Abstract
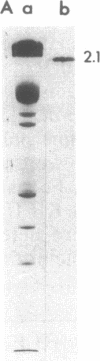
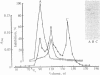
Protein 2.1 is a 210-kilodalton protein that connects erythrocyte spectrin to the NH2-terminal cytoplasmic domain of band 3 and thereby functions as the essential linkage between the membrane skeleton and the bilayer. We cleaved this protein into specific chemical domains by limited digestion with trypsin and alpha-chymotrypsin at 0 degrees C. Intermediate-sized peptides were separated by two-dimensional isoelectric focusing/NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and characterized by high resolution peptide mapping. We have established a provisional structural model of protein 2.1 by comparing the peptide maps of these chemical domains to maps obtained from larger overlapping chymotryptic fragments as well as fragments obtained from 2-nitro-5-thiocyanobenzoic acid cleavage. In addition to providing a provisional structural map of protein 2.1, we have identified two functional domains of protein 2.1, an 83-kilodalton tryptic peptide (T-83) which binds band 3 and a 65-kilodalton tryptic peptide (T-65) which binds spectrin. We have therefore localized the functional domains along our linear map of protein 2.1.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett V. Purification of an active proteolytic fragment of the membrane attachment site for human erythrocyte spectrin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2292–2299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V., Stenbuck P. J. Association between ankyrin and the cytoplasmic domain of band 3 isolated from the human erythrocyte membrane. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6424–6432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V., Stenbuck P. J. Identification and partial purification of ankyrin, the high affinity membrane attachment site for human erythrocyte spectrin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 10;254(7):2533–2541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvert R., Bennett P., Gratzer W. Properties and structural role of the subunits of human spectrin. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):355–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06036.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Pickett R. A., 2nd, Hampton J., Lerner R. A. Radioiodination of proteins in single polyacrylamide gel slices. Tryptic peptide analysis of all the major members of complex multicomponent systems using microgram quantities of total protein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6510–6515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. R., Weidner S. A. Binding of spectrin alpha 2-beta 2 tetramers to human erythrocyte membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 10;255(17):8082–8086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hargreaves W. R., Giedd K. N., Verkleij A., Branton D. Reassociation of ankyrin with band 3 in erythrocyte membranes and in lipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11965–11972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel D. L., Goodman S. R., Branton D. The effect of endogenous proteases on the spectrin binding proteins of human erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jun 6;598(3):517–527. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90032-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speicher D. W., Morrow J. S., Knowles W. J., Marchesi V. T. A structural model of human erythrocyte spectrin. Alignment of chemical and functional domains. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):9093–9101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L. The organization of proteins in the human red blood cell membrane. A review. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jul;62(1):1–19. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler J. M., Hargreaves W. R., Branton D. Purification of two spectrin-binding proteins: biochemical and electron microscopic evidence for site-specific reassociation between spectrin and bands 2.1 and 4.1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5192–5196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu J., Goodman S. R. Syndeins: the spectrin-binding protein(s) of the human erythrocyte membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2340–2344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]