Abstract
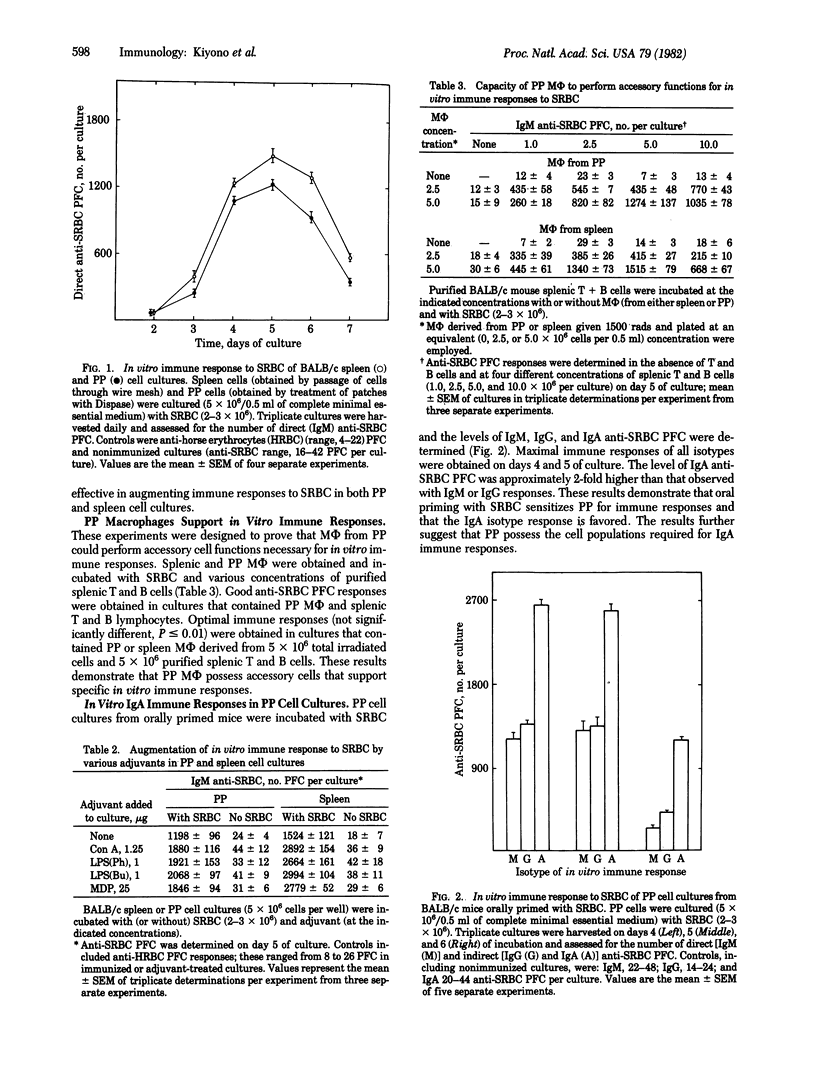
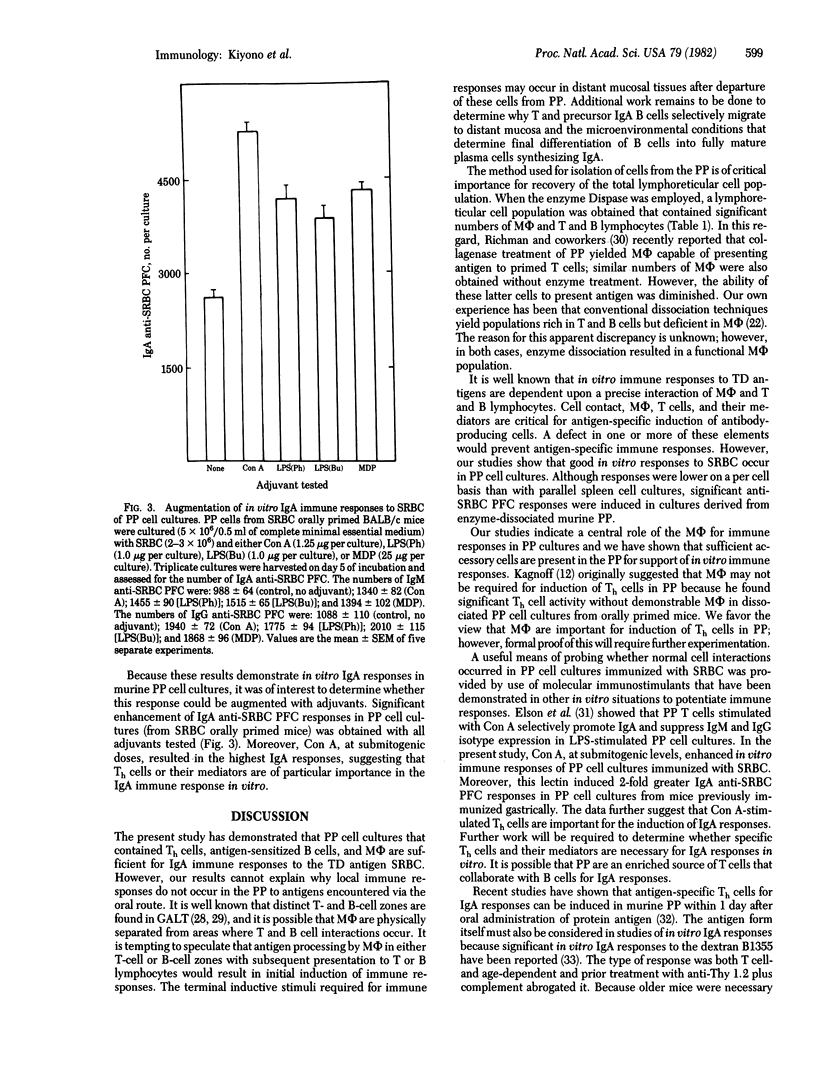
The first line of defense against pathogens that enter the host by the oral route appears to involve the gut-associated lymphoreticular tissue—e.g., Peyer's patches (PP). Although animals can readily be immunized by orally administered antigen that mobilizes the secretory immune system, there is a total lack of local antibody synthesis in the PP and the cellular basis for this deficiency remains a mystery. A lymphoreticular cell population, obtained when murine PP were treated with a neutral protease (Dispase), consisted of accessory cells [macrophages (MΦ)] and T and B lymphocytes. In vitro cultures of these PP cell preparations with the thymic-dependent antigen sheep erythrocytes (SRBC) resulted in good anti-SRBC plaque-forming cell (PFC) responses. The time courses of these responses were identical to those seen with spleen cell cultures. Submitogenic concentrations of concanavalin A (Con A) and optimal doses of N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanyl-D-isoglutamine (MDP) and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) enhanced in vitro responses of PP cell cultures to SRBC. PP possess fully functional antigen-presenting MΦ because incubation of optimal proportions of splenic T and B cells with purified populations of PP MΦ supported good in vitro immune responses. Murine PP possess all of the necessary elements for an IgA immune response because PP cell cultures derived from mice orally primed with SRBC and immunized with SRBC in vitro gave high IgA anti-SRBC PFC responses. All of the adjuvants tested (LPS, MDP, and Con A) enhanced IgA responses in PP cell cultures from orally primed mice; however, Con A induced the greatest enhancement. These results demonstrate that murine PP possess MΦ capable of accessory cell functions for in vitro immune responses and that oral priming with antigen induces the precursor T- and B-cell populations necessary for IgA responses, that are potentiated by adjuvants, in PP cell cultures. Thus, murine PP possess the lymphoreticular cells required for antibody responses; however, the tissue architecture likely prevents local responses in vivo. The finding that enzymatically dissociated PP contain all of the necessary cellular components for antibody synthesis, whereas the in vivo tissue architecture prevents the complex interactions necessary for this response, suggests that the initial inductive events take place in situ, and additional cell interactions are required for final differentiation of IgA-synthesizing plasma cells to occur at distant mucosal sites.
Keywords: macrophages, neutral protease, anti-sheep erythrocyte responses, IgA responses, adjuvancy
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bienenstock J., Dolezel J. Peyer's patches: lack of specific antibody-containing cells after oral and parenteral immunization. J Immunol. 1971 Apr;106(4):938–945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. O., Heck J. A., Strober W. T-cell regulation of murine IgA synthesis. J Exp Med. 1979 Mar 1;149(3):632–643. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.3.632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulk W. P., McCormick J. N., Goodman J. R., Yoffey J. M., Fudenberg H. H. Peyer's patches: morphologic studies. Cell Immunol. 1970 Nov;1(5):500–520. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(70)90038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fevrier M., Birrien J. L., Leclerc C., Chedid L., Liacopoulos P. The macrophage, target cell of the synthetic adjuvant muramyl dipeptide. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Aug;8(8):558–562. