Abstract
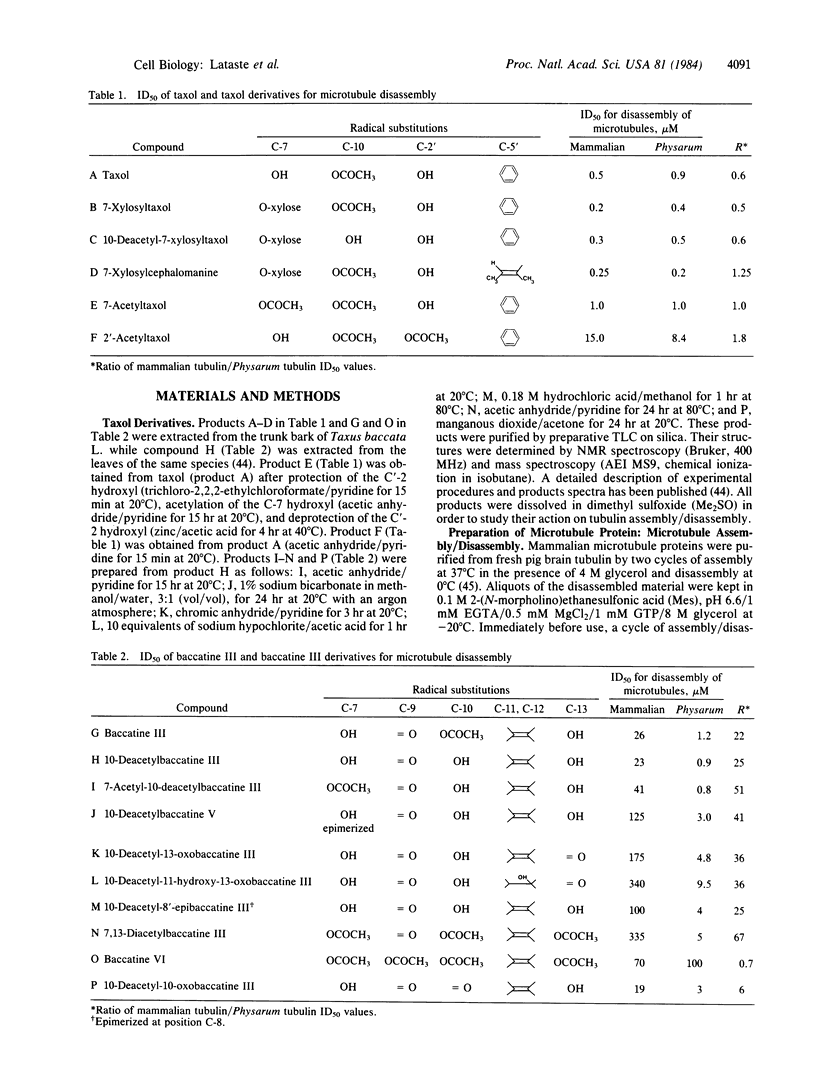
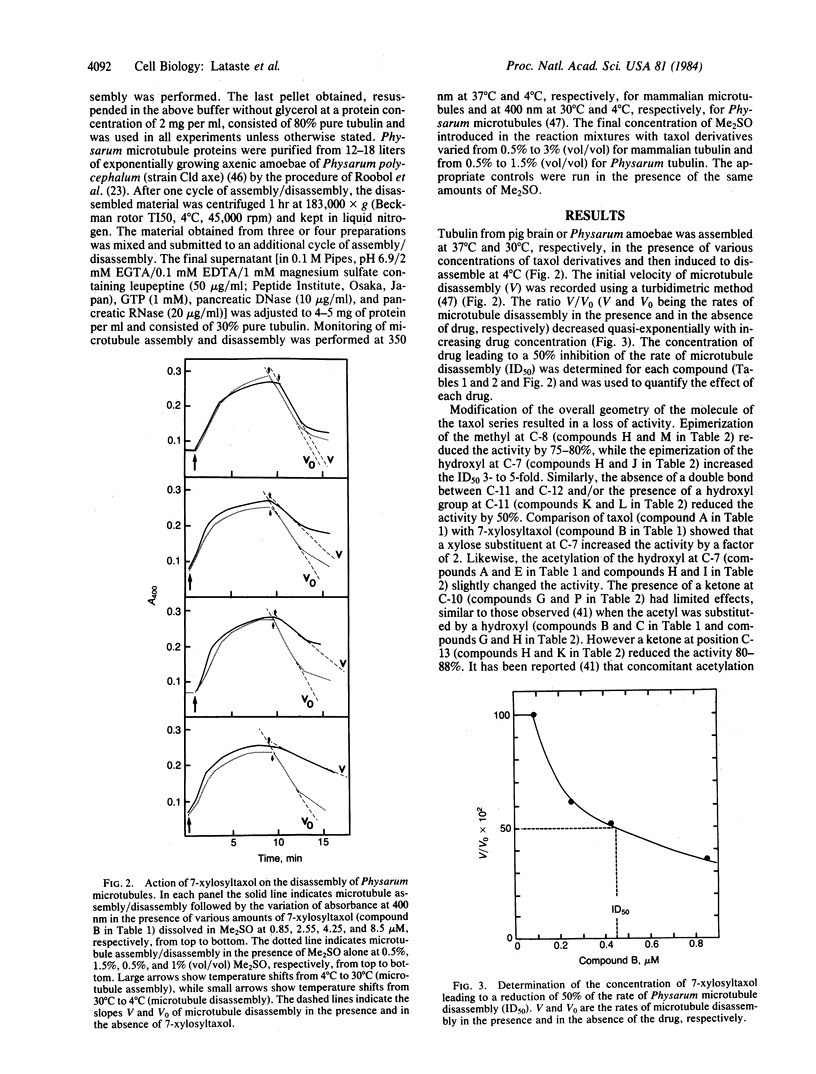
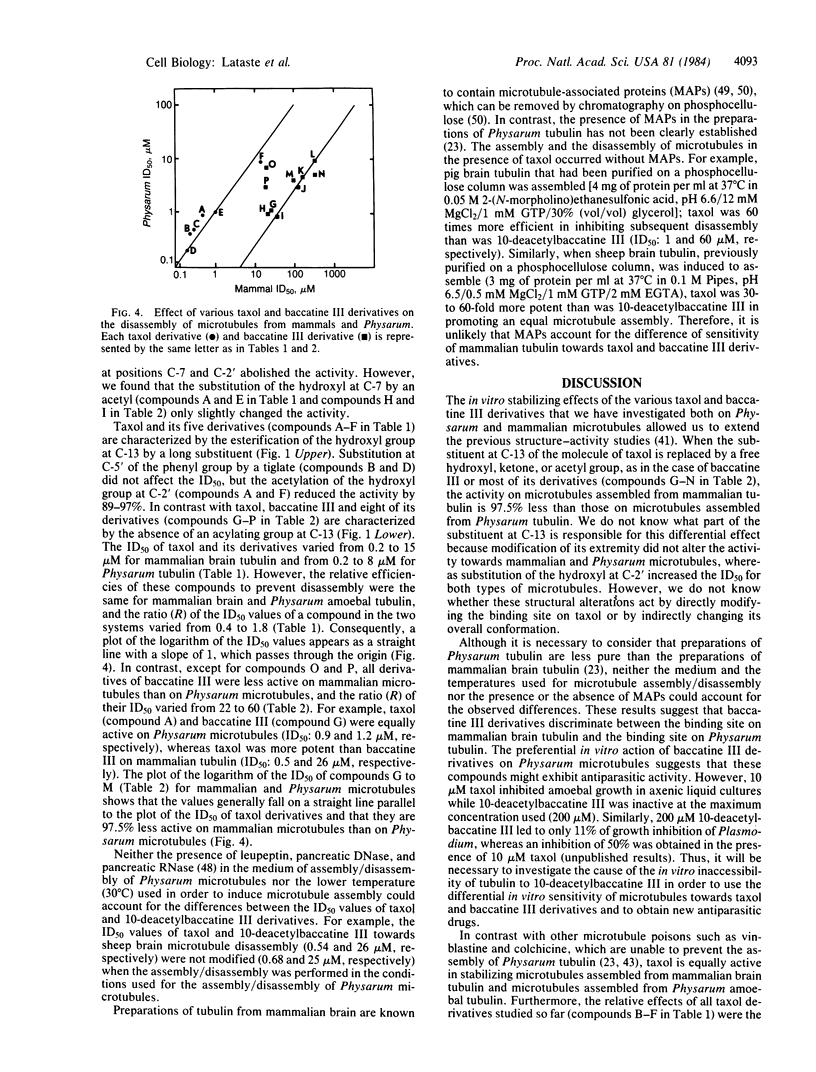
The in vitro disassembly of microtubules from mammalian brain and Physarum is inhibited by various derivatives of taxol and baccatine III. Structure-activity relationships of the taxol derivatives were identical for both mammalian brain and Physarum microtubules. This observation suggests that the site of action of taxol has been preserved during the evolution of these two different eukaryotic lines. The substituent at C-13 of taxol was required to prevent disassembly of brain microtubules with or without microtubule-associated proteins. In contrast, both taxol and baccatine III prevented the disassembly of Physarum microtubules to the same extent, showing that the substituent at C-13 was not required in the interaction with Physarum tubulin. The different effects of baccatine III and taxol derivatives indicate that measuring the disassembly of microtubules from different organisms could be a useful parameter in the search for derivatives exhibiting antiparasitic activity.
