Abstract
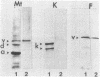
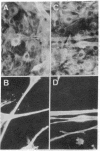
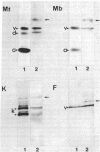
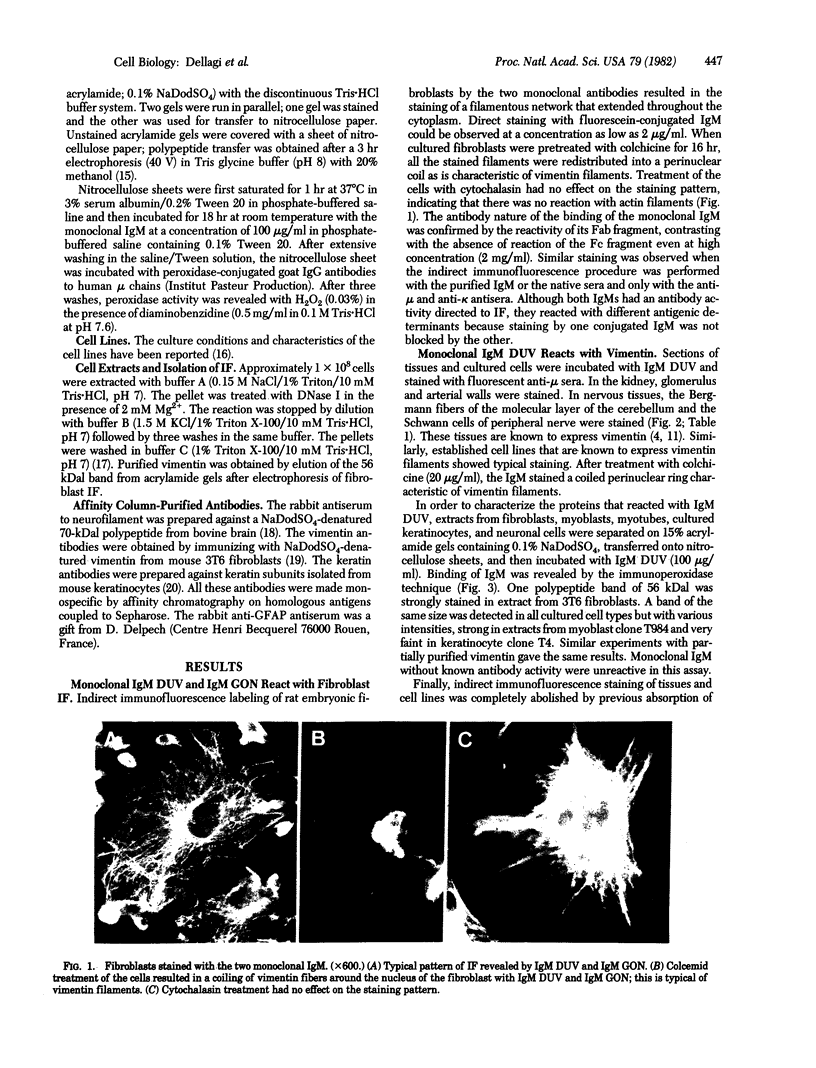
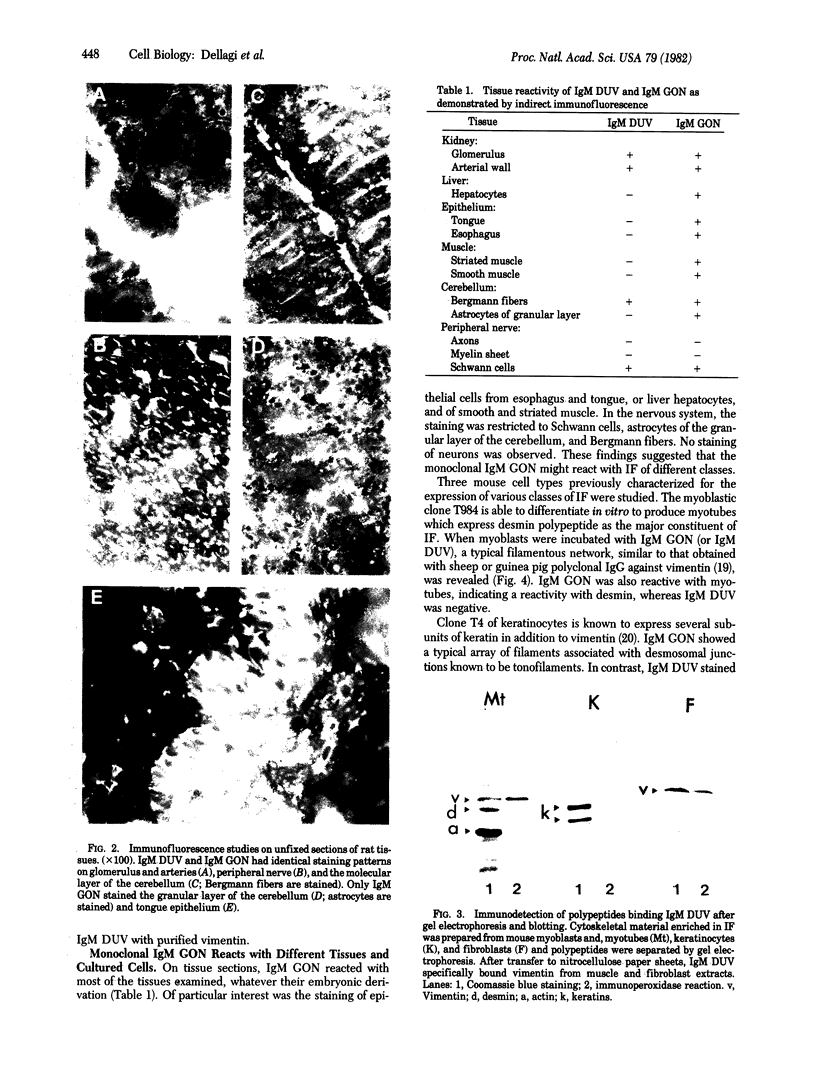
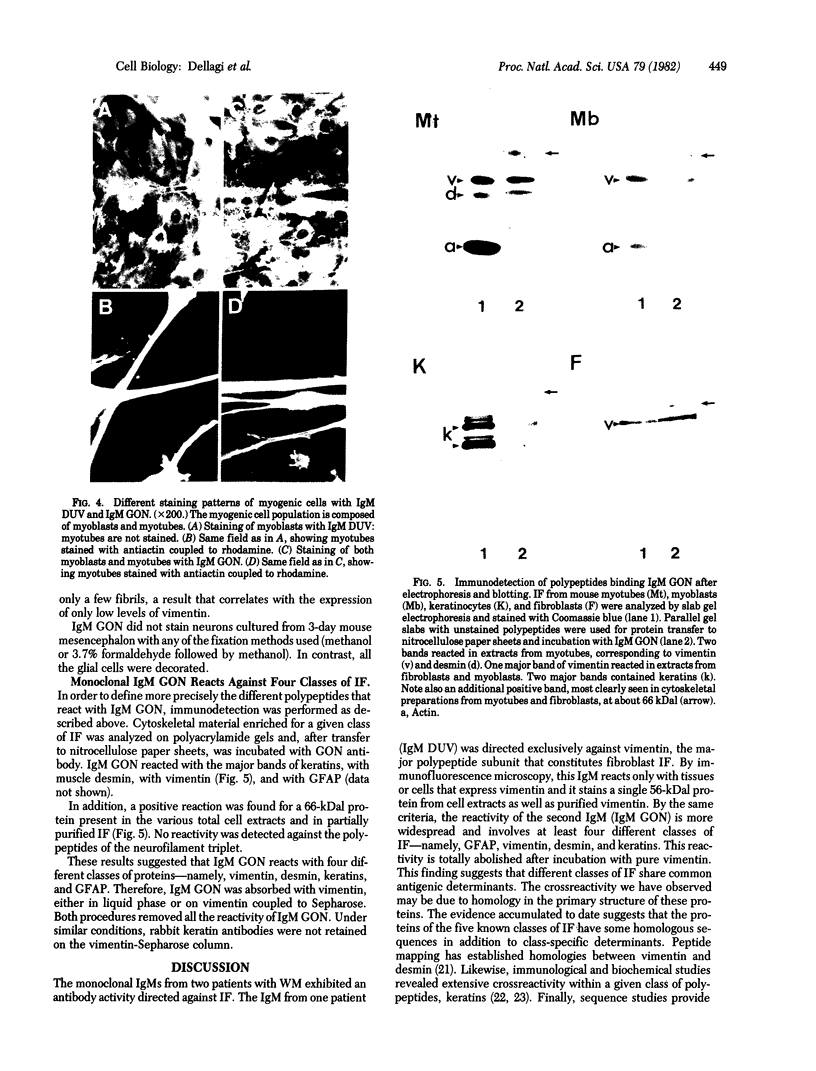
Monoclonal IgMs from two patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia were found to react with intermediate filaments. This was shown by (a) immunostaining of various tissues and cultured cells and (b) immunological characterization of the reactive antigen after blotting of polypeptides separated from total cell extracts by gel electrophoresis or purified intermediate filaments on nitrocellulose sheets. One monoclonal IgM had an activity directed only against vimentin, whereas the other reacted with four different classes of intermediate filaments--vimentin, desmin, glial fibrillary protein, and keratins. All of the reactivity of the latter IgM was absorbed by purified vimentin, suggesting that different classes of proteins of intermediate filaments share common antigenic determinant(s). The significance of such autoantibody activity of human monoclonal IgM is discussed in the light of the startling frequency of IgM anti-intermediate filaments antibodies in various diseases.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bignami A., Eng L. F., Dahl D., Uyeda C. T. Localization of the glial fibrillary acidic protein in astrocytes by immunofluorescence. Brain Res. 1972 Aug 25;43(2):429–435. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90398-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretherton L., Toh B. H., Jack I. IgM autoantibody to intermediate filaments in Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1981 Mar;18(3):425–430. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(81)90135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTENSON W. N., DACIE J. V., CROUCHER B. E., CHARLWOOD P. A. Electrophoretic studies on sera containing high-titre cold haemagglutinins: identification of the antibody as the cause of an abnormal gamma 1 peak. Br J Haematol. 1957 Jul;3(3):262–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1957.tb05795.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delacourte A., Filliatreau G., Boutteau F., Biserte G., Schrevel J. Study of the 10-nm-filament fraction isolated during the standard microtubule preparation. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 1;191(2):543–546. doi: 10.1042/bj1910543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dellagi K., Brouet J. C., Danon F. Cross-idiotypic antigens among monoclonal immunoglobulin M from patients with Waldenström's macroglobulinemia and polyneuropathy. J Clin Invest. 