Abstract
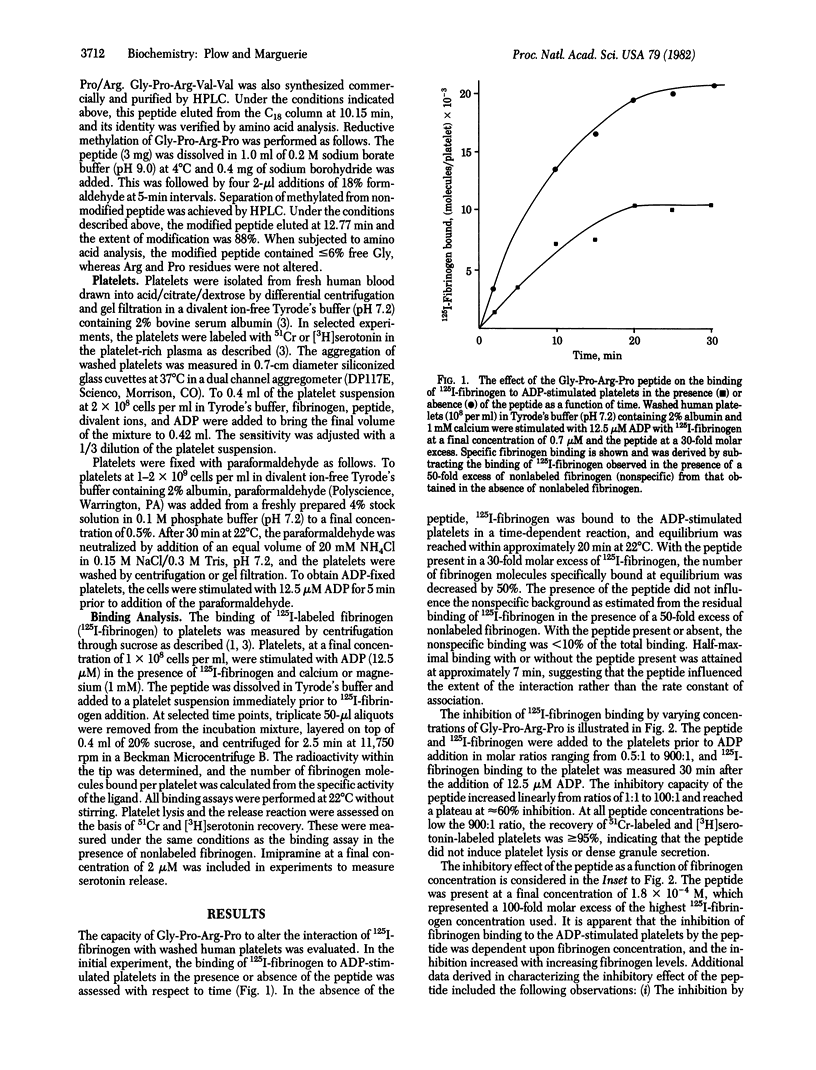
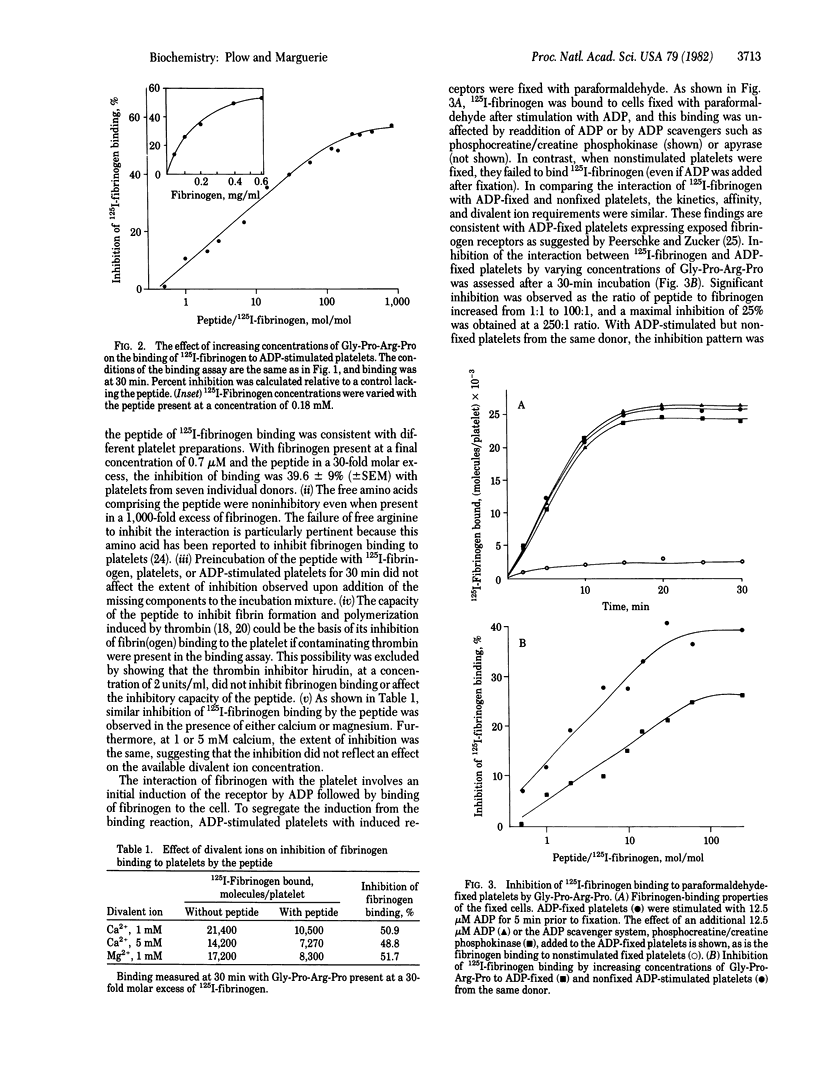
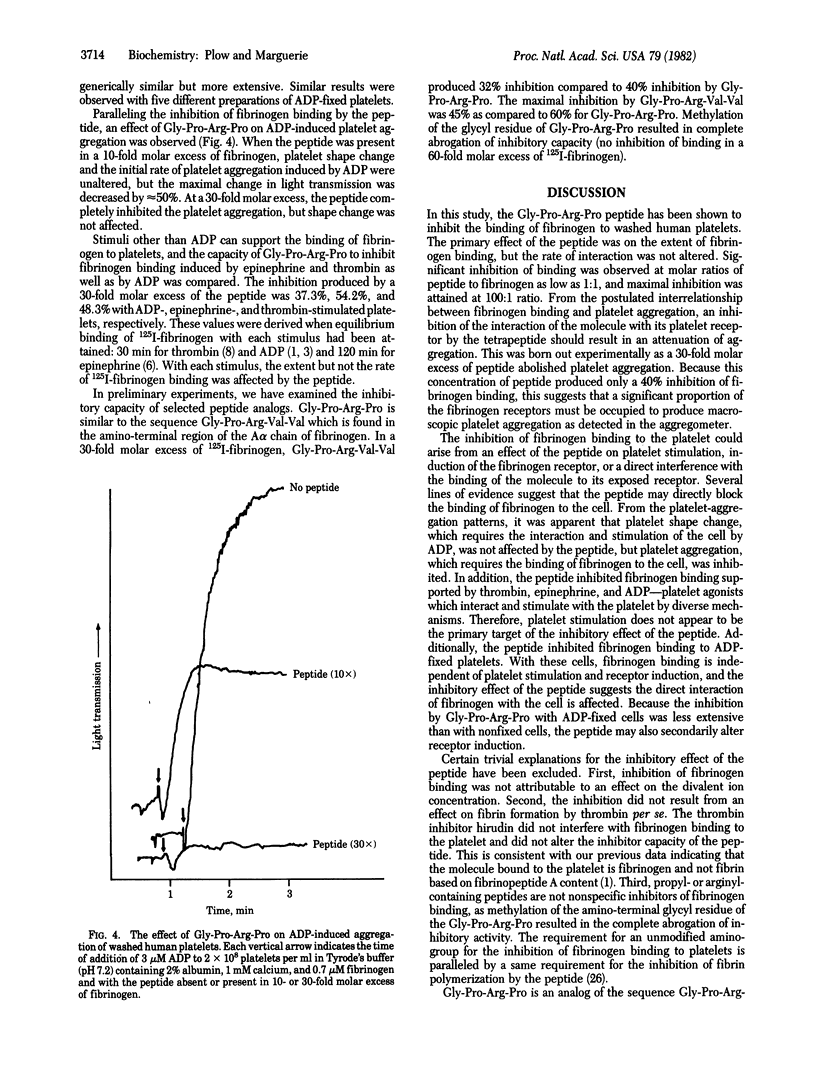
The role of fibrinogen as a cofactor in platelet aggregation is mediated by its binding to platelet receptors that are induced by stimuli such as ADP. In the present study, we demonstrate that the tetrapeptide glycyl-L-prolyl-L-arginyl-L-proline inhibits the interaction of fibrinogen with its platelet receptor. The primary effect of the peptide was on the extent rather than on the rate of fibrinogen binding. Significant inhibition occurred at a 1:1 molar ratio of peptide to fibrinogen and reached maximal levels at 100:1 ratio. The inhibition was dependent upon fibrinogen concentration and occurred in the presence of calcium or magnesium. The peptide inhibited the binding of fibrinogen to platelets with exposed receptors, suggesting that it interfered directly with the ligand-receptor interaction. Fibrinogen binding supported by epinephrine and thrombin as well as ADP was inhibited by the peptide. Fibrinogen-dependent aggregation of washed platelets by ADP was abolished by a 30-fold molar excess of the peptide. The tetrapeptide is an analog of the amino-terminal sequence of the alpha-chain of fibrin and has been shown to inhibit fibrin polymerization [Laudano, A. P. & Doolittle, R. F. (1978) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 75, 3085-3089]. A peptide corresponding to the natural sequence, glycyl-L-prolyl-L-arginyl-L-valyl-L-valine, was also capable of inhibiting fibrinogen binding to the platelet. These results suggest that common structural features within fibrinogen may serve a dual function by permitting the molecule to participate in both platelet aggregation and fibrin formation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett J. S., Vilaire G. Exposure of platelet fibrinogen receptors by ADP and epinephrine. J Clin Invest. 1979 Nov;64(5):1393–1401. doi: 10.1172/JCI109597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller B. S. Asialofibrinogen supports platelet aggregation and adhesion to glass. Blood. 