Abstract
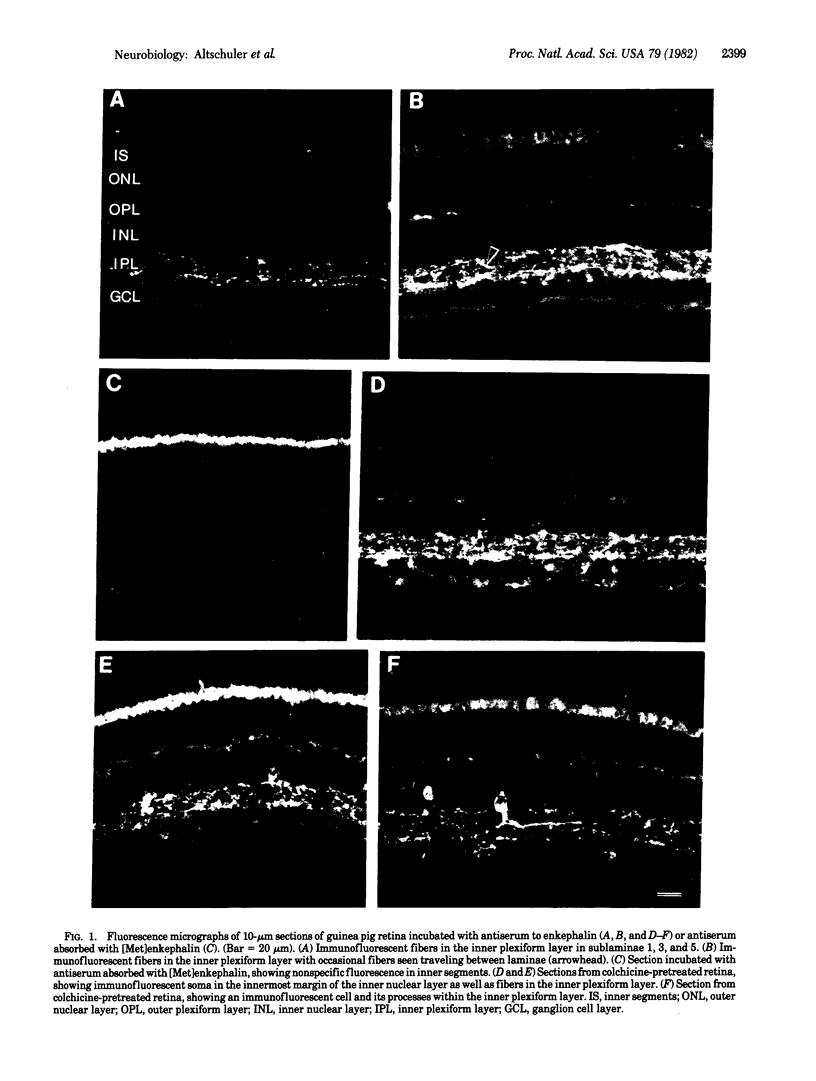
The distribution of enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in the retina of the guinea pig was studied. Indirect immunofluorescence techniques were used on retinae with and without colchicine pretreatment. In retinae not receiving colchicine pretreatment, enkephalin-like immunoreactivity was seen in fibers in the inner plexiform layer, predominantly in laminae 1, 3, and 5. In colchicine-pretreated retinae, enkephalin immunofluorescent cell bodies were seen in the inner margin of the inner nuclear layer in addition to the immunoreactive fibers. These cells showed morphological characteristics of amacrine cells. No enkephalin-like immunofluorescence was seen in the optic nerve, ganglion cell layer, or outer nuclear or plexiform layers. These findings of enkephalin-like immunoreactive cells and fibers in a mammalian retina add to the findings in nonmammalian retinae and suggest that the enkephalins play a role in primary sensory systems of mammalian and nonmammalian species.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atweh S. F., Kuhar M. J. Autoradiographic localization of opiate receptors in rat brain. III. The telencephalon. Brain Res. 1977 Oct 14;134(3):393–405. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90817-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brecha N., Karten H. J., Laverack C. Enkephalin-containing amacrine cells in the avian retina: immunohistochemical localization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):3010–3014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.3010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COONS A. H. Fluorescent antibody methods. Gen Cytochem Methods. 1958;1:399–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell J. H., Daw N. W. Effects of picrotoxin and strychnine on rabbit retinal ganglion cells: changes in centre surround receptive fields. J Physiol. 1978 Mar;276:299–310. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell J. H., Daw N. W., Wyatt H. J. Effects of picrotoxin and strychnine on rabbit retinal ganglion cells: lateral interactions for cells with more complex receptive fields. J Physiol. 1978 Mar;276:277–298. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djamgoz M. B., Stell W. K., Chin C. A., Lam D. M. An opiate system in the goldfish retina. Nature. 1981 Aug 13;292(5824):620–623. doi: 10.1038/292620a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling J. E. Synaptic organization of the frog retina: an electron microscopic analysis comparing the retinas of frogs and primates. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1968 Jun 11;170(1019):205–228. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1968.0034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubin M. W. The inner plexiform layer of the vertebrate retina: a quantitative and comparative electron microscopic analysis. J Comp Neurol. 1970 Dec;140(4):479–505. doi: 10.1002/cne.901400406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elde R., Hökfelt T., Johansson O., Terenius L. Immunohistochemical studies using antibodies to leucine-enkephalin: initial observations on the nervous system of the rat. Neuroscience. 1976 Aug;1(4):349–351. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(76)90063-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fex J., Altschuler R. A. Enkephalin-like immunoreactivity of olivocochlear nerve fibers in cochlea of guinea pig and cat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1255–1259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields H. L., Emson P. C., Leigh B. K., Gilbert R. F., Iversen L. L. Multiple opiate receptor sites on primary afferent fibres. Nature. 1980 Mar 27;284(5754):351–353. doi: 10.1038/284351a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herkenham M., Pert C. B. In vitro autoradiography of opiate receptors in rat brain suggests loci of "opiatergic" pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5532–5536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howells R. D., Groth J., Hiller J. M., Simon E. J. Opiate binding sites in the retina: properties and distribution. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Oct;215(1):60–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J., Smith T. W., Kosterlitz H. W., Fothergill L. A., Morgan B. A., Morris H. R. Identification of two related pentapeptides from the brain with potent opiate agonist activity. Nature. 1975 Dec 18;258(5536):577–580. doi: 10.1038/258577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humbert J., Pradelles P., Gros C., Dray F. Enkephalin-like products in embryonic chicken retina. Neurosci Lett. 1979 May;12(2-3):259–263. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(79)96072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson I. M., Bolaffi J. L., Guillemin R. Presence of immunoreactive beta-endorphin and enkephalin-like material in the retina and other tissues of the frog, Rana pipiens. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1980 Dec;42(4):505–508. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(80)90217-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medzihradsky F. Stereospecific binding of etorphine in isolated neural cells and in retina, determined by a sensitive microassay. Brain Res. 1976 May 21;108(1):212–219. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90180-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Snyder S. H. Opiate receptor: demonstration in nervous tissue. Science. 1973 Mar 9;179(4077):1011–1014. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4077.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon E. J., Hiller J. M., Edelman I. Stereospecific binding of the potent narcotic analgesic (3H) Etorphine to rat-brain homogenate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):1947–1949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



