Abstract
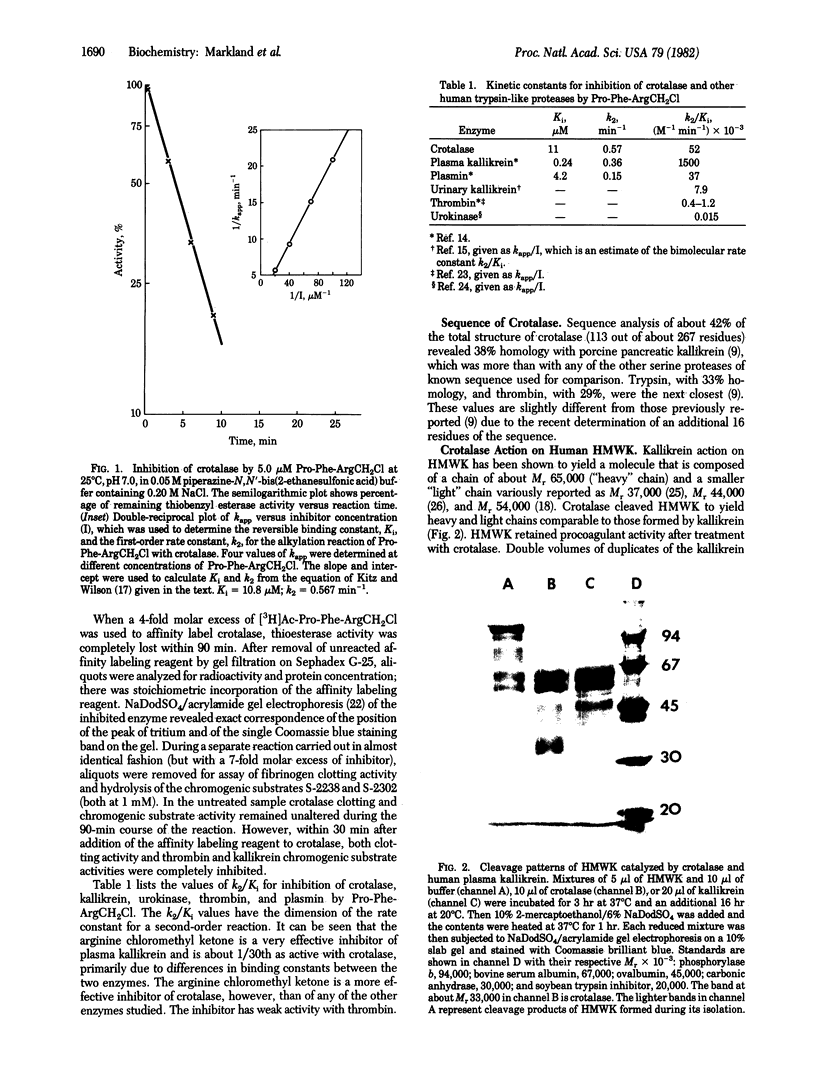
During the amino acid sequence determination of crotalase (EC 3.4.21.30), the thrombin-like enzyme from the venom of Crotalus adamanteus (eastern diamondback rattlesnake), we found that, in addition to the expected structural homology with bovine thrombin (EC 3.4.21.5), there was even greater homology with porcine pancreatic kallikrein (EC 3.4.21.8). In exploring further the similarities between crotalase and kallikrein, several striking observations were made. First, crotalase was rapidly and specifically inhibited by the tripeptide affinity labeling derivative prolylphenylalanylarginine chloromethyl ketone, which is known to be a specific inhibitor of kallikrein. Second, NaDodSO4/acrylamide gel electrophoresis revealed that crotalase cleaves the plasma kallikrein-susceptible bonds in human high molecular weight kininogen, producing an intermediate with procoagulant activity. Crotalase-catalyzed cleavage of high molecular weight kininogen also liberates kinin as evidenced by rat blood pressure bioassay. Finally, crotalase exhibits substrate specificity not only for the thrombin chromogenic substrate S-2238 but also for the kallikrein substrates S-2302 and S-2266. Interestingly, one of the other reactions catalyzed by plasma kallikrein, the activation of plasminogen, was not one of the activities exhibited by crotalase.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams Z., Gattullo D., Losano G., Marsh N. A., Vacca G., Whaler B. C. The effect of Bitis gabonica (gaboon viper) snake venom on blood pressure, stroke volume and coronary circulation in the dog. Toxicon. 1981;19(2):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(81)90030-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajwa S. S., Markland F. S., Jr A new method for purification of the thrombin-like enzyme from the venom of the eastern diamondback rattlesnake. Thromb Res. 1979;16(1-2):11–23. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90265-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claeson G., Aurell L., Friberger P., Gustavsson S., Karlsson G. Designing of peptide substrates. Different approaches exemplified by new chromogenic substrates for kallikreins and urokinase. Haemostasis. 1978;7(2-3):62–68. doi: 10.1159/000214236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman R. W. Activation of plasminogen by human plasma kallikrein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Apr 29;35(2):273–279. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damus P. S., Markland F. S., Davidson T. M., Shanley J. D. A purified procoagulant enzyme from the venom of the eastern diamondback rattlesnake (Crotalus adamanteus): in vivo and in vitro studies. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 Jun;79(6):906–923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 May;82(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egberg N. Coagulation studies in patients treated with defibrase. Acta Med Scand. 1973 Oct;194(4):291–302. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1973.tb19449.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huseby R. M., Smith R. E. Synthetic oligopeptide substrates: their diagnostic application in blood coagulation, fibrinolysis, and other pathologic states. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1980;6(3):175–314. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1005102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KITZ R., WILSON I. B. Esters of methanesulfonic acid as irreversible inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase. J Biol Chem. 1962 Oct;237:3245–3249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerbiriou D. M., Griffin J. H. Human high molecular weight kininogen. Studies of structure-function relationships and of proteolysis of the molecule occurring during contact activation of plasma. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 10;254(23):12020–12027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettner C., Mirabelli C., Pierce J. V., Shaw E. Active site mapping of human and rat urinary kallikreins by peptidyl chloromethyl ketones. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Jul;202(2):420–430. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90446-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettner C., Shaw E. Synthesis of peptides of arginine chloromethyl ketone. Selective inactivation of human plasma kallikrein. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4778–4784. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettner C., Shaw E. The susceptibility of urokinase to affinity labeling by peptides of arginine chloromethyl ketone. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jul 11;569(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90078-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundblad R. L., Kingdon H. S., Mann K. G. Thrombin. Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:156–176. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markland F. S., Damus P. S. Purification and properties of a thrombin-like enzyme from the venom of Crotalus adamanteus (Eastern diamondback rattlesnake). J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov;246(21):6460–6473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markland F. S., Jr Crotalase. Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:223–236. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45022-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markland F. S., Pirkle H. Thrombin-like enzyme from the venom of Crotalus adamanteus (eastern diamondback rattlesnake). Thromb Res. 1977 Mar;10(3):487–494. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90158-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattler L. E., Bang N. U. Serine protease specificity for peptide chromogenic substrates. Thromb Haemost. 1977 Dec 15;38(4):776–792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirkle H., Markland F. S., Theodor I., Baumgartner R., Bajwa S. S., Kirakossian H. The primary structure of crotalase, a thrombin-like venom enzyme, exhibits closer homology to kallikrein than to other serine proteases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Mar 31;99(2):715–721. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91802-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirkle H., Markland F. S., Theodor I. Thrombin-like enzymes of snake venoms: actions on prothrombin. Thromb Res. 1976 May;8(5):619–627. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(76)90243-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy K. N., Markus G. Mechanism of activation of human plasminogen by streptokinase. Presence of active center in streptokinase-plasminogen complex. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 25;247(6):1683–1691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffman S., Lee P., Feinstein D. I., Pecci R. Relationship of contact activation cofactor (CAC) procoagulant activity to kininogen. Blood. 1977 Jun;49(6):935–945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffman S., Mannhalter C., Tyner K. D. Human high molecular weight kininogen. Effects of cleavage by kallikrein on protein structure and procoagulant activity. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6433–6438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. E., Mandle R., Jr, Kaplan A. P. Characterization of human high molecular weight kininogen. Procoagulant activity associated with the light chain of kinin-free high molecular weight kininogen. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):488–499. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibbutt D. A., Chesterman C. N., Williams E. W., Faulkner T., Sharp A. A. Controlled trial of the sequential use of streptokinase and ancrod in the treatment of deep vein thrombosis of lower limb. Thromb Haemost. 1977 Apr 30;37(2):222–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viljoen C. C., Meehan C. M., Botes D. P. Separation of Bitis gabonica (Gaboon adder) venom arginine esterases into kinin-releasing, clotting and fibrinolytic factors. Toxicon. 1979;17(2):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(79)90293-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]