Abstract
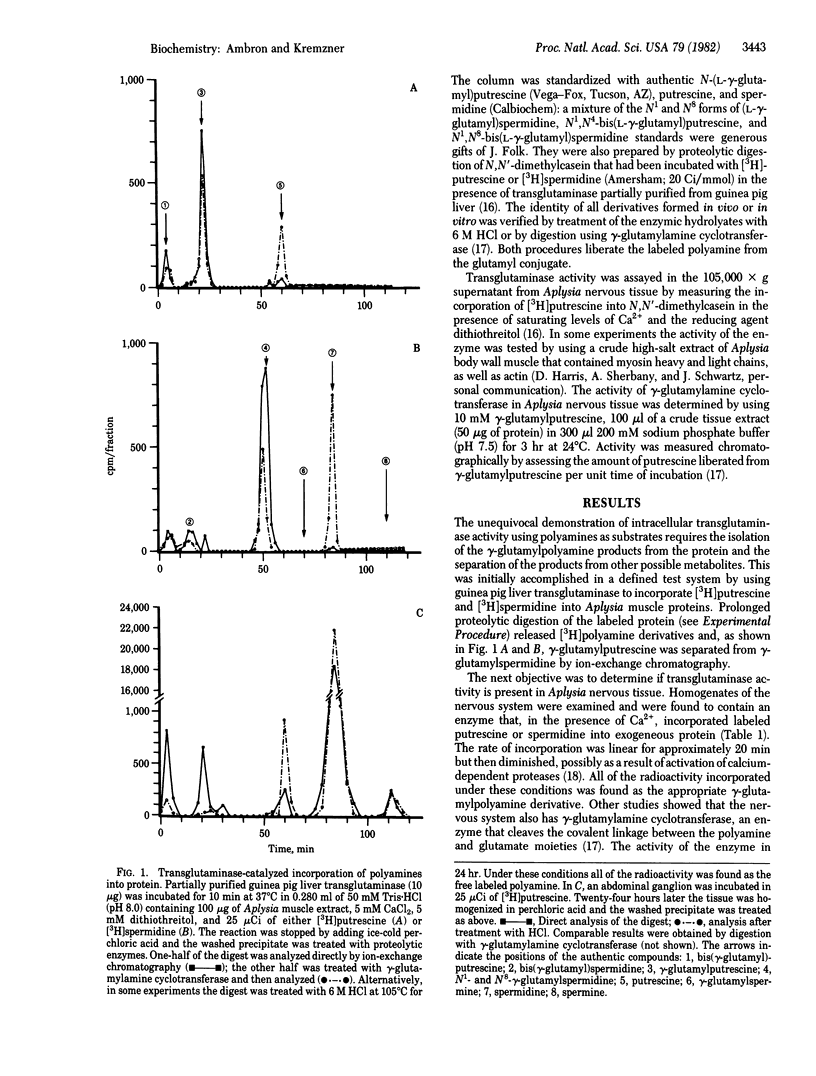
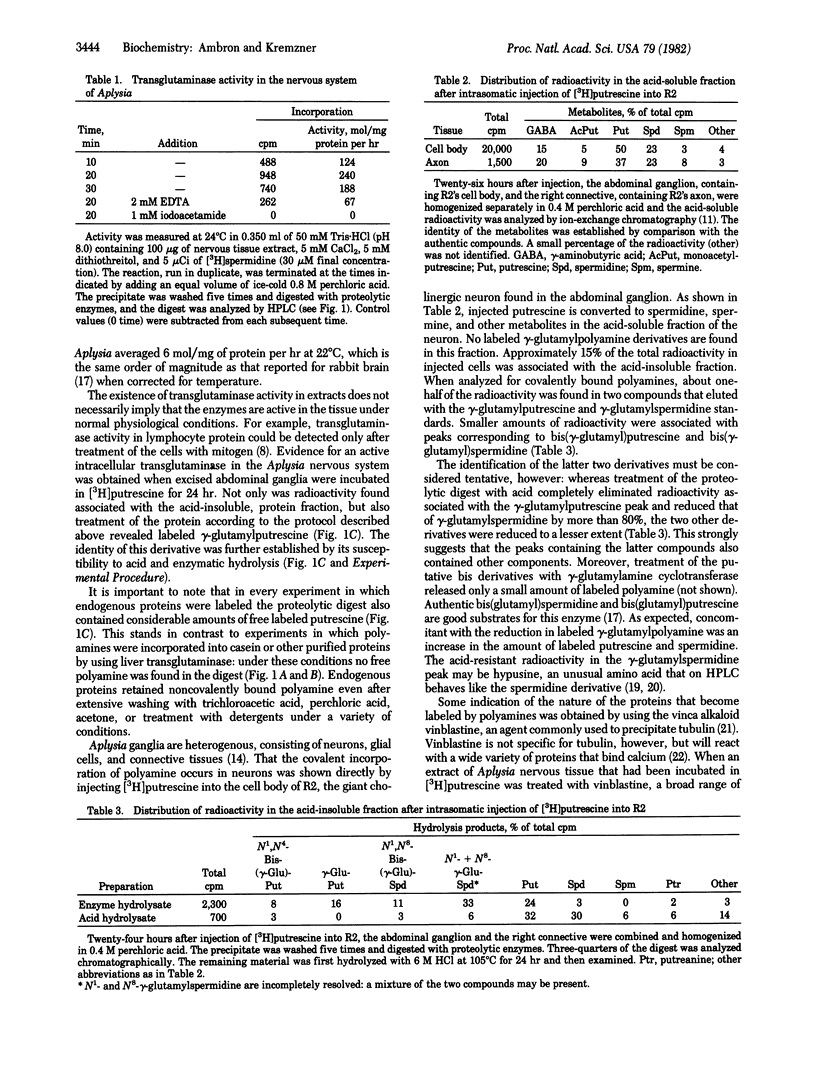
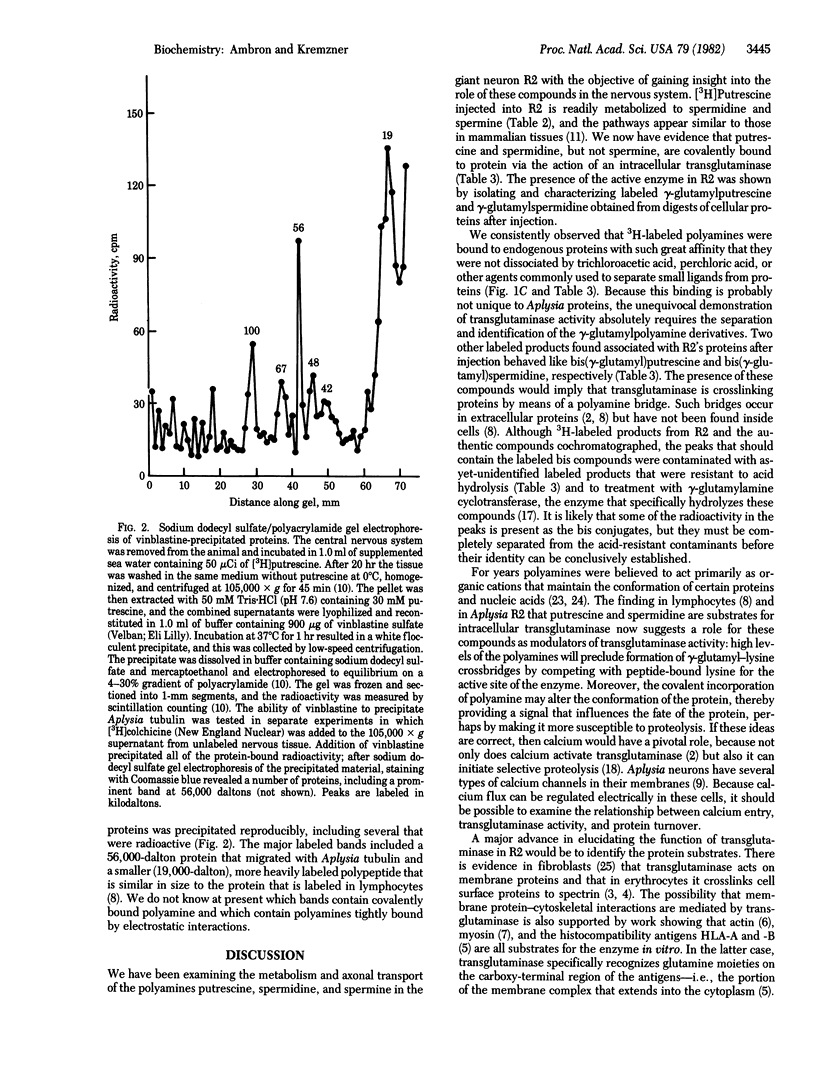
[3H]Putrescine injected into the cell body of the giant neuron R2 of Aplysia was readily converted to gamma-aminobutyric acid, acetylputrescine, spermidine, and spermine. In addition, labeled putrescine and spermidine were found covalently linked to protein through the action of an intracellular transglutaminase. This was shown by exhaustively treating the acid-insoluble fraction from injected cells with Pronase, aminopeptidase M, and carboxypeptidases A and B. High-performance liquid chromatography of the digest revealed labeled gamma-glutamylputrescine and gamma-glutamylspermidine, the products expected from the transglutaminase-catalyzed post-translational modification of intracellular proteins. In vitro assays of Aplysia nervous tissue showed the presence of transglutaminase as well as gamma-glutaminyl cyclotransferase, an enzyme that cleaves the gamma-glutamylpolyamine bond. Incorporation of polyamine into proteins in R2 is a specific process because only a few 3H-labeled polypeptides were found after injection.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambron R. T., Goldman J. E., Thompson E. B., Schwartz J. H. Synthesis of glycoproteins in a single identified neuron of Aplysia californica. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jun;61(3):649–664. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.3.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. R., Davis J. L., Carraway K. L. Calcium-promoted changes of the human erythrocyte membrane. Involvement of spectrin, transglutaminase, and a membrane-bound protease. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 10;252(19):6617–6623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudry M., Bundman M. C., Smith E. K., Lynch G. S. Micromolar calcium stimulates proteolysis and glutamate binding in rat brain synaptic membranes. Science. 1981 May 22;212(4497):937–938. doi: 10.1126/science.7015504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birckbichler P. J., Carter H. A., Orr G. R., Conway E., Patterson M. K., Jr epsilon-(gamma-Glutamyl)lysine isopeptide bonds in normal and virus transformed human fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Sep 14;84(1):232–237. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90287-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connellan J. M., Chung S. I., Whetzel N. K., Bradley L. M., Folk J. E. Structural properties of guinea pig liver transglutaminase. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 25;246(4):1093–1098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derrick N., Laki K. Enzymatic labelling of actin and tropomyosin with 14 C-labelled putrescine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jan 4;22(1):82–88. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90606-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstadt M., Goldman J. E., Kandel E. R., Koike H., Koester J., Schwartz J. H. Intrasomatic injection of radioactive precursors for studying transmitter synthesis in identified neurons of Aplysia californica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3371–3375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink M. L., Chung S. I., Folk J. E. gamma-Glutamylamine cyclotransferase: specificity toward epsilon-(L-gamma-glutamyl)-L-lysine and related compounds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4564–4568. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk J. E., Finlayson J. S. The epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl)lysine crosslink and the catalytic role of transglutaminases. Adv Protein Chem. 1977;31:1–133. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60217-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk J. E., Park M. H., Chung S. I., Schrode J., Lester E. P., Cooper H. L. Polyamines as physiological substrates for transglutaminases. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3695–3700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk J. E. Transglutaminases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:517–531. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Byerly L. Calcium channel. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1981;4:69–125. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.04.030181.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imaoka N., Nakajima T. Hypusine, N6-(4-amino-2-hydroxybutyl)-2,6-diaminohexanoic acid, in tissue proteins of mammals. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Aug 17;320(1):97–103. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90170-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremzner L. T., Ambron R. T. Metabolism and axonal transport of polyamines in a single identified neuron of Aplysia californica. J Neurochem. 1982 Jun;38(6):1719–1727. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb06654.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Weissmann L. B., Epel D. L., Bruner-Lorand J. Role of the intrinsic transglutaminase in the Ca2+-mediated crosslinking of erythrocyte proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4479–4481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park M. H., Cooper H. L., Folk J. E. Identification of hypusine, an unusual amino acid, in a protein from human lymphocytes and of spermidine as its biosynthetic precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2869–2873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Strominger J. L. Transglutaminase modifies the carboxy-terminal intracellular region of HLA-A and -B antigens. Nature. 1981 Feb 26;289(5800):819–821. doi: 10.1038/289819a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohjanpelto P., Virtanen I., Hölttä E. Polyamine starvation causes disappearance of actin filaments and microtubules in polyamine-auxotrophic CHO cells. Nature. 1981 Oct 8;293(5832):475–477. doi: 10.1038/293475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelanski M. L., Taylor E. W. Properties of the protein subunit of central-pair and outer-doublet microtubules of sea urchin flagella. J Cell Biol. 1968 Aug;38(2):304–315. doi: 10.1083/jcb.38.2.304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson L., Bryan J., Ruby A., Mazia D. Precipitation of proteins by vinblastine and calcium ions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):807–814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


