Abstract
HLA-DR5 is associated with a chronic iridocyclitis and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis with onset in early childhood. Previously published data provided indirect evidence for selective linkage between two HLA-B alleles and HLA-DR5. To test this observation further, 38 families, the probands of which have chronic iridocyclitis and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, were HLA typed so that haplotypes associated with disease could be established. HLA-DR5 was linked to HLA-Bw44 or to HLA-Bw35 and to HLA-Cw4 in the majority of haplotypes obtained in the probands. Both HLA-Bw44, -DR5 and HLA-Bw35, -Cw4, -DR5 occurred more commonly in the proband haplotypes than in the control haplotypes. The frequency of the haplotype HLA-Bw44, -DR5 was 0.133 compared with 0.007 (X2 = 27.04, P less than 10(-6] and for HLA-Bw35, -Cw4, -DR5, it was 0.093 compared with 0.11 (X2 = 13.83, P = 0.0002). The relative risks were 20.77 and 9.23, respectively, versus 3.52 for HLA-DR5 alone. HLA-Bw44 occurred much more commonly in proband HLA-DR5 haplotypes (0.455) compared with control HLA-DR5 haplotypes (0.067) (X2 = 8.26, P less than 0.01). Not all HLA-DR5-bearing haplotypes predisposed equally to chronic iridocyclitis and early-onset pauciarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis.
Full text
PDF
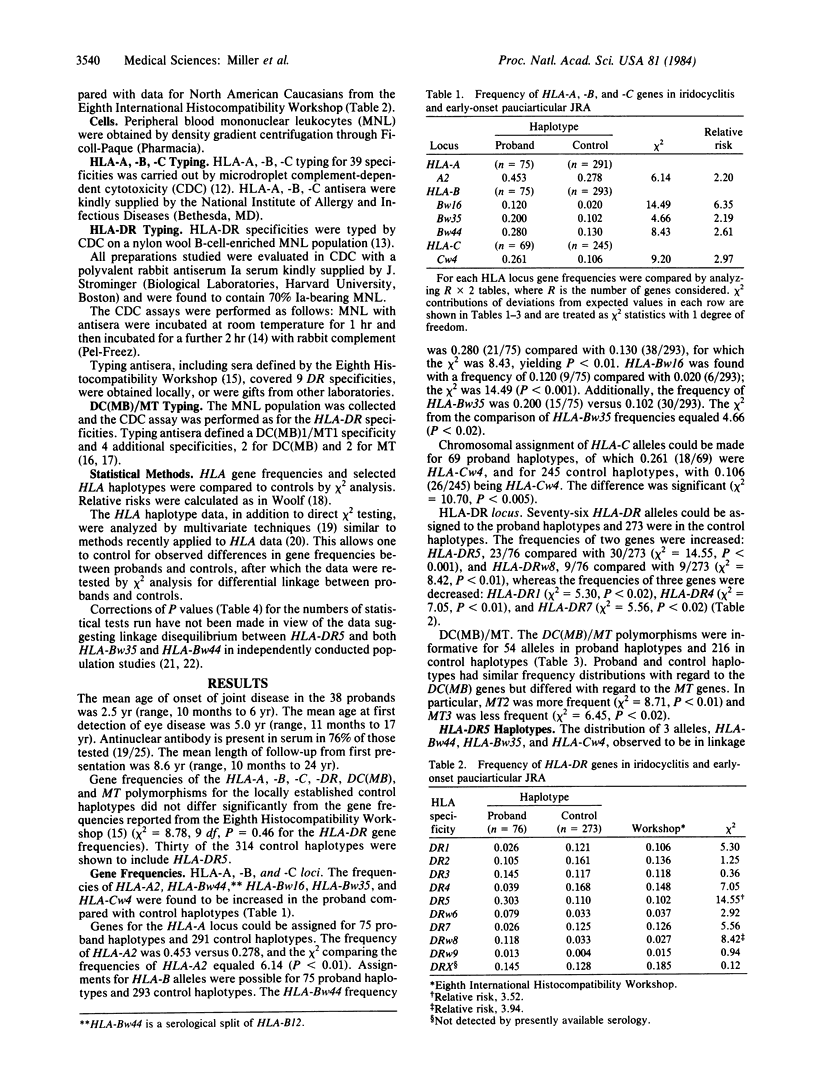
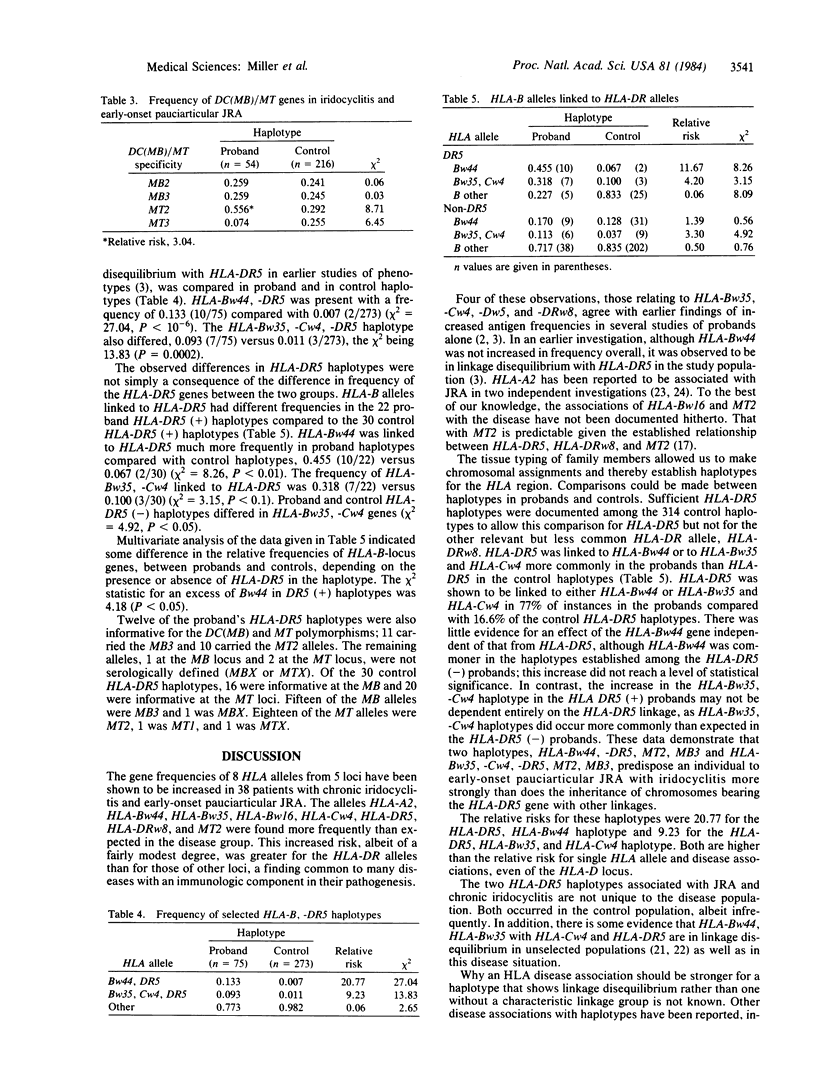

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alper C. A., Awdeh Z. L., Raum D. D., Yunis E. J. Extended major histocompatibility complex haplotypes in man: role of alleles analogous to murine t mutants. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 Aug;24(2):276–285. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(82)90238-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awdeh Z. L., Raum D., Yunis E. J., Alper C. A. Extended HLA/complement allele haplotypes: evidence for T/t-like complex in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):259–263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardin T., Dryll A., Debeyre N., Ryckewaert A., Legrand L., Marcelli A., Dausset J. HLA system and side effects of gold salts and D-penicillamine treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1982 Dec;41(6):599–601. doi: 10.1136/ard.41.6.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer E. J., Jr, Bass J., Baum J., Cassidy J. T., Fink C., Jacobs J., Hanson V., Levinson J. E., Schaller J., Stillman J. S. Current proposed revision of JRA Criteria. JRA Criteria Subcommittee of the Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee of the American Rheumatism Section of The Arthritis Foundation. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Mar;20(2 Suppl):195–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chylack L. T., Jr, Bienfang D. C., Bellows A. R., Stillman J. S. Ocular manifestations of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Ophthalmol. 1975 Jun;79(6):1026–1033. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(75)90689-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawkins R. L., Christiansen F. T., Kay P. H., Garlepp M., McCluskey J., Hollingsworth P. N., Zilko P. J. Disease associations with complotypes, supratypes and haplotypes. Immunol Rev. 1983;70:5–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb00707.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischnick E., Awdeh Z. L., Raum D., Granados J., Alosco S. M., Crigler J. F., Jr, Gerald P. S., Giles C. M., Yunis E. J., Alper C. A. Extended MHC haplotypes in 21-hydroxylase-deficiency congenital adrenal hyperplasia: shared genotypes in unrelated patients. Lancet. 1983 Jan 22;1(8317):152–156. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92757-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Førre O., Dobloug J. H., Høyeraal H. M., Thorsby E. HLA antigens in juvenile arthritis. Genetic basis for the different subtypes. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Jan;26(1):35–38. doi: 10.1002/art.1780260106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass D., Litvin D., Wallace K., Chylack L., Garovoy M., Carpenter C. B., Schur P. H. Early-onset pauciarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis associated with human leukocyte antigen-DRw5, iritis, and antinuclear antibody. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):426–429. doi: 10.1172/JCI109872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpatkin S., Fotino M., Gibofsky A., Winchester R. J. Association of HLA-DRw2 with autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):1085–1088. doi: 10.1172/JCI109378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry R., Goguen J., Carpenter C. B., Strom T. B., Garovoy M. R. Improved B cell typing for HLA-DR using nylon wool column enriched B lymphocyte preparations. Tissue Antigens. 1979 Oct;14(4):325–330. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1979.tb00856.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. L., Glass D. N. The major histocompatibility complex antigens in rheumatoid arthritis and juvenile arthritis. Bull Rheum Dis. 1981;31(5):21–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal K. K., Mickey M. R., Singal D. P., Terasaki P. I. Serotyping for homotransplantation. 