1979 Feb;53(2):325–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Schubert D., Schwartz S. A. Amino acid sequence studies on artiodactyl fibrinopeptides. I. Dromedary camel, mule deer, and cape buffalo. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Feb;118(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90374-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Watt K. W., Cottrell B. A., Strong D. D., Riley M. The amino acid sequence of the alpha-chain of human fibrinogen. Nature. 1979 Aug 9;280(5722):464–468. doi: 10.1038/280464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harfenist E. J., Packham M. A., Mustard J. F. Identical behavior of fibrinogen and asialo-fibrinogen in reactions with platelets during ADP-induced aggregation. Thromb Res. 1980 Nov 1;20(3):353–358. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90239-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harfenist E. J., Packham M. A., Mustard J. F. Reversibility of the association of fibrinogen with rabbit platelets exposed to ADP. Blood. 1980 Aug;56(2):189–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawiger J., Parkinson S., Timmons S. Prostacyclin inhibits mobilisation of fibrinogen-binding sites on human ADP- and thrombin-treated platelets. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):195–197. doi: 10.1038/283195a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt J. C., Mahmoud M., Gaffney P. J. The ability of fibrinogen fragments to support ADP-induced platelet aggregation. Thromb Res. 1979;16(3-4):427–435. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90090-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh K. H., Mudd M. S., Wilner G. D. Fibrin Polymerization. 1. Alkylating peptide inhibitors of fibrin polymerization. J Med Chem. 1981 Mar;24(3):322–327. doi: 10.1021/jm00135a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEKWICK R. A., MACKAY M. E., NANCE M. H., RECORD B. R. The purification of human fibrinogen. Biochem J. 1955 Aug;60(4):671–683. doi: 10.1042/bj0600671b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laudano A. P., Doolittle R. F. Influence of calcium ion on the binding of fibrin amino terminal peptides to fibrinogen. Science. 