1979 Nov;64(5):1530–1534. doi: 10.1172/JCI109612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Weber K., Osborn M. HeLa cells contain intermediate-sized filaments of the prekeratin type. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Jan;118(1):95–109. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90587-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Winter S., Osborn M., Weber K. Widespread occurrence of intermediate-sized filaments of the vimentin-type in cultured cells from diverse vertebrates. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Oct 1;123(1):25–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90418-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Weber K., Osborn M., Schmid E., Freudenstein C. Antibody to prekeratin. Decoration of tonofilament like arrays in various cells of epithelial character. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Oct 15;116(2):429–445. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90466-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E., Green H. The expression of keratin genes in epidermis and cultured epidermal cells. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):887–897. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90273-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gard D. L., Bell P. B., Lazarides E. Coexistence of desmin and the fibroblastic intermediate filament subunit in muscle and nonmuscle cells: identification and comparative peptide analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3894–3898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. Comparison of the proteins of two immunologically distinct intermediate-sized filaments by amino acid sequence analysis: desmin and vimentin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4120–4123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRITZMAN J., KUNKEL H. G., MCCARTHY J., MELLORS R. C. Studies of a Waldenstrom-type macroglobulin with rheumatoid factor properties. J Lab Clin Med. 1961 Jun;57:905–917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Hubbard B. D. Immunological characterization of the subunit of the 100 A filaments from muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4344–4348. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. Intermediate filaments as mechanical integrators of cellular space. Nature. 1980 Jan 17;283(5744):249–256. doi: 10.1038/283249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liem R. K., Yen S. H., Salomon G. D., Shelanski M. L. Intermediate filaments in nervous tissues. J Cell Biol. 1978 Dec;79(3):637–645. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.3.