Abstract
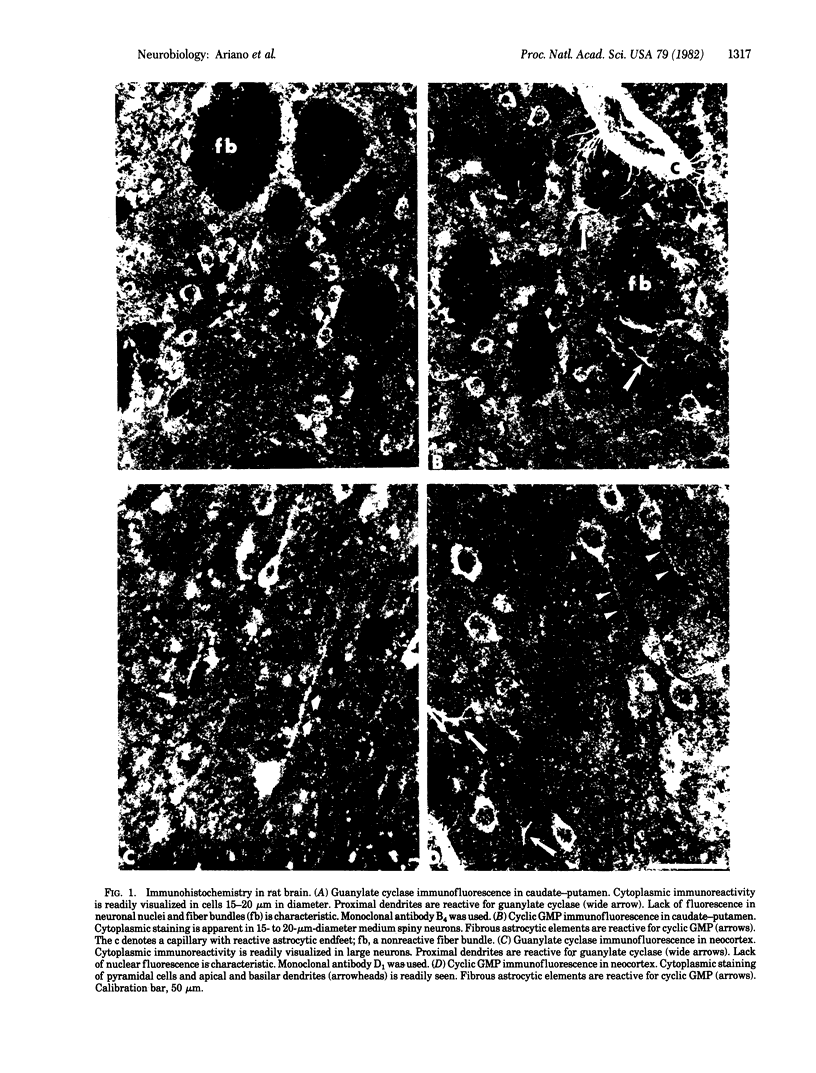
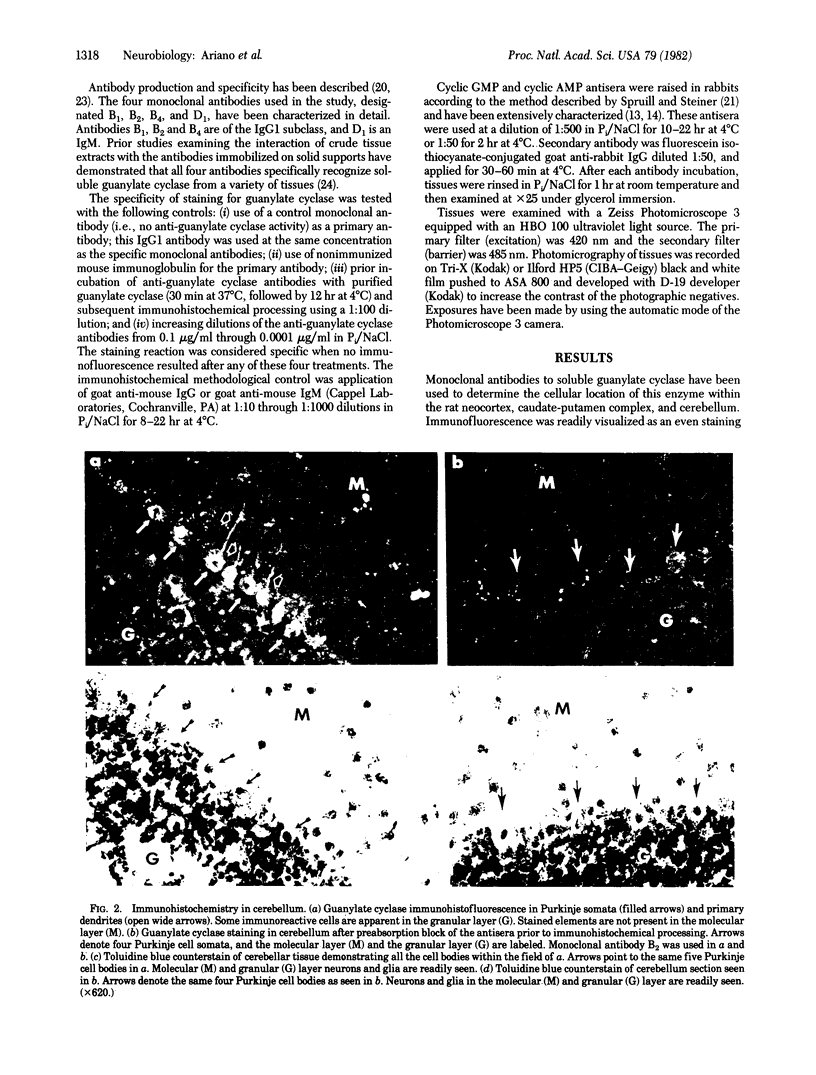
The immunohistochemical localization of guanylate cyclase [GTP pyrophosphate-lyase (cyclizing), EC 4.6.1.2] has been examined in rat neocortex, caudate-putamen, and cerebellum by using specific monoclonal antibodies. Immunofluorescence could be seen within somata and proximal dendrites of neurons in the these regions. A nuclear immunofluorescence reaction to guanylate cyclase was characteristically absent. The staining pattern for guanylate cyclase was coincident with previously described localizations of cyclic GMP immunofluorescence within medium spiny neurons of the caudate-putamen and pyramidal cells of the neocortex. Cerebellar guanylate cyclase immunoreactivity was primarily confined to Purkinje cells and their primary dendrites, similar to the pattern reported for cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase localization. Guanylate cyclase immunofluorescence was abolished when the monoclonal antibodies were exposed to purified enzyme prior to incubation of the tissue slices or when control antibody was substituted for the primary antibody. Immunohistochemical localization of cyclic AMP in these same tissues was readily distinguished from that of guanylate cyclase or cyclic GMP, showing uniform fluorescence throughout the cell bodies of neurons and glial elements.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ariano M. A., Appleman M. M. Biochemical characterization of postsynaptically localized cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Brain Res. 1979 Nov 16;177(2):301–309. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90781-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ariano M. A., Matus A. I. Ultrastructural localization of cyclic GMP and cyclic AMP in rat striatum. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):287–292. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandwein H., Lewicki J., Murad F. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to soluble rat lung guanylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4241–4245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan-Palay V., Palay S. L. Immunocytochemical localization of cyclic GMP: light and electron microscope evidence for involvement of neuroglia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1485–1488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumming R., Arbuthnott G., Steiner A. Characterization of immunofluorescent cyclic GMP-positive fibres in the central nervous system. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979 Dec;5(6):463–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFiglia M., Pasik P., Pasik T. A Golgi study of neuronal types in the neostriatum of monkeys. Brain Res. 1976 Sep 17;114(2):245–256. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90669-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrendelli J. A., Blank A. C., Gross R. A. Relationships between seizure activity and cyclic nucleotide levels in brain. Brain Res. 1980 Oct 27;200(1):93–103. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)91097-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goridis C., Morgan I. G. Guanyl cyclase in rat brain subcellular fractions. FEBS Lett. 1973 Aug 1;34(1):71–73. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80705-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg L. H., Troyer E., Ferrendelli J. A., Weiss B. Enzymatic regulation of the concentration of cyclic GMP in mouse brain. Neuropharmacology. 1978 Sep;17(9):737–745. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(78)90088-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanley M. R., Iversen L. L. Muscarinic cholinergic receptors in rat corpus striatum and regulation of guanosine cyclic 3',5'-monophosphate. Mol Pharmacol. 1978 Mar;14(2):246–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. G., Powell T. P. Electron microscopy of the somatic sensory cortex of the cat. I. Cell types and synaptic organization. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1970 Jan 29;257(812):1–11. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1970.0003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kebabian J. W., Blood F. E., Steiner A. L., Greengard P. Neurotransmitters increase cyclic nucleotides in postganglionic neurons: immunocytochemical demonstration. Science. 1975 Oct 10;190(4210):157–159. doi: 10.1126/science.241121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura H., Murad F. Two forms of guanylate cyclase in mammalian tissues and possible mechanisms for their regulation. Metabolism. 1975 Mar;24(3):439–445. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(75)90123-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. P., Kuo J. F., Greengard P. Role of muscarinic cholinergic receptors in regulation of guanosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate content in mammalian brain, heart muscle, and intestinal smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3287–3291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewicki J. A., Brandwein H. J., Waldman S. A., Murad F. Purified guanylate cyclase: characterization, iodination and preparation of monoclonal antibodies. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1980;6(4):283–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann S. M., Walter U., Miller P. E., Greengard P., De Camilli P. Immunohistochemical localization of cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase in mammalian brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):653–657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao C. C., Guidotti A., Costa E. The regulation of cyclic guanosine monophosphate in rat cerebellum: possible involvement of putative amino acid neurotransmitters. Brain Res. 1974 Oct 25;79(3):510–514. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90449-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlichter D. J., Detre J. A., Aswad D. W., Chehrazi B., Greengard P. Localization of cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase and substrate in mammalian cerebellum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5537–5541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spruill W. A., Steiner A. L. Cyclic nucleotide and protein kinase immunocytochemistry. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:169–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W., Taylor D. A. Microiontophoretic studies of the effects of cylic nucleotides on excitability of neurones in the rat cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1977 Apr;266(3):523–543. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walaas I. The effects of kainic acid injections on guanylate cyclase activity in the rat caudatoputamen, nucleus accumbens and septum. J Neurochem. 1981 Jan;36(1):233–241. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb02399.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weight F. F., Petzold G., Greengard P. Guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate in sympathetic ganglia: increase assoicated with synaptic transmission. Science. 1974 Dec 6;186(4167):942–944. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4167.942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]