1981 Apr 24;212(4493):457–459. doi: 10.1126/science.7209542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laudano A. P., Doolittle R. F. Studies on synthetic peptides that bind to fibrinogen and prevent fibrin polymerization. Structural requirements, number of binding sites, and species differences. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 4;19(5):1013–1019. doi: 10.1021/bi00546a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laudano A. P., Doolittle R. F. Synthetic peptide derivatives that bind to fibrinogen and prevent the polymerization of fibrin monomers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3085–3089. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liakopoulou-Kyriakides M., Galardy R. E. s-Cis and s-trans isomerism of the His-Pro peptide bond in angiotensin and thyroliberin analogues. Biochemistry. 1979 May 15;18(10):1952–1957. doi: 10.1021/bi00577a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marguerie G. A., Edgington T. S., Plow E. F. Interaction of fibrinogen with its platelet receptor as part of a multistep reaction in ADP-induced platelet aggregation. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):154–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marguerie G. A., Plow E. F., Edgington T. S. Human platelets possess an inducible and saturable receptor specific for fibrinogen. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5357–5363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marguerie G. A., Plow E. F. Interaction of fibrinogen with its platelet receptor: kinetics and effect of pH and temperature. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 3;20(5):1074–1080. doi: 10.1021/bi00508a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niewiarowski S., Budzynski A. Z., Lipinski B. Significance of the intact polypeptide chains of human fibrinogen in ADP-induced platelet aggregation. Blood. 