Abstract
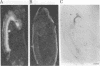
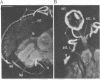
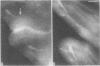
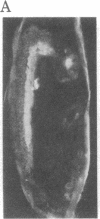
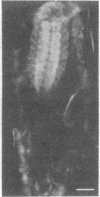
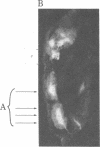
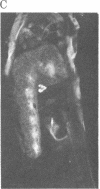
Antibodies specific for horseradish peroxidase (HRPeroxase) bind to neuronal membranes in Drosophila and serve as a specific neuronal marker. Immunocytochemical staining with these antibodies marks sensory neurons, peripheral nerves, and fiber tracks in the central nervous system of embryos, larvae, and adult flies. Similar patterns of staining also were seen in embryos of the grasshopper. It appears that an antigen associated with the nervous system and appearing early in differentiation is recognized by antibodies to HRPeroxase. Using this staining method, we followed embryogenesis of the central nervous system in Drosophila and found that the organization of central fiber tracks resembled that in the previously well-characterized grasshopper. We have used the anti-HRPeroxase antibodies to show that mutations affecting segmentation in Drosophila affect the organization of the embryonic nervous system.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bate C. M., Grunewald E. B. Embryogenesis of an insect nervous system II: a second class of neuron precursor cells and the origin of the intersegmental connectives. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1981 Feb;61:317–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bate C. M. Pioneer neurones in an insect embryo. Nature. 1976 Mar 4;260(5546):54–56. doi: 10.1038/260054a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman C. S., Bate M., Spitzer N. C. Embryonic development of identified neurons: origin and transformation of the H cell. J Neurosci. 1981 Jan;1(1):94–102. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-01-00094.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janning W. Aldehyde oxidase as a cell marker for internal organs in Drosophila melanogaster. Naturwissenschaften. 1972 Nov;59(11):516–517. doi: 10.1007/BF00609828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kankel D. R., Hall J. C. Fate mapping of nervous system and other internal tissues in genetic mosaics of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1976 Jan;48(1):1–24. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90041-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshishian H. The origin and morphogenesis of pioneer neurons in the grasshopper metathoracic leg. Dev Biol. 1980 Dec;80(2):388–397. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90413-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence P. A. A general cell marker for clonal analysis of Drosophila development. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1981 Aug;64:321–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis E. B. A gene complex controlling segmentation in Drosophila. Nature. 1978 Dec 7;276(5688):565–570. doi: 10.1038/276565a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nüsslein-Volhard C., Wieschaus E. Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila. Nature. 1980 Oct 30;287(5785):795–801. doi: 10.1038/287795a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb J. A. Maintenance of imaginal discs of Drosophila melanogaster in chemically defined media. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jun;41(3):876–885. doi: 10.1083/jcb.41.3.876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White K. Defective neural development in Drosophila melanogaster embryos deficient for the tip of the X chromosome. Dev Biol. 1980 Dec;80(2):332–344. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90409-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]