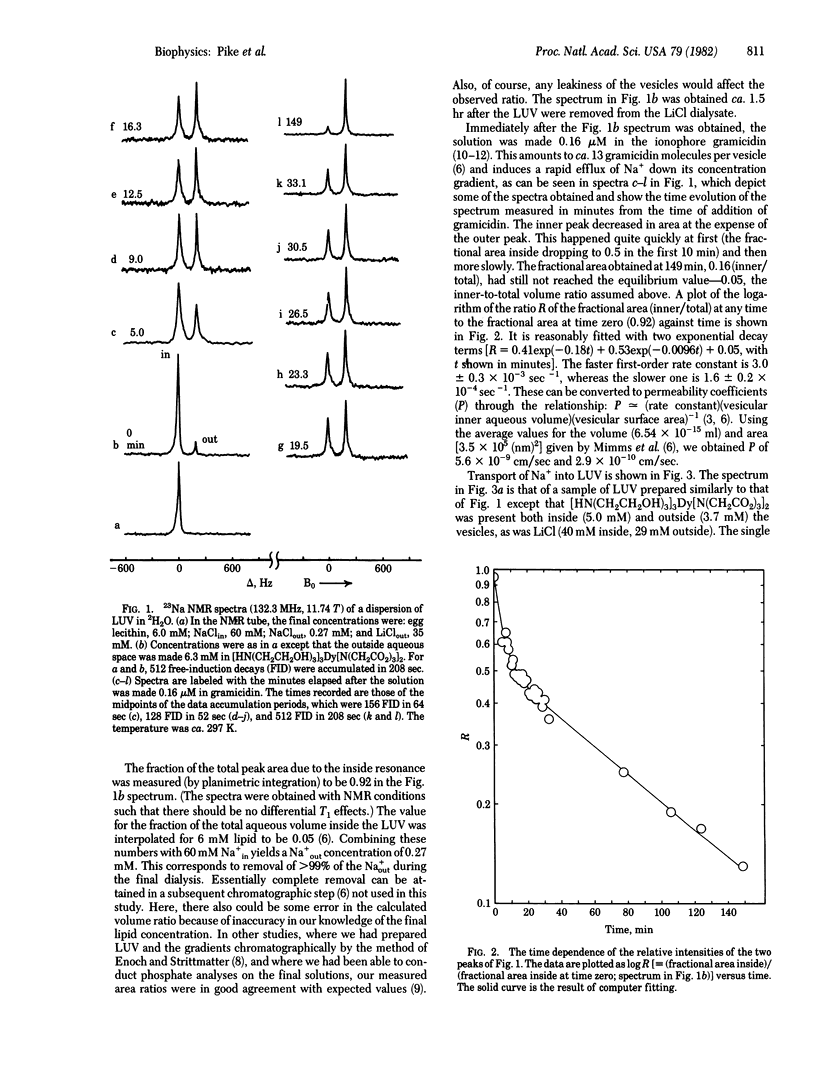
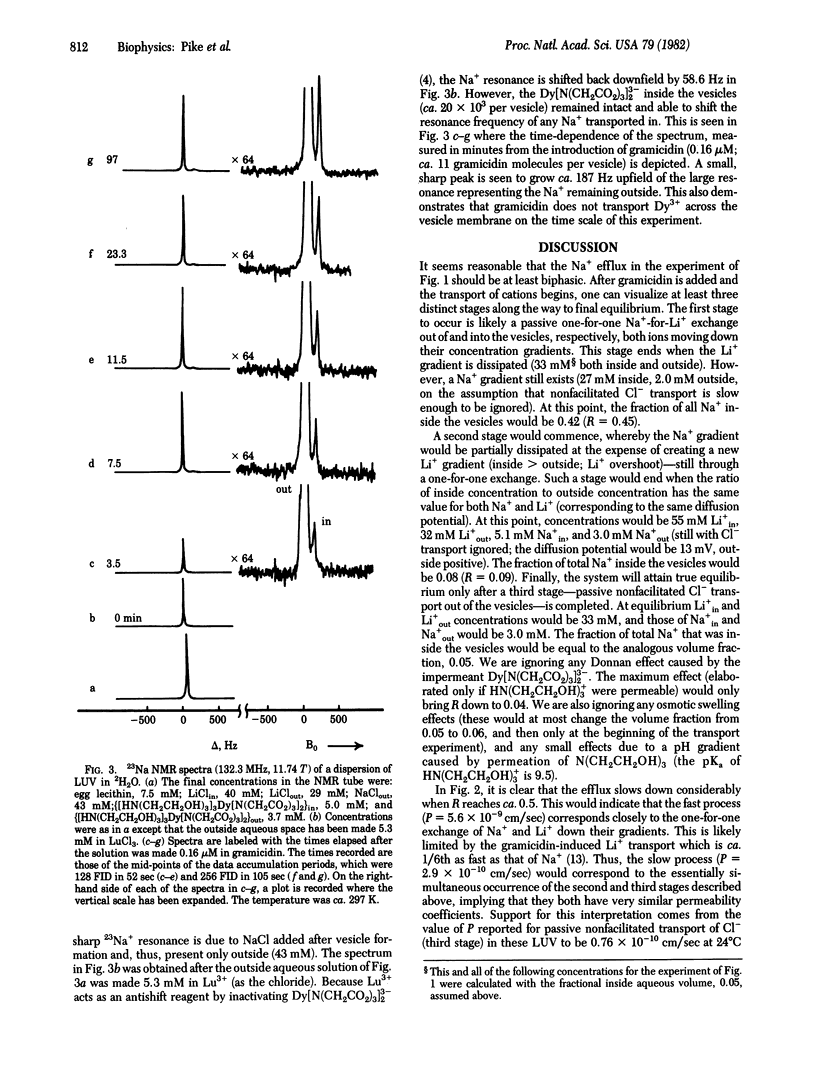
Abstract
23Na NMR studies of large unilamellar vesicles of egg lecithin in salt solutions are reported. A shift reagent, the dysprosium nitrilotriacetate ion Dy[N(CH2CO2)3]3-2 has been used to distinguish between 23Na+ inside and outside the vesicles. When both are present and the shift reagent is present on only one side, two clearly distinct resonances are observed. Creation of a Na+ concentration gradient and subsequent catalysis of passive transport induced by the introduction of gramicidin can be monitored easily by using the relative intensities of the two resonances. We report the observation of transport both out of and into vesicles.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alger J. R., Prestegard J. H. Nuclear magnetic resonance study of acetic acid permeation of large unilamellar vesicle membranes. Biophys J. 1979 Oct;28(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85154-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrzeszczyk A., Wishnia A., Springer C. S., Jr Evidence for cooperative effects in the bind of polyvalent metal ions to pure phosphatidylcholine bilayer vesicle surfaces. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Oct 20;648(1):28–48. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90121-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clement N. R., Gould J. M. Kinetics for development of gramicidin-induced ion permeability in unilamellar phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 17;20(6):1544–1548. doi: 10.1021/bi00509a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani J. A., Levitt D. G. Water transport and ion-water interaction in the gramicidin channel. Biophys J. 1981 Aug;35(2):501–508. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84805-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch H. G., Strittmatter P. Formation and properties of 1000-A-diameter, single-bilayer phospholipid vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):145–149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein A., Andersen O. S. The gramicidin A channel: a review of its permeability characteristics with special reference to the single-file aspect of transport. J Membr Biol. 1981 Apr 30;59(3):155–171. doi: 10.1007/BF01875422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldin S. M. Active transport of sodium and potassium ions by the sodium and potassium ion-activated adenosine triphosphatase from renal medulla. Reconstitution of the purified enzyme into a well defined in vitro transport system. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 25;252(16):5630–5642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs A. S., Albers R. W. The structure of proteins involved in active membrane transport. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1980;9:259–291. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.09.060180.001355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurland R., Newton C., Nir S., Papahadjopoulos D. Specificity of Na+ binding to phosphatidylserine vesicles from a 23Na NMR relaxation rate study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 20;551(1):137–147. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Läuger P. Kinetic properties of ion carriers and channels. J Membr Biol. 1980 Dec 30;57(3):163–78(-RETURN-). doi: 10.1007/BF01869585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimms L. T., Zampighi G., Nozaki Y., Tanford C., Reynolds J. A. Phospholipid vesicle formation and transmembrane protein incorporation using octyl glucoside. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):833–840. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore H. P., Raftery M. A. Direct spectroscopic studies of cation translocation by Torpedo acetylcholine receptor on a time scale of physiological relevance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4509–4513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szoka F., Jr, Papahadjopoulos D. Comparative properties and methods of preparation of lipid vesicles (liposomes). Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1980;9:467–508. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.09.060180.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ting D. Z., Hagan P. S., Chan S. I., Doll J. D., Springer C. S., Jr Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of cation transport across vesicle bilayer membranes. Biophys J. 1981 May;34(2):189–216. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84845-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W., Venkatachalam C. M., Spisni A., Läuger P., Khaled M. A. Rate theory calculation of gramicidin single-channel currents using NMR-derived rate constants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2028–2032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villegas R., Villegas G. M. Nerve sodium channel incorporation in vesicles. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1981;10:387–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.10.060181.002131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