18. Refinement of microdroplet lymphocyte cytotoxicity test. Transplantation. 1968 Nov;6(8):913–927. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196811000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oen K., Petty R. E., Schroeder M. L. An association between HLA-A2 and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis in girls. J Rheumatol. 1982 Nov-Dec;9(6):916–920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park M. S., Terasaki P. I., Ahmed A. R., Tiwari J. L. HLA-DRW4 in 91% of Jewish pemphigus vulgaris patients. Lancet. 1979 Sep 1;2(8140):441–442. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91493-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMILEY W. K., MAY E., BYWATERS E. G. Ocular presentations of Still's disease and their treatment: iridocyclitis in Still's disease: its complications and treatment. Ann Rheum Dis. 1957 Sep;16(3):371–383. doi: 10.1136/ard.16.3.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller J. G., Johnson G. D., Holborow E. J., Ansell B. M., Smiley W. K. The association of antinuclear antibodies with the chronic iridocyclitis of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (Still's disease). Arthritis Rheum. 1974 Jul-Aug;17(4):409–416. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller J. G., Ochs H. D., Thomas E. D., Nisperos B., Feigl P., Wedgwood R. J. Histocompatibility antigens in childhood-onset arthritis. J Pediatr. 1976 Jun;88(6):926–930. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)81043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smouse P. E., Williams R. C. Multivariate analysis of HLA-disease associations. Biometrics. 1982 Sep;38(3):757–768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stastny P., Fink C. W. Different HLA-D associations in adult and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jan;63(1):124–130. doi: 10.1172/JCI109265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOLF B. On estimating the relation between blood group and disease. Ann Hum Genet. 1955 Jun;19(4):251–253. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1955.tb01348.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Rood J. J., van Leeuwen A., Keuning J. J., van Oud Alblas A. B. The serological recognition of the human MLC determinants using a modified cytotoxicity technique. Tissue Antigens. 1975 Apr;5(2):73–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1975.tb00532.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