Full text
PDF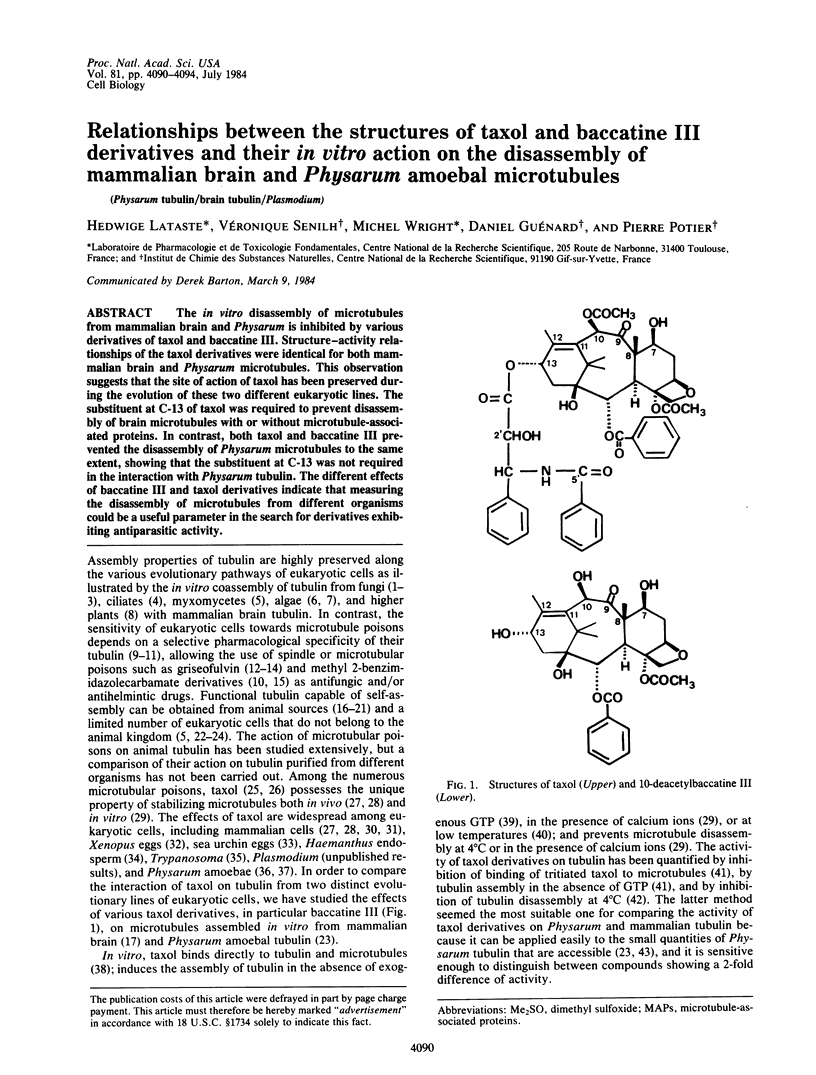

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen C., Borisy G. G. Structural polarity and directional growth of microtubules of Chlamydomonas flagella. J Mol Biol. 1974 Dec 5;90(2):381–402. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90381-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajer A. S., Cypher C., Molè-Bajer J., Howard H. M. Taxol-induced anaphase reversal: evidence that elongating microtubules can exert a pushing force in living cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6569–6573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum S. G., Wittner M., Nadler J. P., Horwitz S. B., Dennis J. E., Schiff P. B., Tanowitz H. B. Taxol, a microtubule stabilizing agent, blocks the replication of Trypanosoma cruzi. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4571–4575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder L. I., Dentler W. L., Rosenbaum J. L. Assembly of chick brain tubulin onto flagellar microtubules from Chlamydomonas and sea urchin sperm. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1122–1126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borisy G. G., Olmsted J. B. Nucleated assembly of microtubules in porcine brain extracts. Science. 1972 Sep 29;177(4055):1196–1197. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4055.1196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabral F., Abraham I., Gottesman M. M. Isolation of a taxol-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cell mutant that has an alteration in alpha-tubulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4388–4391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton L., Pogson C. I., Gull K. Microtubule proteins in the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett. 1979 Oct 1;106(1):67–70. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80696-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton L., Quinlan R. A., Roobol A., Pogson C. I., Gull K. A comparison of tubulins from mammalian brain and Physarum polycephalum using SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophorsis and peptide mapping. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jun 30;115(2):301–305. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81192-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidse L. C., Flach W. Differential binding of methyl benzimidazol-2-yl carbamate to fungal tubulin as a mechanism of resistance to this antimitotic agent in mutant strains of Aspergillus nidulans. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jan;72(1):174–193. doi: 10.1083/jcb.72.1.174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Brabander M., Geuens G., Nuydens R., Willebrords R., De Mey J. Taxol induces the assembly of free microtubules in living cells and blocks the organizing capacity of the centrosomes and kinetochores. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5608–5612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson H. P., Voter W. A. Polycation-induced assembly of purified tubulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2813–2817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Euteneuer U., Jackson W. T., McIntosh J. R. Polarity of spindle microtubules in Haemanthus endosperm. J Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;94(3):644–653. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.3.644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs D. A., Johnson R. K. Cytologic evidence that taxol, an antineoplastic agent from Taxus brevifolia, acts as a mitotic spindle poison. Cancer Treat Rep. 1978 Aug;62(8):1219–1222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaskin F., Cantor C. R., Shelanski M. L. Turbidimetric studies of the in vitro assembly and disassembly of porcine neurotubules. J Mol Biol. 1974 Nov 15;89(4):737–755. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L. H., Brandis J. W., Turner F. R., Raff R. A. Cytoplasmic microtubule proteins of the embryo of Drosophila melanogaster. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 7;14(20):4487–4491. doi: 10.1021/bi00691a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath I. B. Colchicine and colcemid binding components of the fungus Saprolegnia ferax. Protoplasma. 1975;85(2-4):177–192. doi: 10.1007/BF01567944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidemann S. R., Gallas P. T. The effect of taxol on living eggs of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1980 Dec;80(2):489–494. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90421-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidemann S. R., McIntosh J. R. Visualization of the structural polarity of microtubules. Nature. 1980 Jul 31;286(5772):517–519. doi: 10.1038/286517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., Field D. J., Lee L. L. Effects of nocodazole on structures of calf brain tubulin. Biochemistry. 1980 Dec 23;19(26):6209–6215. doi: 10.1021/bi00567a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little M., Ludueña R. F., Langford G. M., Asnes C. F., Farrell K. Comparison of proteolytic cleavage patterns of alpha-tubulins and beta-tubulins from taxonomically distant species. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 15;149(1):95–107. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maekawa S., Sakai H. Characterization and in vitro polymerization of Tetrahymena tubulin. J Biochem. 1978 Apr;83(4):1065–1075. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masurovsky E. B., Peterson E. R., Crain S. M., Horwitz S. B. Microtubule arrays in taxol-treated mouse dorsal root ganglion-spinal cord cultures. Brain Res. 1981 Aug 3;217(2):392–398. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCullough C. H., Dee J. Defined and semi-defined media for the growth of amoebae of Physarum polycephalum. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Jul;95(1):151–158. doi: 10.1099/00221287-95-1-151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morejohn L. C., Fosket D. E. Higher plant tubulin identified by self-assembly into microtubules in vitro. Nature. 1982 Jun 3;297(5865):426–428. doi: 10.1038/297426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. B., Borisy G. G. Association of high-molecular-weight proteins with microtubules and their role in microtubule assembly in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2696–2700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle B. W., Doenges K. H., Bryan J. Assembly of tubulin from cultured cells and comparison with the neurotubulin model. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):573–586. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90258-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parness J., Horwitz S. B. Taxol binds to polymerized tubulin in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):479–487. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parness J., Kingston D. G., Powell R. G., Harracksingh C., Horwitz S. B. Structure-activity study of cytotoxicity and microtubule assembly in vitro by taxol and related taxanes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Apr 14;105(3):1082–1089. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91080-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan R. A., Roobol A., Pogson C. I., Gull K. A correlation between in vivo and in vitro effects of the microtubule inhibitors colchicine, parbendazole and nocodazole on myxamoebae of Physarum polycephalum. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Jan;122(1):1–6. doi: 10.1099/00221287-122-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roobol A., Gull K., Pogson C. I. Griseofulvin-induced aggregation of microtubule protein. Biochem J. 1977 Oct 1;167(1):39–43. doi: 10.1042/bj1670039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roobol A., Pogson C. I., Gull K. Identification and characterization of microtubule proteins from myxamoebae of Physarum polycephalum. Biochem J. 1980 Aug 1;189(2):305–312. doi: 10.1042/bj1890305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roobol A., Pogson C. I., Gull K. In vitro assembly of microtubule proteins from myxamoebae of Physarum polycephalum. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Nov;130(1):203–215. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90057-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatten G., Schatten H., Bestor T. H., Balczon R. Taxol inhibits the nuclear movements during fertilization and induces asters in unfertilized sea urchin eggs. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):455–465. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff P. B., Fant J., Horwitz S. B. Promotion of microtubule assembly in vitro by taxol. Nature. 1979 Feb 22;277(5698):665–667. doi: 10.1038/277665a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff P. B., Horwitz S. B. Taxol assembles tubulin in the absence of exogenous guanosine 5'-triphosphate or microtubule-associated proteins. Biochemistry. 1981 May 26;20(11):3247–3252. doi: 10.1021/bi00514a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff P. B., Horwitz S. B. Taxol stabilizes microtubules in mouse fibroblast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1561–1565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheir-Neiss G., Nardi R. V., Gealt M. A., Morris N. R. Tubulin-like protein from Aspergillus nidulans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Mar 22;69(2):285–290. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelanski M. L., Gaskin F., Cantor C. R. Microtubule assembly in the absence of added nucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):765–768. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stearns M. E., Brown D. L. Purification of cytoplasmic tubulin and microtubule organizing center proteins functioning in microtubule initiation from the alga Polytomella. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5745–5749. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W. C., Wilson L., Purich D. L. Taxol induces microtubule assembly at low temperature. Cell Motil. 1981;1(4):445–454. doi: 10.1002/cm.970010405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wani M. C., Taylor H. L., Wall M. E., Coggon P., McPhail A. T. Plant antitumor agents. VI. The isolation and structure of taxol, a novel antileukemic and antitumor agent from Taxus brevifolia. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 May 5;93(9):2325–2327. doi: 10.1021/ja00738a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Wehland J., Herzog W. Griseofulvin interacts with microtubules both in vivo and in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1976 Apr 25;102(4):817–829. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90293-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehland J., Herzog W., Weber K. Interaction of griseofulvin with microtubules, microtubule protein and tubulin. J Mol Biol. 1977 Apr 15;111(3):329–342. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingarten M. D., Lockwood A. H., Hwo S. Y., Kirschner M. W. A protein factor essential for microtubule assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1858–1862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisenberg R. C. Microtubule formation in vitro in solutions containing low calcium concentrations. Science. 1972 Sep 22;177(4054):1104–1105. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4054.1104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


