Abstract
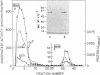
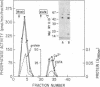
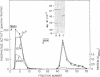
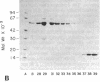
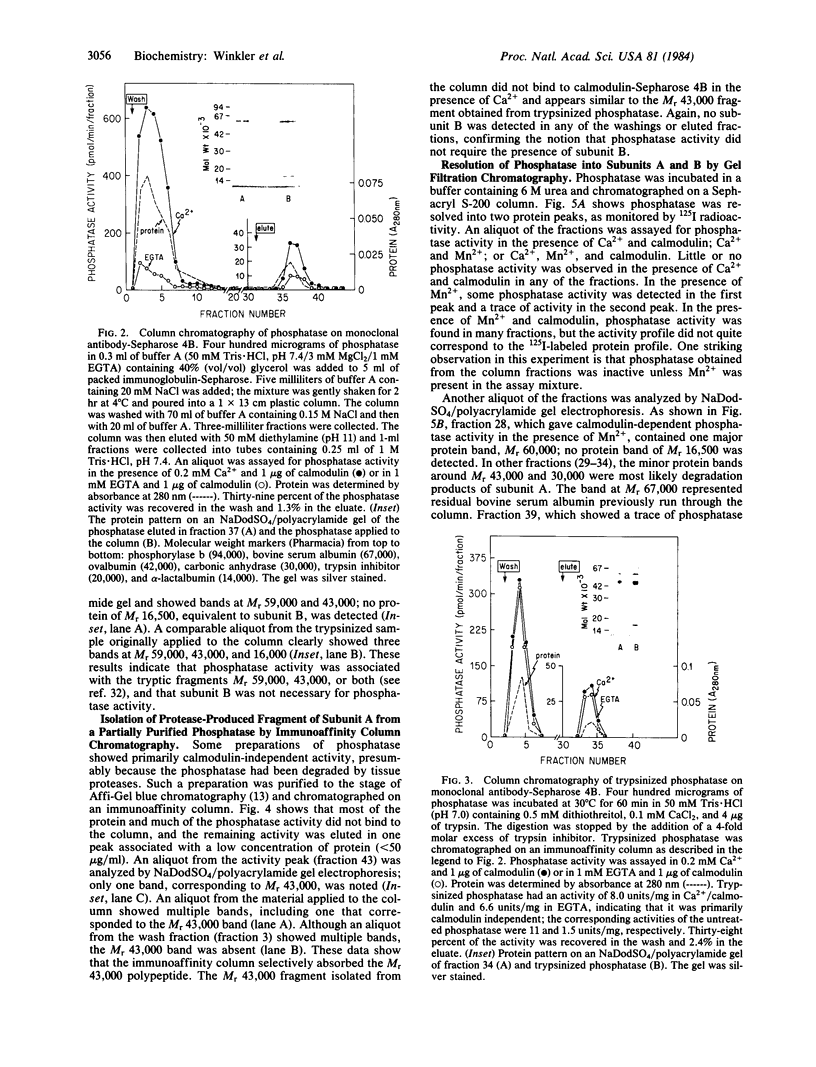
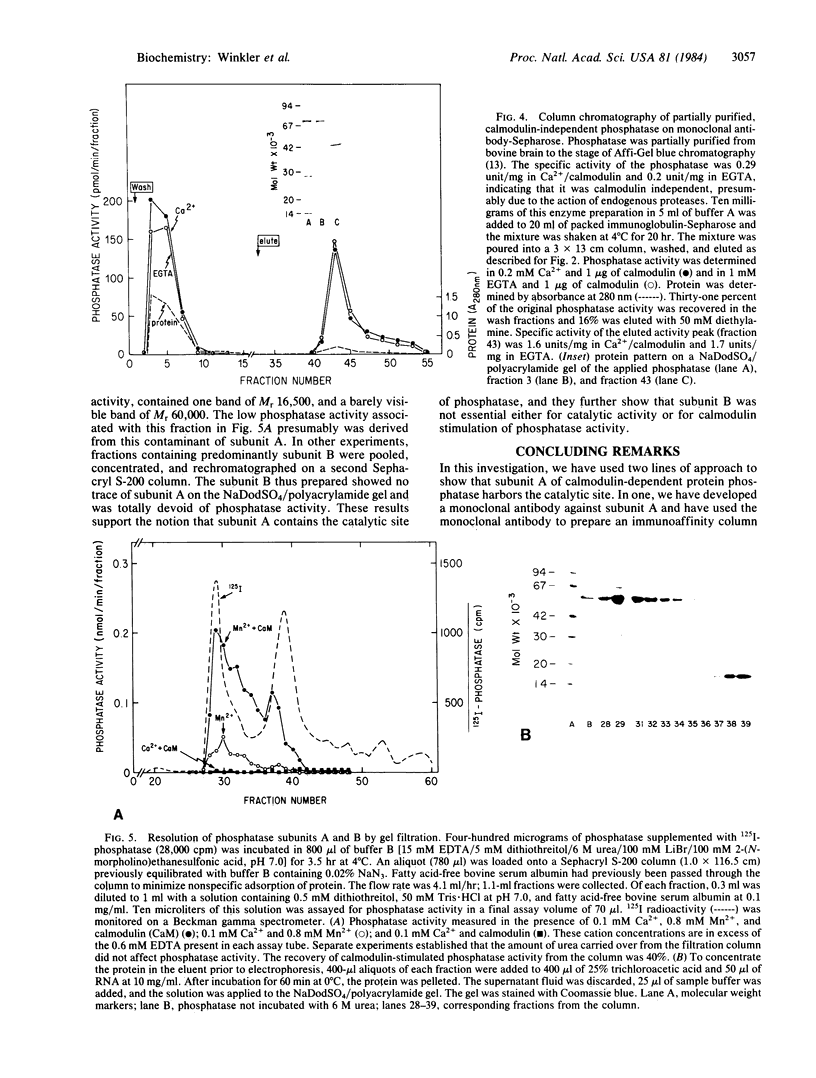
The calmodulin-dependent protein phosphatase from bovine brain is composed of two subunits: subunit A, Mr 60,000, and subunit B, Mr 16,500. Using in vitro immunization techniques, we have produced a monoclonal antibody specific for the phosphatase. The antibody was immobilized to Sepharose 4B to prepare an immunoabsorbent column, which was used to purify the enzyme. Phosphatase isolated from the column showed a polypeptide with Mr 60,000, equivalent to subunit A, which showed calmodulin-dependent phosphatase activity. Subunit B was not obtained from the column. Limited trypsin digestion stimulated phosphatase activity, yielding polypeptides of Mr 59,000, 43,000, and 16,000; the phosphatase activity after trypsin digestion was calmodulin independent. Chromatography of trypsin-treated phosphatase on an immunoaffinity column yielded two proteins, Mr 59,000 and 43,000, that were catalytically active and calmodulin independent. In a separate experiment, the two subunits of the phosphatase were separated by gel filtration in 6 M urea. Subunit A isolated from the filtration column showed little or no activity in the presence of Ca2+ and calmodulin, but it showed calmodulin-dependent phosphatase activity in the presence of 0.8 mM Mn2+. Subunit B was catalytically inactive. Collectively, these results indicate that subunit A and its proteolytic fragment contain the catalytic site and the antigenic determinant for the monoclonal antibody.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitken A., Cohen P., Santikarn S., Williams D. H., Calder A. G., Smith A., Klee C. B. Identification of the NH2-terminal blocking group of calcineurin B as myristic acid. FEBS Lett. 1982 Dec 27;150(2):314–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80759-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y. Calmodulin plays a pivotal role in cellular regulation. Science. 1980 Jan 4;207(4426):19–27. doi: 10.1126/science.6243188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfrè G., Milstein C. Preparation of monoclonal antibodies: strategies and procedures. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):3–46. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard P. Phosphorylated proteins as physiological effectors. Science. 1978 Jan 13;199(4325):146–152. doi: 10.1126/science.22932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khandelwal R. L., Vandenheede J. R., Krebs E. G. Purification, properties, and substrate specificities of phosphoprotein phosphatase(s) from rabbit liver. