Abstract
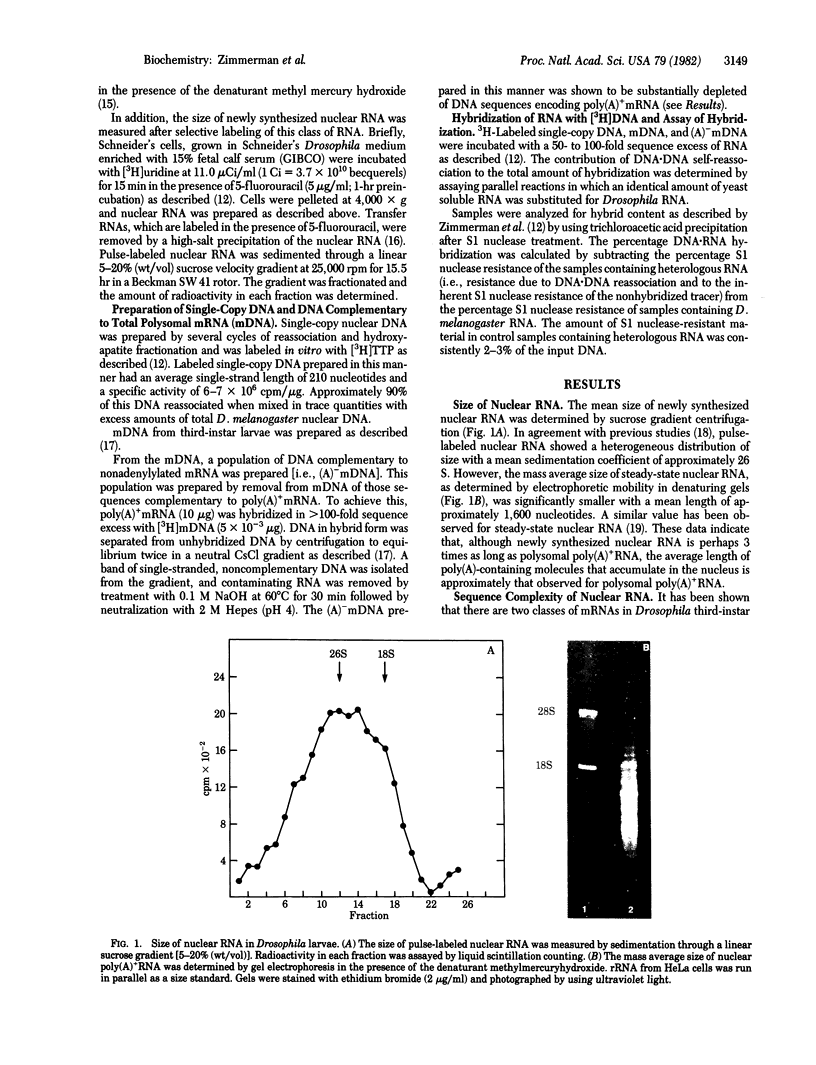
The sequence complexity of nuclear total RNA and nuclear poly(A)+RNA from Drosophila third-instar larvae was determined by hybridization of these RNAs to labeled single-copy DNA. At saturation, the nuclear poly(A)+ - and total RNA hybridized to 11% and 22.5% of the single-copy DNA, respectively. The increase in complexity of nuclear total RNA over that observed for nuclear poly(A)+RNA indicates the presence of a discrete class of nonoadenylylated nuclear RNA molecules. The relationship between DNA sequences coding for nuclear RNA and mRNA was then determined by hybridization of nuclear total and poly(A)+RNA to DNA enriched for mRNA coding sequences. The results of these studies show that those single-copy DNA sequences that are represented in either the poly(A)+ - or poly(A)- mRNA population are transcribed into RNA molecules that appear in the nuclear poly(A)+RNA population.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bantle J. A., Hahn W. E. Complexity and characterization of polyadenylated RNA in the mouse brain. Cell. 1976 May;8(1):139–150. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90195-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoff S., Nadal-Ginard B. Transient induction of poly(A)-short myosin heavy chain messenger RNA during terminal differentiation of L6E9 myoblasts. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jun 25;140(2):283–298. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90106-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann I. E., Brawerman G. Loss of the polyadenylate segment from mammalian messenger RNA. Selective cleavage of this sequence from polyribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1980 May 25;139(3):439–454. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90140-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chikaraishi D. M. Complexity of cytoplasmic polyadenylated and nonpolyadenylated rat brain ribonucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1979 Jul 24;18(15):3249–3256. doi: 10.1021/bi00582a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jelinek W. R., Molloy G. R. Biogenesis of mRNA: genetic regulation in mammalian cells. Science. 1973 Sep 28;181(4106):1215–1221. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4106.1215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galau G. A., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. A measurement of the sequence complexity of polysomal messenger RNA in sea urchin embryos. Cell. 1974 May;2(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galau G. A., Klein W. H., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Significance of rare m RNA sequences in liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Mar;179(2):584–599. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90147-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpold M. M., Evans R. M., Salditt-Georgieff M., Darnell J. E. Production of mRNA in Chinese hamster cells: relationship of the rate of synthesis to the cytoplasmic concentration of nine specific mRNA sequences. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):1025–1035. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90341-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereford L. M., Rosbash M. Number and distribution of polyadenylated RNA sequences in yeast. Cell. 1977 Mar;10(3):453–462. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90032-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren R., Livak K., Morimoto R., Freund R., Meselson M. Studies of cloned sequences from four Drosophila heat shock loci. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1359–1370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90246-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hough B. R., Smith M. J., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Sequence complexity of heterogeneous nuclear RNA in sea urchin embryos. Cell. 1975 Jul;5(3):291–299. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90104-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel J. A., Ransom L. J., Graham M. L., Pardue M. L. Transcription and metabolism of RNA from the Drosophila melanogaster heat shock puff site 93D. Chromosoma. 1980;80(3):237–252. doi: 10.1007/BF00292683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel J., Penman S. hnRNA size and processing as related to different DNA content in two dipterans: Drosophila and Aedes. Cell. 1975 Jul;5(3):281–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90103-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev Z., Thomas T. L., Lee A. S., Angerer R. C., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Developmental expression of two cloned sequences coding for rare sea urchin embryo messages. Dev Biol. 1980 May;76(2):322–340. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90382-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy B., Johnson C. B., McCarthy B. J. Diversity of sequences in total and polyadenylated nuclear RNA from Drosophila cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Jul;3(7):1777–1789. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.7.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy L. S., Manning J. E. Messenger RNA sequence complexity and homology in developmental stages of Drosophila. Dev Biol. 1981 Jul 15;85(1):141–149. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90243-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning J. E., Schmid C. W., Davidson N. Interspersion of repetitive and nonrepetitive DNA sequences in the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Cell. 1975 Feb;4(2):141–155. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90121-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medford R. M., Wydro R. M., Nguyen H. T., Nadal-Ginard B. Cytoplasmic processing of myosin heavy chain messenger RNA: evidence provided by using a recombinant DNA plasmid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5749–5753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. E., Arendes J., Zahn R. K., Schröder H. C. Control of enzymic hydrolysis of polyadenylate segment of messenger RNA: role of polyadenylate-associated proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1978 May;86(1):283–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12309.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. E. Endoribonuclease IV. A poly(A)-specific ribonuclease from chick oviduct. 1. Purification of the enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Nov 1;70(1):241–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10975.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. E., Schröder H. C., Arendes J., Steffen R., Zahn R. K., Dose K. Alterations of activities of ribonucleases and polyadenylate polymerase in synchronized mouse L cells. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jun 15;76(2):531–540. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11623.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. E., Seibert G., Steffen R., Zahn R. K. Endoribonuclease IV. 2. Further investigation on the specificity. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Nov 1;70(1):249–258. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10976.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordstrom J. L., Roop D. R., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Identification of potential ovomucoid mRNA precursors in chick oviduct nuclei. Nature. 1979 Mar 22;278(5702):328–331. doi: 10.1038/278328a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roop D. R., Nordstrom J. L., Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Transcription of structural and intervening sequences in the ovalbumin gene and identification of potential ovalbumin mRNA precursors. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):671–685. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90035-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder H. C., Zahn R. K., Dose K., Müller W. E. Purification and characterization of a poly(A)-specific exoribonuclease from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4535–4538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilghman S. M., Curtis P. J., Tiemeier D. C., Leder P., Weissmann C. The intervening sequence of a mouse beta-globin gene is transcribed within the 15S beta-globin mRNA precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1309–1313. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timberlake W. E. Low repetitive DNA content in Aspergillus nidulans. Science. 1978 Dec 1;202(4371):973–975. doi: 10.1126/science.362530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timberlake W. E., Shumard D. S., Goldberg R. B. Relationship between nuclear and polysomal RNA populations of Achlya: a simple eucaryotic system. Cell. 1977 Apr;10(4):623–632. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90095-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda M., Ohshima Y., Suzuki Y. Assumed initiation site of fibroin gene transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4872–4876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ness J., Maxwell I. H., Hahn W. E. Complex population of nonpolyadenylated messenger RNA in mouse brain. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1341–1349. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90244-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold B. J., Klein W. H., Hough-Evans B. R., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Sea urchin embryo mRNA sequences expressed in the nuclear RNA of adult tissues. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):941–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90348-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman J. L., Fouts D. L., Manning J. E. Evidence for a complex class of nonadenylated mRNA in Drosophila. Genetics. 1980 Jul;95(3):673–691. doi: 10.1093/genetics/95.3.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