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder E., Kurki P., Andersson L. C. Autoantibody to "intermediate filament" in infectious mononucleosis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1979 Dec;14(4):411–417. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger H. Myeloma proteins and antibodies. Am J Med. 1969 Dec;47(6):837–844. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(69)90198-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstone L. M., McGuire J. Different polypeptides form the intermediate filaments in bovine hoof and esophageal epithelium and in aortic endothelium. J Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;88(2):312–316. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.2.312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas J. F., Avner P., Gaillard J., Guenet J. L., Jakob H., Jacob F. Cell lines derived from teratocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 1976 Nov;36(11 Pt 2):4224–4231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulin D., Babinet C., Weber K., Osborn M. Antibodies as probes of cellular differentiation and cytoskeletal organization in the mouse blastocyst. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Dec;130(2):297–304. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulin D. Cytoskeleton organization in differentiating mouse teratocarcinoma cells. Biochimie. 1981 Apr;63(4):347–363. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(81)80121-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulin D., Nicolas J. F., Yaniv M., Jacob F., Weber K., Osborn M. Actin and tubulin in teratocarcinoma cells. Amount and intracellular organization upon cytodifferentiation. Dev Biol. 1978 Oct;66(2):488–499. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90254-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaut A. G., Tomasi T. B., Jr Immunoglobulin M: pentameric Fcmu fragments released by trypsin at higher temperatures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Feb;65(2):318–322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.2.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M. Myeloma proteins (M-components) with antibody-like activity. N Engl J Med. 1971 Apr 15;284(15):831–838. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197104152841507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligmann M., Brouet J. C. Antibody activity of human myeloma globulins. Semin Hematol. 1973 Apr;10(2):163–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun T. T., Green H. Immunofluorescent staining of keratin fibers in cultured cells. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):469–476. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90233-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]