1977 Apr;49(4):635–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niewiarowski S., Budzynski A. Z., Morinelli T. A., Brudzynski T. M., Stewart G. J. Exposure of fibrinogen receptor on human platelets by proteolytic enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):917–925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olexa S. A., Budzynski A. Z. Evidence for four different polymerization sites involved in human fibrin formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1374–1378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olexa S. A., Budzynski A. Z. Localization of a fibrin polymerization site. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3544–3549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peerschke E. I., Zucker M. B. Fibrinogen receptor exposure and aggregation of human blood platelets produced by ADP and chilling. Blood. 1981 Apr;57(4):663–670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peerschke E. I., Zucker M. B., Grant R. A., Egan J. J., Johnson M. M. Correlation between fibrinogen binding to human platelets and platelet aggregability. Blood. 1980 May;55(5):841–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Marguerie G. A. Induction of the fibrinogen receptor on human platelets by epinephrine and the combination of epinephrine and ADP. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10971–10977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Marguerie G. A. Participation of ADP in the binding of fibrinogen to thrombin-stimulated platelets. Blood. 1980 Sep;56(3):553–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soria J., Soria C., Bertrand O., Samama M. Fibrinogen and platelet aggregation. Role of the glycopeptidic part and of the fibrinopeptide B. Description of a new technique of fibrinoglycopeptide isolation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 May 30;82(2):442–450. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90895-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomikawa M., Iwamoto M., Söderman S., Blombäck B. Effect of fibrinogen on ADP-induced platelet aggregation. Thromb Res. 1980 Sep 15;19(6):841–855. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallén P. Plasmic degradation of fibrinogen. Scand J Haematol Suppl. 1971;13:3–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1971.tb01979.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


