Abstract
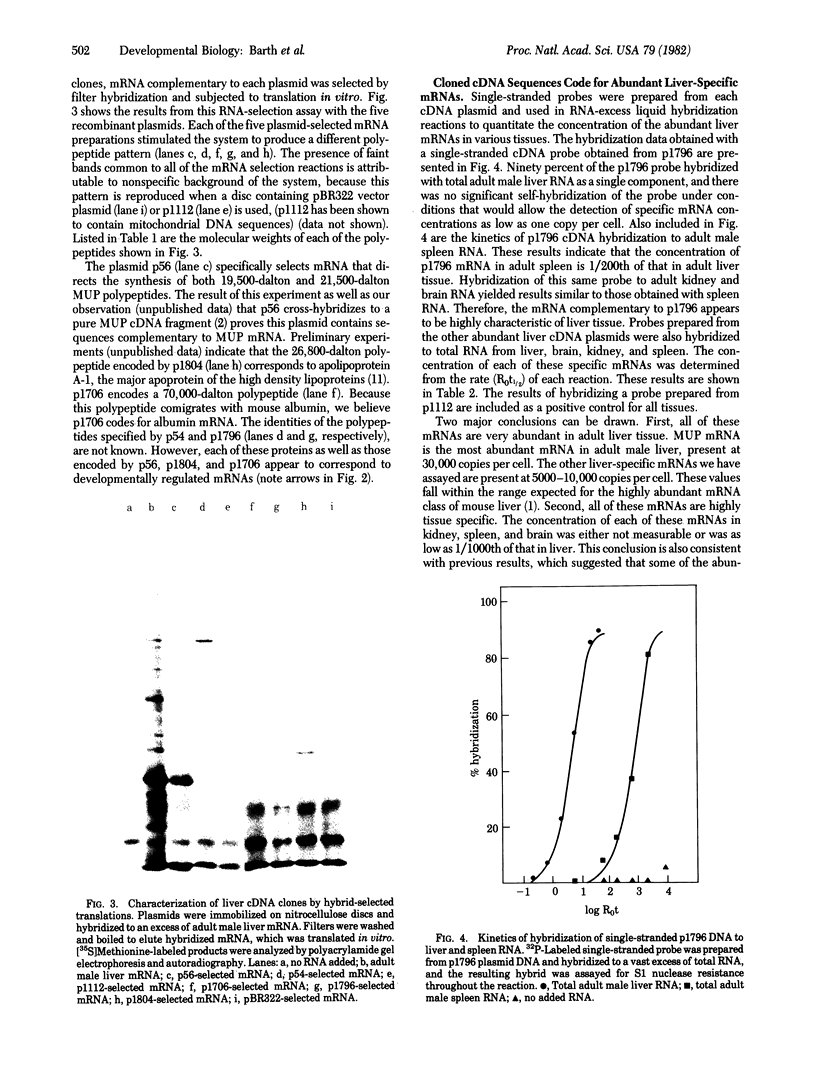
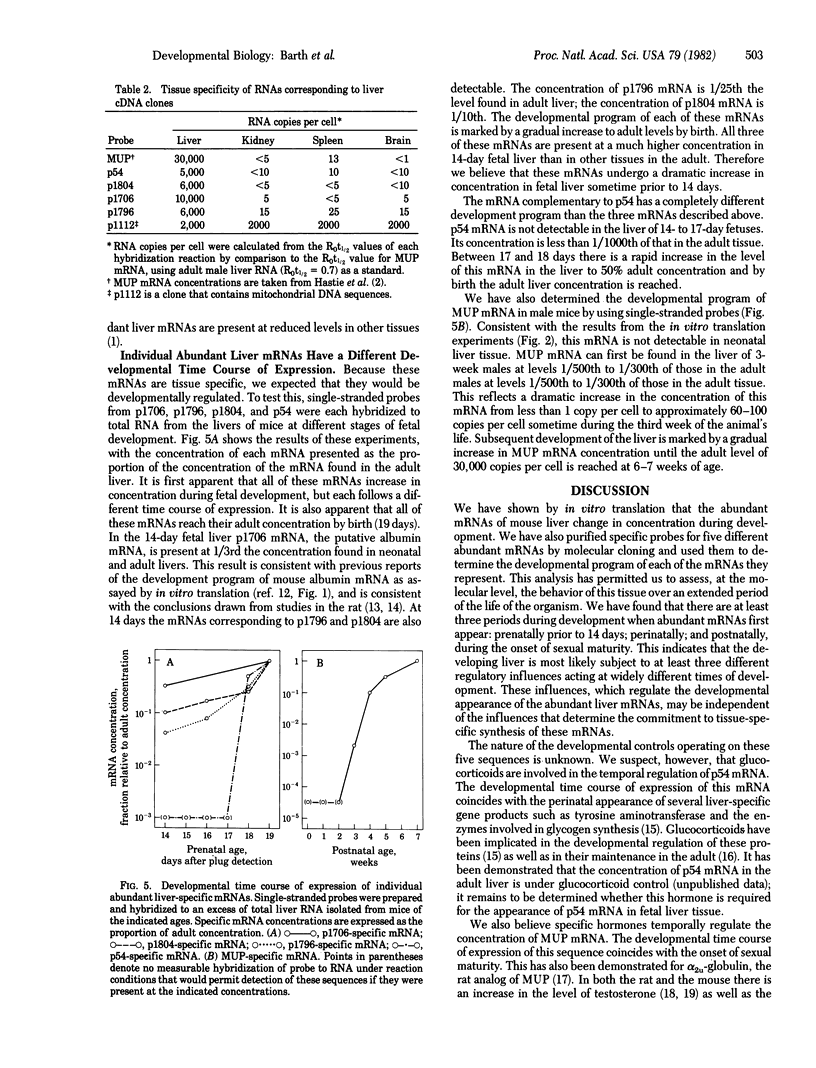
The mouse liver contains a group of 10--12 different tissue-specific mRNAs, each present at an average concentration of 12,000--15,000 copies per cell [Hastie, N. D. & Bishop, J. O. (1976) Cell 9, 761--774]. We have determined, by translation in vitro, that these mRNAs are developmentally regulated in the liver. We have also used specific cloned probes to quantitate the developmental time course of expression of five different abundant liver mRNAs. We have found that there are at least three periods during liver development when specific abundant mRNAs are first detectable: prior to 14 days postconception, at birth, and during the onset of sexual maturity. These results indicate that all the members of this mRNA group are not under common developmental regulation. One of the abundant liver mRNAs (p54 mRNA) increases more than 1000-fold in the liver 1 day before birth. We discuss factors that may be involved in the developmental regulation of expression of the genes encoding these mRNAs.
