Abstract
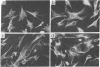
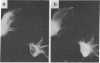
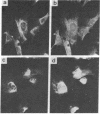
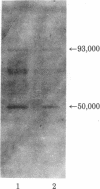
A monoclonal antibody directed against eukaryotic mRNA 5'-cap-binding protein (anti-CBP antibody) was used to localize cap-binding protein (CBP) in BHK-21 baby hamster kidney cells by immunofluorescence microscopy. It was found that the antibody reacts with a fibrous network extending through the cytoplasm in a radial arrangement. The network behaves like intermediate filaments in colchicine-treated cells, suggesting a direct or indirect linkage of CBP with intermediate filaments. The association of CBP with a cytoskeletal element was further confirmed by isolation of proteins from Triton X-100-extracted cells and identification of CBP in the cytoskeletal fraction with anti-CBP antibody. The major polypeptide reacting with anti-CBP antibody is a Mr 50,000 component. Tryptic peptide mapping showed that this polypeptide is related to a Mr 24,000 polypeptide identified as CBP in earlier experiments [Sonenberg, N., Morgan, M. A., Testa, D., Colonna, R. J. & Shatkin, A. J. (1978) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 75, 4843-4847].
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cebra J. J., Goldstein G. Chromatographic purification of tetramethylrhodamine-immune globulin conjugates and their use in the cellular localization of rabbit gamma-globulin polypeptide chains. J Immunol. 1965 Aug;95(2):230–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cervera M., Dreyfuss G., Penman S. Messenger RNA is translated when associated with the cytoskeletal framework in normal and VSV-infected HeLa cells. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):113–120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90276-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Pickett R. A., 2nd, Hampton J., Lerner R. A. Radioiodination of proteins in single polyacrylamide gel slices. Tryptic peptide analysis of all the major members of complex multicomponent systems using microgram quantities of total protein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6510–6515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisby D., Eaton M., Fellner P. Absence of 5' terminal capping in encephalomyocarditis virus RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Oct;3(10):2771–2787. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.10.2771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara K., Pollard T. D. Fluorescent antibody localization of myosin in the cytoplasm, cleavage furrow, and mitotic spindle of human cells. J Cell Biol. 1976 Dec;71(3):848–875. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.3.848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller G. M., Brinkley B. R., Boughter J. M. Immunofluorescence of mitotic spindles by using monospecific antibody against bovine brain tubulin. Science. 1975 Mar 14;187(4180):948–950. doi: 10.1126/science.1096300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger B. L., Lazarides E. Desmin and vimentin coexist at the periphery of the myofibril Z disc. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1053–1063. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman R., Zieve G., Williams F., Lenk R., Penman S. Cellular skeletons and RNA messages. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1976;19:379–401. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60933-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett M. J., Rose J. K., Baltimore D. 5'-terminal structure of poliovirus polyribosomal RNA is pUp. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):327–330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klootwijk J., Klein I., Zabel P., van Kammen A. Cowpea mosaic virus RNAs have neither m7GpppN ... nor mono-, di- or triphosphates at their 5' ends. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):73–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90318-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenk R., Penman S. The cytoskeletal framework and poliovirus metabolism. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):289–301. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenk R., Ransom L., Kaufmann Y., Penman S. A cytoskeletal structure with associated polyribosomes obtained from HeLa cells. Cell. 1977 Jan;10(1):67–78. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90141-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Lee Y. F., Wimmer E. The 5' end of poliovirus mRNA is not capped with m7G(5')ppp(5')Np. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):375–380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Trachsel H., Leong K., Baltimore D. Inhibition of translation by poliovirus: inactivation of a specific initiation factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2732–2736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier M. H., Erni B., Staehelin T. Initiation of mammalian protein synthesis. I. Purification and characterization of seven initiation factors. J Mol Biol. 1977 Nov;116(4):727–753. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90268-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J. Capping of eucaryotic mRNAs. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 2):645–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelanski M. L., Gaskin F., Cantor C. R. Microtubule assembly in the absence of added nucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):765–768. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skup D., Millward S. Reovirus-induced modification of cap-dependent translation in infected L cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):152–156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N. ATP/Mg++-dependent cross-linking of cap binding proteins to the 5' end of eukaryotic mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 10;9(7):1643–1656. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.7.1643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N., Morgan M. A., Merrick W. C., Shatkin A. J. A polypeptide in eukaryotic initiation factors that crosslinks specifically to the 5'-terminal cap in mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4843–4847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N., Morgan M. A., Testa D., Colonno R. J., Shatkin A. J. Interaction of a limited set of proteins with different mRNAs and protection of 5'-caps against pyrophosphatase digestion in initiation complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Sep 11;7(1):15–29. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N., Rupprecht K. M., Hecht S. M., Shatkin A. J. Eukaryotic mRNA cap binding protein: purification by affinity chromatography on sepharose-coupled m7GDP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4345–4349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N., Skup D., Trachsel H., Millward S. In vitro translation in reovirus- and poliovirus-infected cell extracts. Effects of anti-cap binding protein monoclonal antibody. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4138–4141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N., Trachsel H., Hecht S., Shatkin A. J. Differential stimulation of capped mRNA translation in vitro by cap binding protein. Nature. 1980 May 29;285(5763):331–333. doi: 10.1038/285331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starger J. M., Goldman R. D. Isolation and preliminary characterization of 10-nm filaments from baby hamster kidney (BHK-21) cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2422–2426. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stähli C., Staehelin T., Miggiano V., Schmidt J., Häring P. High frequencies of antigen-specific hybridomas: dependence on immunization parameters and prediction by spleen cell analysis. J Immunol Methods. 1980;32(3):297–304. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90194-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trachsel H., Sonenberg N., Shatkin A. J., Rose J. K., Leong K., Bergmann J. E., Gordon J., Baltimore D. Purification of a factor that restores translation of vesicular stomatitis virus mRNA in extracts from poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):770–774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingarten M. D., Lockwood A. H., Hwo S. Y., Kirschner M. W. A protein factor essential for microtubule assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1858–1862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimmer E., Chang A. Y., Clark J. M., Jr, Reichmann M. E. Sequence studies of satellite tobacco necrosis virus RNA. Isolation and characterization of a 5'-terminal trinucleotide. J Mol Biol. 1968 Nov 28;38(1):59–73. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90128-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolosewick J. J., Porter K. R. Microtrabecular lattice of the cytoplasmic ground substance. Artifact or reality. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jul;82(1):114–139. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolosewick J. J., Porter K. R. Stereo high-voltage electron microscopy of whole cells of the human diploid line, WI-38. Am J Anat. 1976 Nov;147(3):303–323. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001470305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]