Abstract
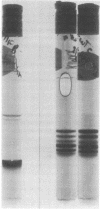
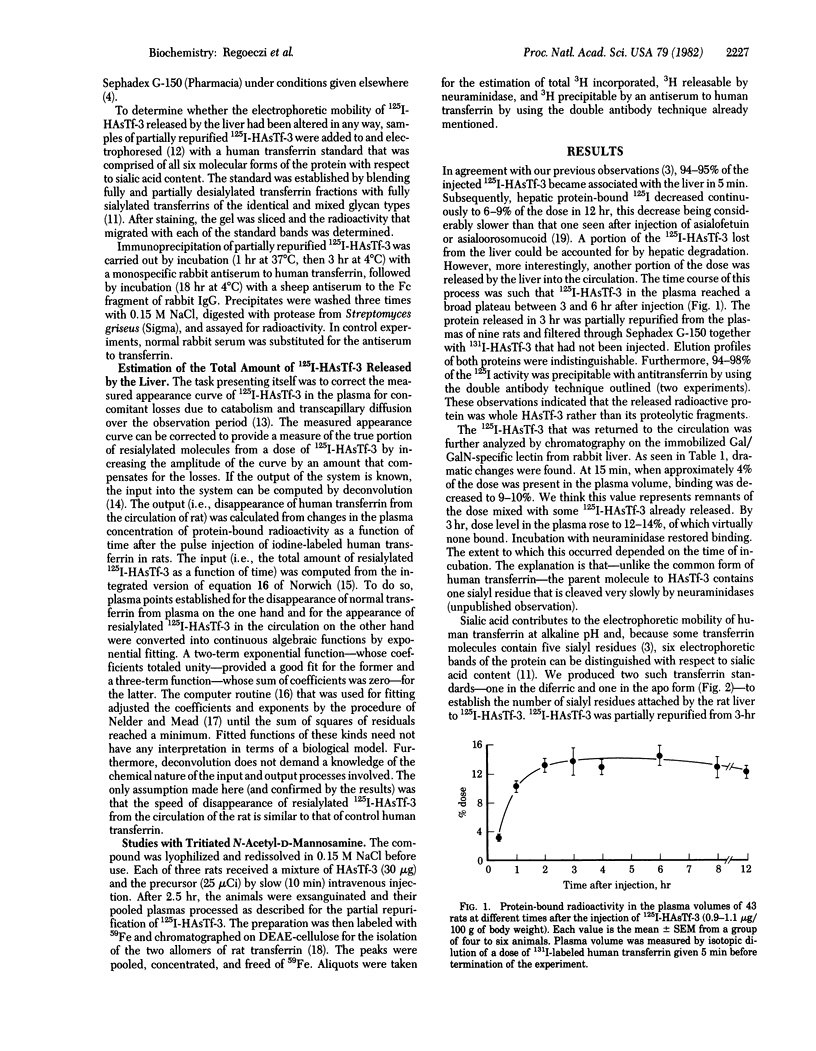
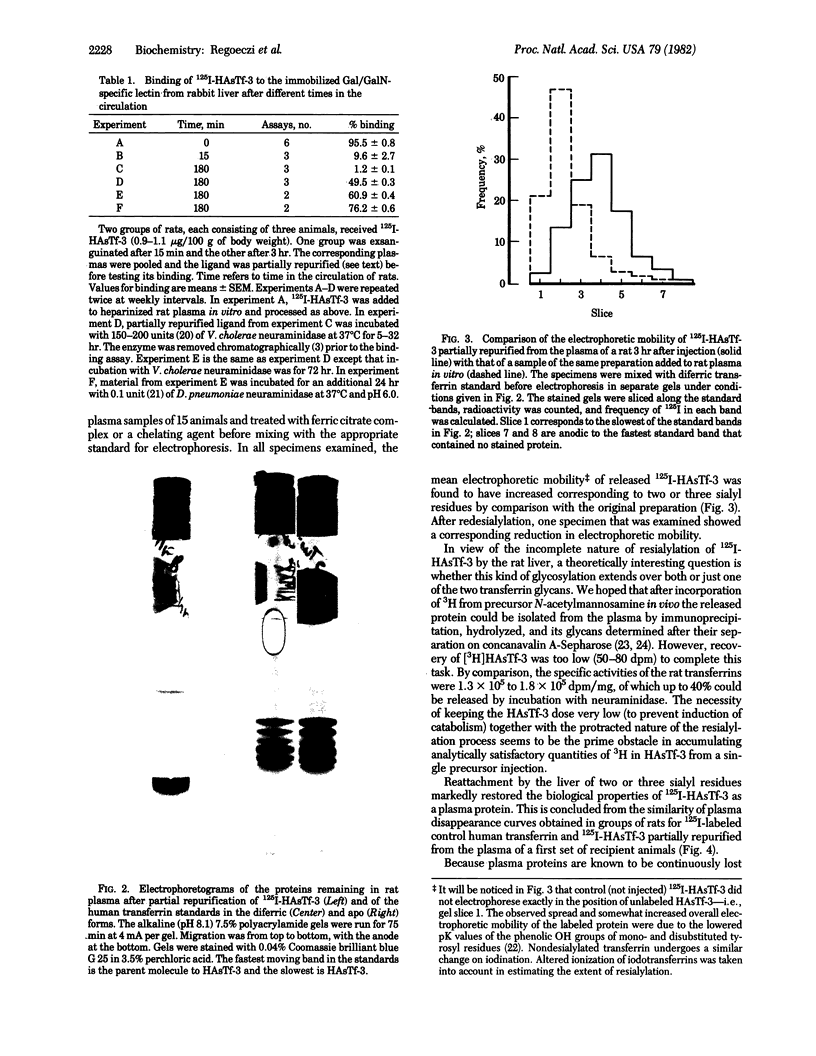
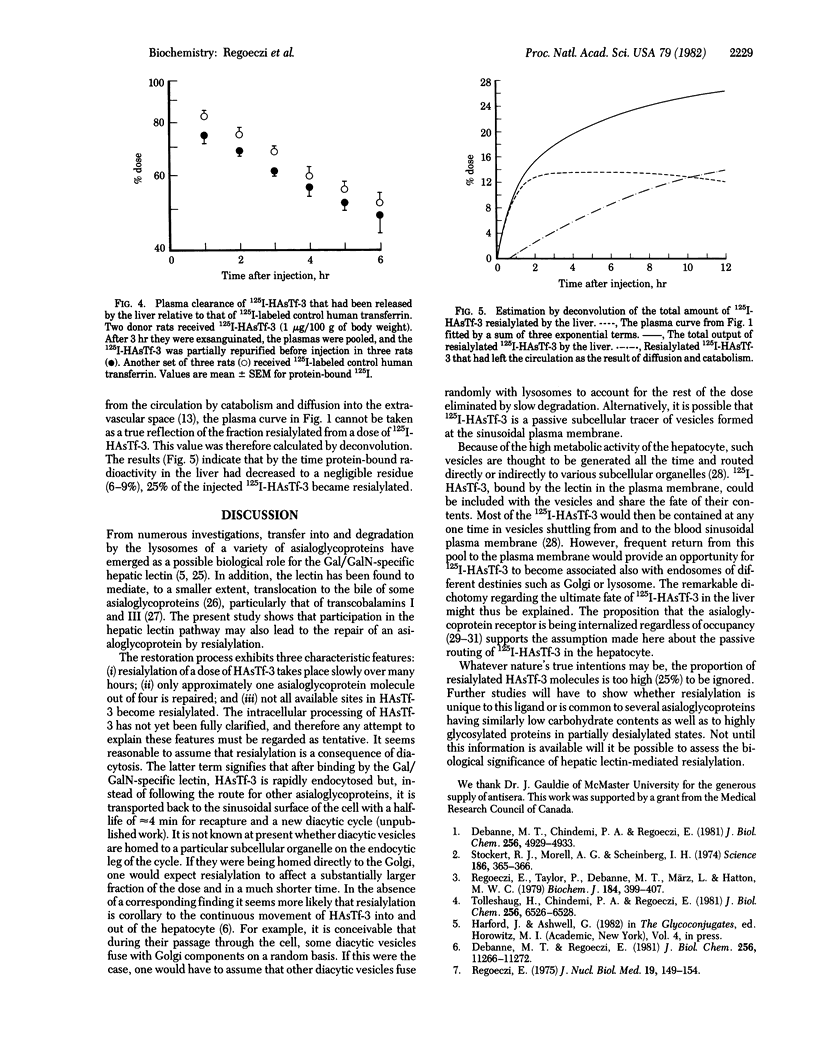
After the injection of a small dose (1 micrograms/100 g of body weight) of 125I-labeled human asialotransferrin type 3 in rats, the radioactivity became rapidly associated with the liver. However, during the ensuing 12 hr a significant fraction of the dose returned to the circulation as protein-bound 125I. The protein released by the liver was indistinguishable by gel filtration from the original preparation and was precipitable by an antiserum to human transferrin. Nevertheless, it no longer bound to the immobilized Gal/GalN-specific lectin from rabbit liver. However, binding could be restored to a large extent by treatment with neuraminidase, indicating that the loss of binding was due to resialylation. Changes in the electrophoretic mobility of asialotransferrin released by the liver showed that resialylation was partial--i.e., it involved the attachment of two or three sialyl residues. From analysis by deconvolution of the plasma curve of partially resialylated asialotransferrin it was calculated that the liver "repaired" this way approximately one asialotransferrin molecule out of four. Plasma clearance of partially resialylated asialotransferrin was similar to that of nondesialylated transferrin.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burger R. L., Schneider R. J., Mehlman C. S., Allen R. H. Human plasma R-type vitamin B12-binding proteins. II. The role of transcobalamin I, transcobalamin III, and the normal granulocyte vitamin B12-binding protein in the plasma transport of vitamin B12. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7707–7713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE J. T. SIMPLIFIED "DISC" (POLYACRYLAMIDE GEL) ELECTROPHORESIS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:428–436. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14214.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlwood P. A., Regoeczi E., Hatton M. W. Hepatic uptake and degradation of trace doses of asialofetuin and asialoorosomucoid in the intact rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jun 1;585(1):61–70. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90325-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debanne M. T., Chindemi P. A., Regoeczi E. Binding of asialotransferrins by purified rat liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4929–4933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debanne M. T., Regoeczi E. Subcellular distribution of human asialotransferrin type 3 in the rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11266–11272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. H. A biochemical dissection of the functional polarity of the plasma membrane of the hepatocyte. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 27;604(1):27–64. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90584-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON A. H., LOUIS L. N. PREPARATION AND PROPERTIES OF RAT TRANSFERRIN. Biochem J. 1963 Sep;88:409–414. doi: 10.1042/bj0880409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatton M. W., März L., Berry L. R., Debanne M. T., Regoeczi E. Bi-and tri-antennary human transferrin glycopeptides and their affinities for the hepatic lectin specific for asialo-glycoproteins. Biochem J. 1979 Sep 1;181(3):633–638. doi: 10.1042/bj1810633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudgin R. L., Pricer W. E., Jr, Ashwell G., Stockert R. J., Morell A. G. The isolation and properties of a rabbit liver binding protein specific for asialoglycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 10;249(17):5536–5543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki T., Ashwell G. Carbohydrate structure of glycopeptides isolated from an hepatic membrane-binding protein specific for asialoglycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 10;251(17):5292–5299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koj A., McFarlane A. S. Effect of endotoxin on plasma albumin and fibrinogen synthesis rates in rabbits as measured by the [14C] carbonate method. Biochem J. 1968 Jun;108(1):137–146. doi: 10.1042/bj1080137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolset S. O., Tolleshaug H., Berg T. The effects of colchicine and cytochalasin B on uptake and degradation of asialo-glycoproteins in isolated rat hepatocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Aug;122(1):159–167. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90570-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krusius T., Finne J., Rauvala H. The structural basis of the different affinities of two types of acidic N-glycosidic glycopeptides for concanavalin A--sepharose. FEBS Lett. 1976 Nov 15;72(1):117–120. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80911-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norwich K. H. Rates of plasma protein synthesis by deconvolution. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;126(5):1124–1126. doi: 10.1042/bj1261124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoeczi E., Hatton M. W., Long K. L. Studies of the metabolism of asialotransferrins: potentiation of the catabolism of human asialotransferrin in the rabbit. Can J Biochem. 1974 Mar;52(3):155–161. doi: 10.1139/o74-026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoeczi E. Hepatic uptake of asialoglycoproteins in vivo: quantification using a dual-isotope technique. J Nucl Biol Med. 1975 Jul-Sep;19(3):149–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoeczi E., Taylor P., Debanne M. T., März L., Hatton M. W. Three types of human asialo-transferrin and their interactions with the rat liver. Biochem J. 1979 Nov 15;184(2):399–407. doi: 10.1042/bj1840399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockert R. J., Morell A. G., Scheinberg I. H. Mammalian hepatic lectin. Science. 1974 Oct 25;186(4161):365–366. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4161.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P., Summers J. W. The biliary excretion of circulating asialoglycoproteins in the rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Jan 30;80(2):335–339. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90681-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolleshaug H., Berg T. Chloroquine reduces the number of asialo-glycoprotein receptors in the hepatocyte plasma membrane. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Oct 1;28(19):2919–2922. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90586-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolleshaug H., Chindemi P. A., Regoeczi E. Diacytosis of human asialotransferrin type 3 by isolated rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6526–6528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. L., Charlwood P. A., Hatton M. W., Regoeczi E. Studies of the metabolism of asialotransferrins: evidence that transferrin does not undergo desialylation in vivo. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1974 Jun;46(6):763–774. doi: 10.1042/cs0460763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. L., Debanne M. T., Hatton M. W., Regoeczi E. Human transferrin, asialotransferrin and the intermediate forms. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1978 Jul;12(1):27–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1978.tb02864.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]