Full text
PDF

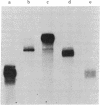
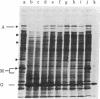
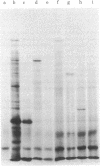
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Derman E., Krauter K., Walling L., Weinberger C., Ray M., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional control in the production of liver-specific mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):731–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90436-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Kafatos F. C., Maxam A. M., Maniatis T. Enzymatic in vitro synthesis of globin genes. Cell. 1976 Feb;7(2):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90027-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigelson P., Kurtz D. T. Hormonal modulation of alpha2u globulin mRNA: sequence measurements using a specific cDNA probe. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):659–663. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastie N. D., Bishop J. O. The expression of three abundance classes of messenger RNA in mouse tissues. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 2):761–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90139-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastie N. D., Held W. A. Analysis of mRNA populations by cDNA.mRNA hybrid-mediated inhibition of cell-free protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1217–1221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastie N. D., Held W. A., Toole J. J. Multiple genes coding for the androgen-regulated major urinary proteins of the mouse. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):449–457. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90171-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iatrou K., Tsitilou S. G., Goldsmith M. R., Kafatos F. C. Molecular analysis of the GrB mutation in Bombyx mori through the use of chorion cDNA library. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):659–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90312-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao W. S., Conn A. R., Taylor J. M. Changes in rat alpha 1-fetoprotein and albumin mRNA levels during fetal and neonatal development. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10036–10039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney T. D., Desjardins C. Postnatal development of the testis, fighting behavior, and fertility in house mice. Biol Reprod. 1973 Oct;9(3):279–294. doi: 10.1093/biolreprod/9.3.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrisett J. D., Jackson R. L., Gotto A. M., Jr Lipoproteins: structure and function. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:183–207. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.001151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resko J. A., Feder H. H., Goy R. W. Androgen concentrations in plasma and testis of developing rats. J Endocrinol. 1968 Apr;40(4):485–491. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0400485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojkind M., Gatmaitan Z., Mackensen S., Giambrone M. A., Ponce P., Reid L. M. Connective tissue biomatrix: its isolation and utilization for long-term cultures of normal rat hepatocytes. J Cell Biol. 1980 Oct;87(1):255–263. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.1.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A. K., Milin B. S., McMinn D. M. Androgen receptor in rat liver: hormonal and developmental regulation of the cytoplasmic receptor and its correlation with the androgen-dependent synthesis of alpha2u-globulin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 4;354(2):213–232. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(74)90008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sala-Trepat J. M., Dever J., Sargent T. D., Thomas K., Sell S., Bonner J. Changes in expression of albumin and alpha-fetoprotein genes during rat liver development and neoplasia. Biochemistry. 1979 May 29;18(11):2167–2178. doi: 10.1021/bi00578a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. R., Jr, Bonney R. J. Extended expression of differentiated function in primary cultures of adult liver parenchymal cells maintained on nitrocellulose filters. I. Induction of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and tyrosine aminotransferase. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Jul;114(2):307–315. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90488-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel-Haueter S. E., Schlegel W., Chou J. Y. Establishment of a fetal rat liver cell line that retains differentiated liver functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2731–2734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki T., Thomas K., Schindler I. Cell-free studies of developmental changes in synthesis of alpha-foetoprotein and albumin in the mouse liver. Nature. 1974 May 17;249(454):269–271. doi: 10.1038/249269b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villa-Komaroff L., Efstratiadis A., Broome S., Lomedico P., Tizard R., Naber S. P., Chick W. L., Gilbert W. A bacterial clone synthesizing proinsulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3727–3731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widman L. E., Golden J. J., Chasin L. A. Immortalization of normal liver functions in cell culture: rat hepatocyte-hepatoma cell hybrids expressing ornithine carbamoyltransferase activity. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Sep;100(3):391–400. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041000302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]