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 25;251(16):4850–4858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Crouch T. H., Krinks M. H. Calcineurin: a calcium- and calmodulin-binding protein of the nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6270–6273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Vanaman T. C. Calmodulin. Adv Protein Chem. 1982;35:213–321. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60470-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luben R. A., Mohler M. A. In vitro immunization as an adjunct to the production of hybridomas producing antibodies against the lymphokine osteoclast activating factor. Mol Immunol. 1980 May;17(5):635–639. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(80)90161-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manalan A. S., Klee C. B. Activation of calcineurin by limited proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4291–4295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March S. C., Parikh I., Cuatrecasas P. A simplified method for cyanogen bromide activation of agarose for affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jul;60(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90139-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshak-Rothstein A., Fink P., Gridley T., Raulet D. H., Bevan M. J., Gefter M. L. Properties and applications of monoclonal antibodies directed against determinants of the Thy-1 locus. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2491–2497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means A. R., Tash J. S., Chafouleas J. G. Physiological implications of the presence, distribution, and regulation of calmodulin in eukaryotic cells. Physiol Rev. 1982 Jan;62(1):1–39. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1982.62.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallen C. J., Wang J. H. Calmodulin-stimulated dephosphorylation of p-nitrophenyl phosphate and free phosphotyrosine by calcineurin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8550–8553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. Determination of total protein. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:95–119. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman P. G., Klee C. B. Interaction of 125I-labeled Ca2+-dependent regulator protein with cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase and its inhibitory protein. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 25;253(18):6323–6326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. A., Ingebritsen T. S., Manalan A., Klee C. B., Cohen P. Discovery of a Ca2+- and calmodulin-dependent protein phosphatase: probable identity with calcineurin (CaM-BP80). FEBS Lett. 1982 Jan 11;137(1):80–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80319-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden P. H., Holladay L. A., Reimann E. M., Corbin J. D. Purification and characterization of the catalytic subunit of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate-dependent protein kinase from bovine liver. Biochem J. 1976 Nov;159(2):409–422. doi: 10.1042/bj1590409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tallant E. A., Cheung W. Y. Activation of bovine brain calmodulin-dependent protein phosphatase by limited trypsinization. Biochemistry. 1984 Feb 28;23(5):973–979. doi: 10.1021/bi00300a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tallant E. A., Cheung W. Y. Calmodulin-dependent protein phosphatase: a developmental study. Biochemistry. 1983 Jul 19;22(15):3630–3635. doi: 10.1021/bi00284a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. W., Lynch T. J., Tallant E. A., Cheung W. Y. An endogenous inhibitor protein of brain adenylate cyclase and cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Apr 30;187(2):328–334. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90042-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. W., Lynch T. J., Tallant E. A., Cheung W. Y. Purification and characterization of an inhibitor protein of brain adenylate cyclase and cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):377–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. W., Tallant E. A., Cheung W. Y. High levels of a heat-labile calmodulin-binding protein (CaM-BP80) in bovine neostriatum. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 29;19(9):1831–1837. doi: 10.1021/bi00550a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. H., Desai R. A brain protein and its effect on the Ca2+-and protein modulator-activated cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Oct 4;72(3):926–932. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80220-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. H., Desai R. Modulator binding protein. Bovine brain protein exhibiting the Ca2+-dependent association with the protein modulator of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4175–4184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. G., Wallace R. W., Whitaker J. N., Cheung W. Y. Immunocytochemical localization of calmodulin and a heat-labile calmodulin-binding protein (CaM-BP80) in basal ganglia of mouse brain. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jan;84(1):66–76. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.1.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. D., Tallant E. A., Cheung W. Y. Calcineurin is a calmodulin-dependent protein phosphatase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jun 30;106(4):1419–1425. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91272-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]