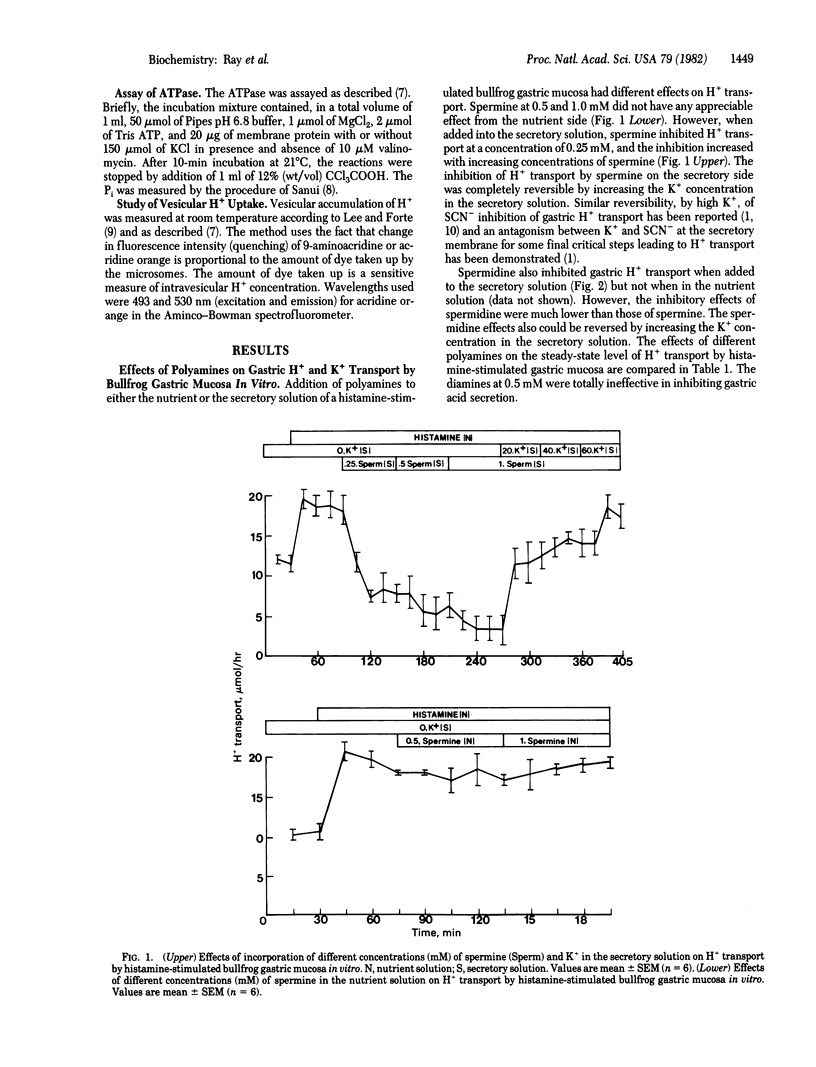
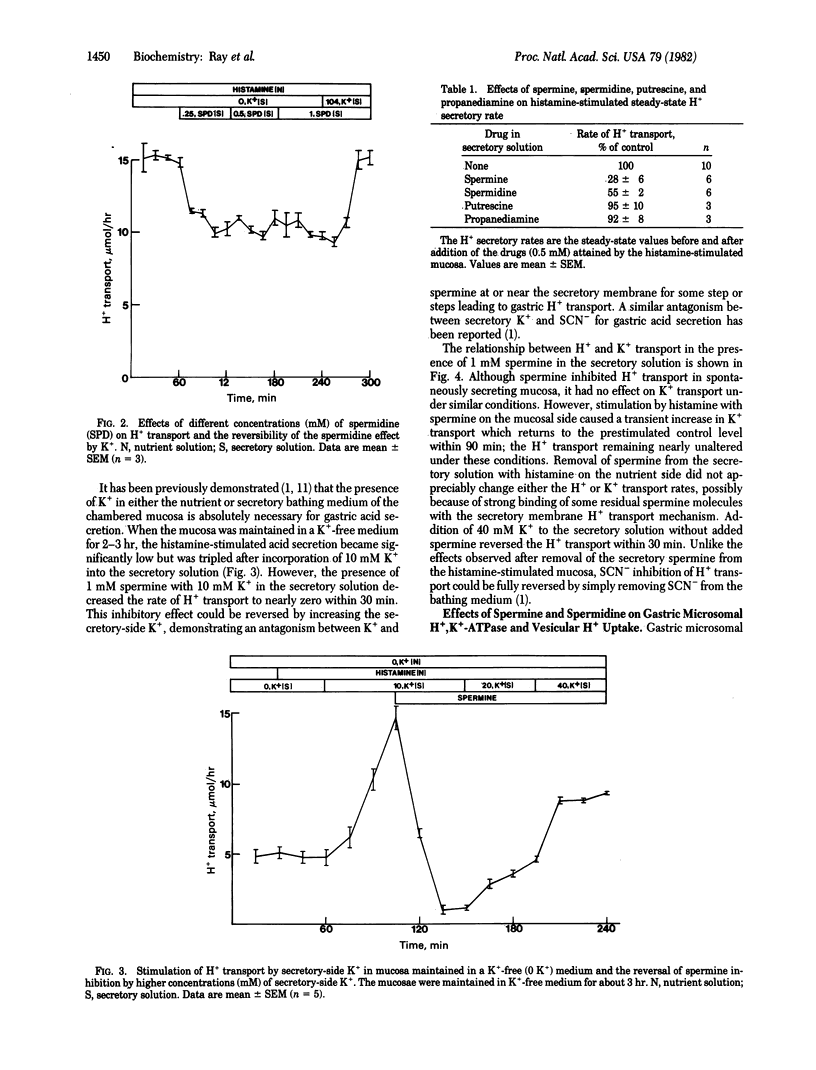
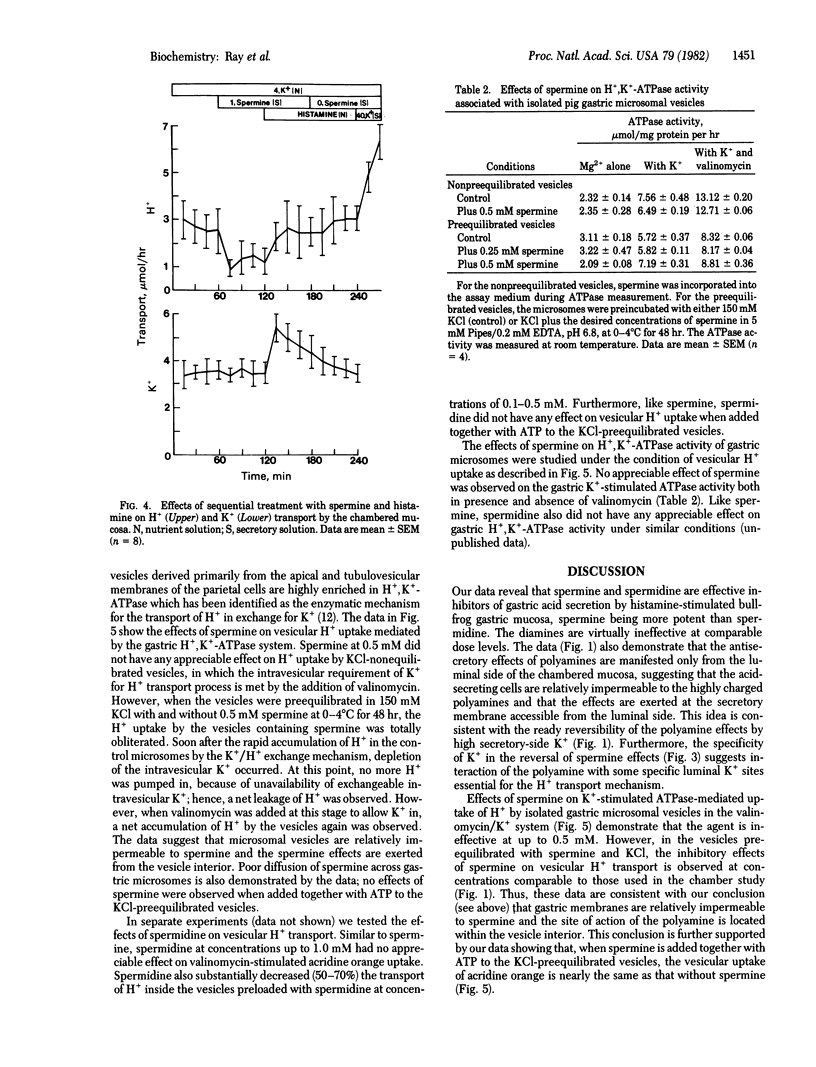
Abstract
The naturally occurring organic polycations such as spermine and spermidine inhibit histamine-stimulated gastric acid secretion by bullfrog gastric mucosa in vitro; spermine is much more potent than spermidine. Unlike the H2 receptor antagonists, the polyamines are completely ineffective from the nutrient side and are effective only from the secretory side of the chambered mucosa. The polyamine effects could be reversed by increasing K+ concentration in the secretory solution. Studies with isolated gastric microsomal vesicles demonstrate that the polyamines do not inhibit the gastric H+,K+-ATPase but greatly decrease the ATPase-mediated uptake of H+ under appropriate conditions. For the latter effects the presence of polyamine within the vesicle interior was found to be essential. Our data strongly suggest an uncoupling of the gastric H+,K+-ATPase system by the polyamines. The therapeutic potential of these and similar compounds in the treatment of hyperacidity and peptic ulcer is discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aigner-Held R., Daves G. D., Jr Polyamine metabolites and conjugates in man and higher animals: a review of the literature. Physiol Chem Phys. 1980;12(5):389–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forte J. G., Machen T. E., Obrink K. J. Mechanisms of gastric H+ and Cl- transport. Annu Rev Physiol. 1980;42:111–126. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.42.030180.000551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forte J. G., Ray T. K., Poulter J. L. A method for preparing oxyntic cells from frog gastric mucosa. J Appl Physiol. 1972 May;32(5):714–717. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1972.32.5.714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. C., Forte J. G. A study of H+ transport in gastric microsomal vesicles using fluorescent probes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 4;508(2):339–356. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90336-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray T. K. Gastric K+-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase. Demonstration of an endogenous activator. FEBS Lett. 1978 Aug 1;92(1):49–52. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80719-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray T. K., Tague L. L. Secretagogue-induced transport of H+ and K+ by in vitro amphibian gastric mucosa. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 Oct 15;29(20):2755–2758. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs G., Chang H. H., Rabon E., Schackman R., Lewin M., Saccomani G. A nonelectrogenic H+ pump in plasma membranes of hog stomach. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 10;251(23):7690–7698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders S. S., Noyes D. H., Spangler S. G., Rehm W. S. Demonstration of a barium-potassium antagonism on lumen side of in vitro frog stomach. Am J Physiol. 1973 Jun;224(6):1254–1259. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.6.1254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanui H. Measurement of inorganic orthophosphate in biological materials: extraction properties of butyl acetate. Anal Biochem. 1974 Aug;60(2):489–504. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90259-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen P. C., Ai Z. M., Ray T. K. Bilayer orientation of membrane-bound NH2 groups across microsomal vesicles and their role in the function of gastric K+-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Dec;205(2):340–351. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


