. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jan 2;50(2):425–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb09819.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katinka M., Cossart P., Sibilli L., Saint-Girons I., Chalvignac M. A., Le Bras G., Cohen G. N., Yaniv M. Nucleotide sequence of the thrA gene of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5730–5733. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert-Gero M., Le Borgne L., Cohen G. N. Concerted feedback inhibition of the aspartokinase of Rhodospirillum tenue by threonine and methionine: a novel pattern. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):251–258. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.251-258.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert-Gero M., Poiret M., Cohen G. N. The aspartate kinase of Pseudomonas putida. Regulation of synthesis and activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Apr 22;206(1):17–30. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90077-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robichon-Szulmajster H., Surdin Y., Mortimer R. K. Genetic and biochemical studies of genes controlling the synthesis of threonine and methionine in Saccharomyces. Genetics. 1966 Mar;53(3):609–619. doi: 10.1093/genetics/53.3.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibilli L., Le Bras G., Le Bras G., Cohen G. N. Two regions of the bifunctional protein aspartokinase I- homoserine dehydrogenase I are connected by a short hinge. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 25;256(20):10228–10230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. F., Waterman M. S., Fitch W. M. Comparative biosequence metrics. J Mol Evol. 1981;18(1):38–46. doi: 10.1007/BF01733210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truffa-Bachi P., Heck H. A. Threonine-sensitive aspartokinase-homoserine dehydrogenase of Escherichia coli K 12. Reaction with 6-mercapto-9- -D-ribofuranosylpurine 5'-triphosphate. Biochemistry. 1971 Jul 6;10(14):2700–2706. doi: 10.1021/bi00790a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Véron M., Falcoz-Kelly F., Cohen G. N. The threonine-sensitive homoserine dehydrogenase and aspartokinase activities of Escherichia coli K12. The two catalytic activities are carried by two independent regions of the polypeptide chain. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Aug 4;28(4):520–527. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01939.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Véron M., Saari J. C., Villar-Palasi C., Cohen G. N. The threonine-sensitive homoserine dehydrogenase and aspartokinase activities of Escherichia coli K 12. Intra and intersubunit interactions between the catalytic regions of the bifunctional enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Oct 5;38(2):325–335. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03065.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakin M. M., Duchange N., Ferrara P., Cohen G. N. Nucleotide sequence of the metL gene of Escherichia coli. Its product, the bifunctional aspartokinase ii-homoserine dehydrogenase II, and the bifunctional product of the thrA gene, aspartokinase I-homoserine dehydrogenase I, derive from a common ancestor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3028–3031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakin M. M., Poskus E., Langton A. A., Ferrara P., Santomé J. A., Dellacha J. M., Paladini A. C. Primary structure of equine growth hormone. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1976;8(5):435–444. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1976.tb02523.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


