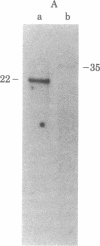
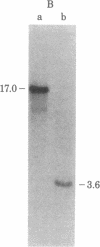
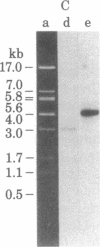
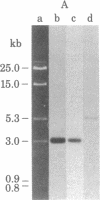
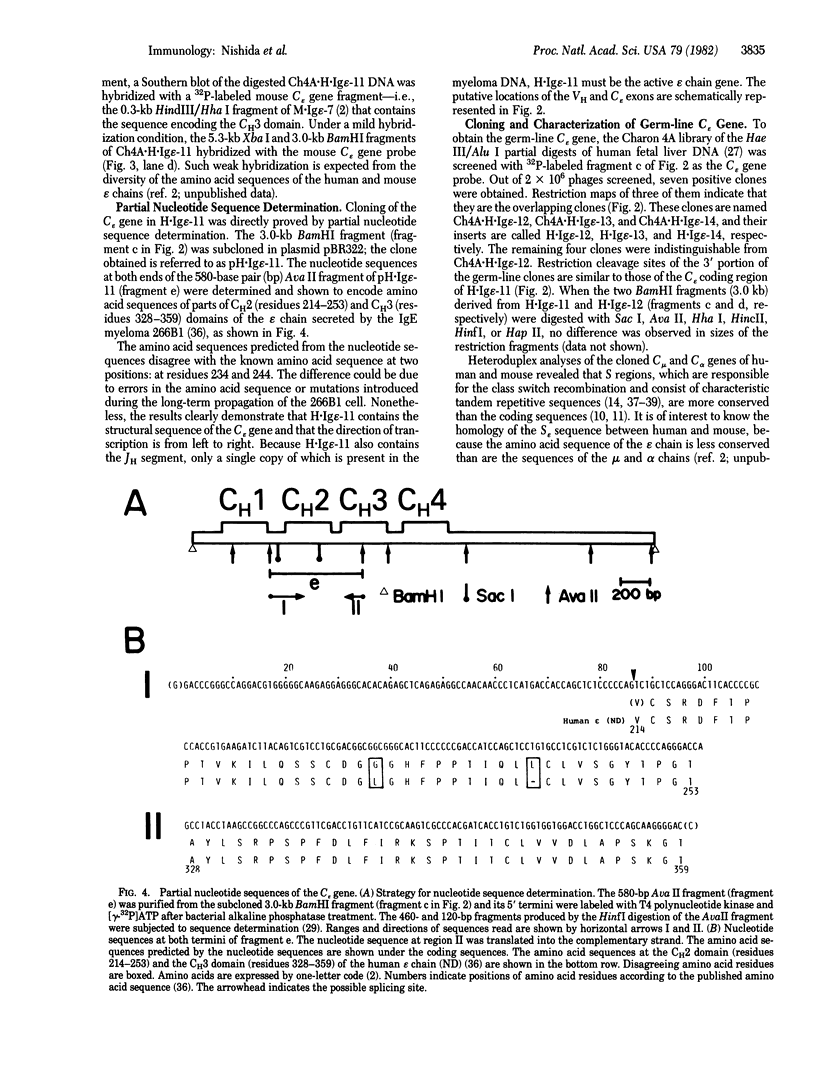
Abstract
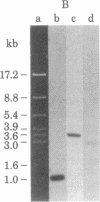
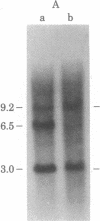
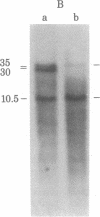
An active human epsilon chain gene was cloned from a phage library containing partial EcoRI digests of IgE-producing myeloma DNA, using the human JH (joining) gene fragment as a probe. The epsilon chain gene clone was identified by partial nucleotide sequence determination. The germ-line constant region gene of the epsilon chain (C epsilon gene) was cloned from a human fetal liver DNA library, using the cloned epsilon chain gene as a probe. Comparative studies on the human and mouse germ-line epsilon chain genes revealed that the switch (S) sequence is more conserved than the coding sequence. Restriction endonuclease BamHI digestion of human DNA produced three C epsilon fragments of 3.0, 6.5, and 9.2 kilobases, which were named C epsilon 1, C epsilon 2, and C epsilon 3 genes, respectively. We found the three C epsilon gene fragments in all of the human DNA preparations from eleven individuals. The C epsilon gene expressed in the myeloma was identified as the C epsilon 1 gene. Because the C epsilon 2 gene is deleted from the myeloma DNA, the order of the C epsilon genes is likely to be 5'-C epsilon 2-C epsilon 1-C epsilon 3-3', assuming that all the C epsilon genes are on chromosome 14. The germ-line C epsilon 3 gene was also cloned from the myeloma DNA. Characterization of the C epsilon 3 gene revealed that it does not have the S region, suggesting that it might be a pseudogene.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOYUM A. SEPARATION OF WHITE BLOOD CELLS. Nature. 1964 Nov 21;204:793–794. doi: 10.1038/204793a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Blechl A. E., Denniston-Thompson K., Faber H. E., Richards J. E., Slightom J. L., Tucker P. W., Smithies O. Cloning human fetal gamma globin and mouse alpha-type globin DNA: preparation and screening of shotgun collections. Science. 1978 Dec 22;202(4374):1279–1284. doi: 10.1126/science.725603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Williams B. G., Blechl A. E., Denniston-Thompson K., Faber H. E., Furlong L., Grunwald D. J., Kiefer D. O., Moore D. D., Schumm J. W. Charon phages: safer derivatives of bacteriophage lambda for DNA cloning. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):161–169. doi: 10.1126/science.847462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleclough C., Perry R. P., Karjalainen K., Weigert M. Aberrant rearrangements contribute significantly to the allelic exclusion of immunoglobulin gene expression. Nature. 1981 Apr 2;290(5805):372–378. doi: 10.1038/290372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Shander M., Martinis J., Cicurel L., D'Ancona G. G., Dolby T. W., Koprowski H. Chromosomal location of the genes for human immunoglobulin heavy chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3416–3419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. M., Calame K., Early P. W., Livant D. L., Joho R., Weissman I. L., Hood L. An immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene is formed by at least two recombinational events. Nature. 1980 Feb 21;283(5749):733–739. doi: 10.1038/283733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early P., Huang H., Davis M., Calame K., Hood L. An immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region gene is generated from three segments of DNA: VH, D and JH. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):981–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90089-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieter P. A., Korsmeyer S. J., Waldmann T. A., Leder P. Human immunoglobulin kappa light-chain genes are deleted or rearranged in lambda-producing B cells. Nature. 1981 Apr 2;290(5805):368–372. doi: 10.1038/290368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Obata M., Yamawaki-Katoaka Y., Kataoka T., Kawakami T., Takahashi N., Mano Y. Cloning and complete nucleotide sequence of mouse immunoglobulin gamma 1 chain gene. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):559–568. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90072-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K., Ishizaka T. Physicochemical properties of reaginic antibody. 1. Association of reaginic activity with an immunoglobulin other than gammaA- or gammaG-globulin. J Allergy. 1966 Mar;37(3):169–185. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(66)90091-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka T., Kawakami T., Takahashi N., Honjo T. Rearrangement of immunoglobulin gamma 1-chain gene and mechanism for heavy-chain class switch. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):919–923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka T., Miyata T., Honjo T. Repetitive sequences in class-switch recombination regions of immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):357–368. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90131-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Tiemeier D., Enquist L. EK2 derivatives of bacteriophage lambda useful in the cloning of DNA from higher organisms: the lambdagtWES system. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):175–177. doi: 10.1126/science.322278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. P., Tucker P. W., Mushinski J. F., Blattner F. R. Mapping of heavy chain genes for mouse immunoglobulins M and D. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1348–1353. doi: 10.1126/science.6774414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki R., Traunecker A., Sakano H., Roeder W., Tonegawa S. Exon shuffling generates an immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2138–2142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata T., Yasunaga T., Yamawaki-Kataoka Y., Obata M., Honjo T. Nucleotide sequence divergence of mouse immunoglobulin gamma 1 and gamma 2b chain genes and the hypothesis of intervening sequence-mediated domain transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2143–2147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido T., Nakai S., Honjo T. Switch region of immunoglobulin Cmu gene is composed of simple tandem repetitive sequences. Nature. 1981 Aug 27;292(5826):845–848. doi: 10.1038/292845a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson K. Characteristics of established myeloma and lymphoblastoid cell lines derived from an E myeloma patient: a comparative study. Int J Cancer. 1971 May 15;7(3):380–396. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910070303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida Y., Kataoka T., Ishida N., Nakai S., Kishimoto T., Böttcher I., Honjo T. Cloning of mouse immunoglobulin epsilon gene and its location within the heavy chain gene cluster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1581–1585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obata M., Kataoka T., Nakai S., Yamagishi H., Takahashi N., Yamawaki-Kataoka Y., Nikaido T., Shimizu A., Honjo T. Structure of a rearranged gamma 1 chain gene and its implication to immunoglobulin class-switch mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2437–2441. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polisky B., Greene P., Garfin D. E., McCarthy B. J., Goodman H. M., Boyer H. W. Specificity of substrate recognition by the EcoRI restriction endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3310–3314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbitts T. H., Forster A., Milstein C. P. Human immunoglobulin heavy chain genes: evolutionary comparisons of C mu, C delta and C gamma genes and associated switch sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 25;9(18):4509–4524. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.18.4509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Kirsch I. R., Leder P. Evolutionary approach to the question of immunoglobulin heavy chain switching: evidence from cloned human and mouse genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6734–6738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder W., Maki R., Traunecker A., Tonegawa S. Linkage of the four gamma subclass heavy chain genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):474–478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakano H., Maki R., Kurosawa Y., Roeder W., Tonegawa S. Two types of somatic recombination are necessary for the generation of complete immunoglobulin heavy-chain genes. Nature. 1980 Aug 14;286(5774):676–683. doi: 10.1038/286676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu A., Takahashi N., Yamawaki-Kataoka Y., Nishida Y., Kataoka T., Honjo T. Ordering of mouse immunoglobulin heavy chain genes by molecular cloning. Nature. 1981 Jan 15;289(5794):149–153. doi: 10.1038/289149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu A., Takahashi N., Yaoita Y., Honjo T. Organization of the constant-region gene family of the mouse immunoglobulin heavy chain. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):499–506. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90204-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Kataoka T., Honjo T. Nucleotide sequences of class-switch recombination region of the mouse immunoglobulin gamma 2b-chain gene. Gene. 1980 Oct;11(1-2):117–127. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90092-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Nakai S., Honjo T. Cloning of human immunoglobulin mu gene and comparison with mouse mu gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):5983–5991. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.5983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiemeier D. C., Tilghman S. M., Leder P. Purification and cloning of a mouse ribosomal gene fragment in coliphage lambda. Gene. 1977;2(3-4):173–191. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(77)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamawaki-Kataoka Y., Miyata T., Honjo T. The complete nucleotide sequence of mouse immunoglobin gamma 2a gene and evolution of heavy chain genes: further evidence for intervening sequence-mediated domain transfer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 25;9(6):1365–1381. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.6.1365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]