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronowicz E., Coutinho A. Functional analysis of B cell heterogeneity. Transplant Rev. 1975;24:3–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1975.tb00164.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry C., Faulk W. P., Kuhn L., Yoffey J. M., Fudenberg H. H. Peyer's patches: immunologic studies. J Exp Med. 1970 Jun 1;131(6):1200–1210. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.6.1200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann M. K., Galanos C., Koenig S., Oettgen H. F. B-cell activation by lipopolysaccharide. Distinct pathways for induction of mitosis and antibody production. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1640–1647. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs D. M. Synergy between T cell-replacing factor and bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS) in the primary antibody response in vitro: a model for lipopolysaccharide adjuvant action. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1421–1426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joel D. D., Hess M. W., Cottier H. Thymic origin of lymphocytes in developing Peyer's patches of newborn mice. Nat New Biol. 1971 May 5;231(18):24–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagnoff M. F., Billings P., Cohn M. Functional characteristics of Peyer's patch lymphoid cells. II. Lipopolysaccharide is thymus dependent. J Exp Med. 1974 Feb 1;139(2):407–413. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.2.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagnoff M. F., Campbell S. Functional characteristics of Peyer's patch lymphoid cells. I. Induction of humoral antibody and cell-mediated allograft reactions. J Exp Med. 1974 Feb 1;139(2):398–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.2.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagnoff M. F. Functional characteristics of Peyer's patch cells. III. Carrier priming of T cells by antigen feeding. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1425–1435. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagnoff M. F. Functional characteristics of Peyer's patch lymphoid cells. IV. Effect of antigen feeding on the frequency of antigen-specific B cells. J Immunol. 1977 Mar;118(3):992–997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyono H., Babb J. L., Michalek S. M., McGhee J. R. Cellular basis for elevated IgA responses in C3H/HeJ mice. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):732–737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ly I. A., Mishell R. I. Separation of mouse spleen cells by passage through columns of sephadex G-10. J Immunol Methods. 1974 Aug;5(3):239–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(74)90108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löwy I., Bona C., Chedid L. Target cells for the activity of a synthetic adjuvant: muramyl dipeptide. Cell Immunol. 1977 Mar 1;29(1):195–199. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90288-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDermott M. R., Bienenstock J. Evidence for a common mucosal immunologic system. I. Migration of B immunoblasts into intestinal, respiratory, and genital tissues. J Immunol. 1979 May;122(5):1892–1898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDermott M. R., Clark D. A., Bienenstock J. Evidence for a common mucosal immunologic system. II. Influence of the estrous cycle on B immunoblast migration into genital and intestinal tissues. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2536–2539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. R., Farrar J. J., Michalek S. M., Mergenhagen S. E., Rosenstreich D. L. Cellular requirements for lipopolysaccharide adjuvanticity. A role for both T lymphocytes and macrophages for in vitro responses to particulate antigens. J Exp Med. 1979 Apr 1;149(4):793–807. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.4.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntire F. C., Sievert H. W., Barlow G. H., Finley R. A., Lee A. Y. Chemical, physical, biological properties of a lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli K-235. Biochemistry. 1967 Aug;6(8):2363–2372. doi: 10.1021/bi00860a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishell R. I., Dutton R. W. Immunization of dissociated spleen cell cultures from normal mice. J Exp Med. 1967 Sep 1;126(3):423–442. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.3.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Leive L. Fractions of lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli O111:B4 prepared by two extraction procedures. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 25;250(8):2911–2919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ryan J. L. Bacterial endotoxins and host immune responses. Adv Immunol. 1979;28:293–450. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60802-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagao S., Tanaka A., Yamamoto Y., Koga T., Onoue K., Shiba T., Kusumoto K., Kotani S. Inhibition of macrophage migration by muramyl peptides. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):308–312. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.308-312.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman L. K., Graeff A. S., Strober W. Antigen presentation by macrophage-enriched cells from the mouse Peyer's patch. Cell Immunol. 1981 Jul 15;62(1):110–118. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90304-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman L. K., Graeff A. S., Yarchoan R., Strober W. Simultaneous induction of antigen-specific IgA helper T cells and IgG suppressor T cells in the murine Peyer's patch after protein feeding. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2079–2083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Nussenzweig M. C. Dendritic cells: features and functions. Immunol Rev. 1980;53:127–147. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb01042.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trefts P. E., Rivier D. A., Kagnoff M. F. T cell-dependent IgA anti-polysaccharide response in vitro. Nature. 1981 Jul 9;292(5819):163–164. doi: 10.1038/292163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksman B. H. The homing pattern of thymus-derived lymphocytes in calf and neonatal mouse Peyer's patches. J Immunol. 1973 Sep;111(3):878–884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J., Whitlock C. Effect of a synthetic adjuvant on the induction of primary immune responses in T cell-depleted spleen cultures. J Immunol. 1978 Jul;121(1):383–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisz-Carrington P., Roux M. E., McWilliams M., PHILLIPS-Quagliata J. M., Lamm M. E. Organ and isotype distribution of plasma cells producing specific antibody after oral immunization: evidence for a generalized secretory immune system. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1705–1708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yam L. T., Li C. Y., Crosby W. H. Cytochemical identification of monocytes and granulocytes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971 Mar;55(3):283–290. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/55.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


