Abstract
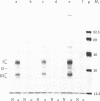
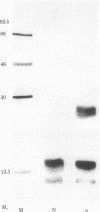
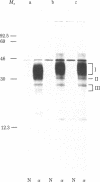
Immunoprecipitation of [35S]methionine-labeled extracts of BALB/c thymocytes with mouse Lyt-2.2 monoclonal antibody yielded three components with subunit Mrs of 37,000, 32,000, and 28,000 on NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gel in the presence of a reducing agent. Two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel analysis revealed that, in the absence of a reducing agent, the three polypeptide chains exist in the form of two heterodimers, each consisting of one molecule of a Mr 28,000 subunit covalently associated through disulfide bonds with either one Mr 37,000 subunit or one Mr 32,000 subunit. These two molecular structures are present in about equimolar ratios in the immunoprecipitate. Immunoautoradiographic analysis after electrophoretic transfer of proteins from a NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gel to a nitrocellulose membrane indicated that the Lyt-2.2 determinant detected by the monoclonal antibody resides on the Mr 28,000 component, the common subunit of both heterodimeric structures. Lyt-2 precipitated from extracts of different T-cell growth factor-dependent cloned T-cell lines also showed similar structures, although the exact apparent Mrs of the respective components varied somewhat. The structure of the Lyt-2 antigen is of importance, particularly in the light of recent suggestions that it may be involved in the construction of one class of T-cell receptors.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyse E. A., Itakura K., Stockert E., Iritani C. A., Miura M. Ly-C: a third locus specifying alloantigens expressed only on thymocytes and lymphocytes. Transplantation. 1971 Mar;11(3):351–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyse E. A., Miyazawa M., Aoki T., Old L. J. Ly-A and Ly-B: two systems of lymphocyte isoantigens in the mouse. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1968 Jun 11;170(1019):175–193. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1968.0032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor H., Boyse E. A. Functional subclasses of T-lymphocytes bearing different Ly antigens. I. The generation of functionally distinct T-cell subclasses is a differentiative process independent of antigen. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1376–1389. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor H., Boyse E. A. Lymphocytes as models for the study of mammalian cellular differentiation. Immunol Rev. 1977 Jan;33:105–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1977.tb00364.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durda P. J., Gottlieb P. D. Sequential precipitation of mouse thymocyte extracts with anti-Lyt-2 and anti-Lyt-3 sera. I. Lyt-2.1 and Lyt-3.1 antigenic determinants reside on separable molecular species. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):983–989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durda P. J., Gottlieb P. D. The Ly-3 antigens on mouse thymocytes: immune precipitation and molecular weight characterization. J Exp Med. 1976 Aug 1;144(2):476–493. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.2.476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan J., Bonavida B. Studies on the induction and expression of T cell-mediated immunity. XII. The concomitant loss and recovery of membrane-associated Lyt-2 antigens, lymphocyte-target cell binding, and the antigen-specific and -nonspecific cytotoxic activity of alloimmune T lymphocytes after treatment with trypsin. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1856–1864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. M., Taylor B. A., Cherry M. Evidence for close linkage of a mouse light chain marker with the Ly-2,3 locus. J Immunol. 1978 Oct;121(4):1585–1590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb P. D. Genetic correlation of a mouse light chain variable region marker with a thymocyte surface antigen. J Exp Med. 1974 Nov 1;140(5):1432–1437. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.5.1432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollander N., Pillemer E., Weissman I. L. Blocking effect of lyt-2 antibodies on T cell functions. J Exp Med. 1980 Sep 1;152(3):674–687. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.3.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollander N., Pillemer E., Weissman I. L. Effects of Lyt antibodies on T-cell functions: augmentation by anti-Lyt-1 as opposed to inhibition by anti-Lyt-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1148–1151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itakura K., Hutton J. J., Boyse E. A., Old L. J. Genetic linkage relationships of loci specifying differentiation alloantigens in the mouse. Transplantation. 1972 Mar;13(3):239–243. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197203000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itakura K., Hutton J. J., Boyse E. A., Old L. J. Linkage groups of the theta and Ly-A loci. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 24;230(12):126–126. doi: 10.1038/newbio230126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay G., Jay F. T., Friedman R. M., Levine A. S. Simian virus 40-specific ribosome-binding proteins induced by a nondefective adenovirus 2-simian virus 40 hybrid. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):692–699. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.692-699.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay G., Shiu R. P., Jay F. T., Levine A. S., Pastan I. Identification of a transformation-specific protein induced by a Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):527–534. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90326-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisielow P., Hirst J. A., Shiku H., Beverley P. C., Hoffman M. K., Boyse E. A., Oettgen H. F. Ly antigens as markers for functionally distinct subpopulations of thymus-derived lymphocytes of the mouse. Nature. 1975 Jan 17;253(5488):219–220. doi: 10.1038/253219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Herzenberg L. A. Xenogeneic monoclonal antibodies to mouse lymphoid differentiation antigens. Immunol Rev. 1979;47:63–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Seaman W. E., Tsu T. T., Herzenberg L. A. Lyt-2 and lyt-3 antigens are on two different polypeptide subunits linked by disulfide bonds. Relationship of subunits to T cell cytolytic activity. J Exp Med. 1981 Jun 1;153(6):1503–1516. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.6.1503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald H. R., Thiernesse N., Cerottini J. C. Inhibition of T cell-mediated cytolysis by monoclonal antibodies directed against Lyt-2: heterogeneity of inhibition at the clonal level. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1671–1675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama E., Dippold W., Shiku H., Oettgen H. F., Old L. J. Alloantigen-induced T-cell proliferation: Lyt phenotype of responding cells and blocking of proliferation by Lyt antisera. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2890–2894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama E., Shiku H., Stockert E., Oettgen H. F., Old L. J. Cytotoxic T cells: Lyt phenotype and blocking of killing activity by Lyt antisera. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1977–1981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly E. B., Auditore-Hargreaves K., Hämmerling U., Gottlieb P. D. Lyt-2 and Lyt-3 alloantigens: precipitation with monoclonal and conventional antibodies and analysis on one- and two-dimensional polyacrylamide gels. J Immunol. 1980 Nov;125(5):2245–2251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento M., Glasebrook A. L., Fitch F. W. IgG or IgM monoclonal antibodies reactive with different determinants on the molecular complex bearing Lyt 2 antigen block T cell-mediated cytolysis in the absence of complement. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2665–2672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiku H., Kisielow P., Bean M. A., Takahashi T., Boyse E. A., Oettgen H. F., Old L. J. Expression of T-cell differentiation antigens on effector cells in cell-mediated cytotoxicity in vitro. Evidence for functional heterogeneity related to the surface phenotype of T cells. J Exp Med. 1975 Jan 1;141(1):227–241. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.1.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara N., Sachs D. H. Mouse alloantibodies capable of blocking cytotoxic T-cell function. I. Relationship between the antigen reactive with blocking antibodies and the Lyt-2 locus. J Exp Med. 1979 Sep 19;150(3):432–444. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.3.432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tumor immunology. Transplant Proc. 1975 Mar;7(1 Suppl 1):473–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]