Abstract
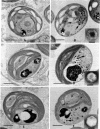
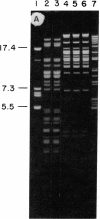
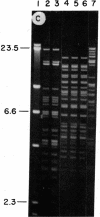
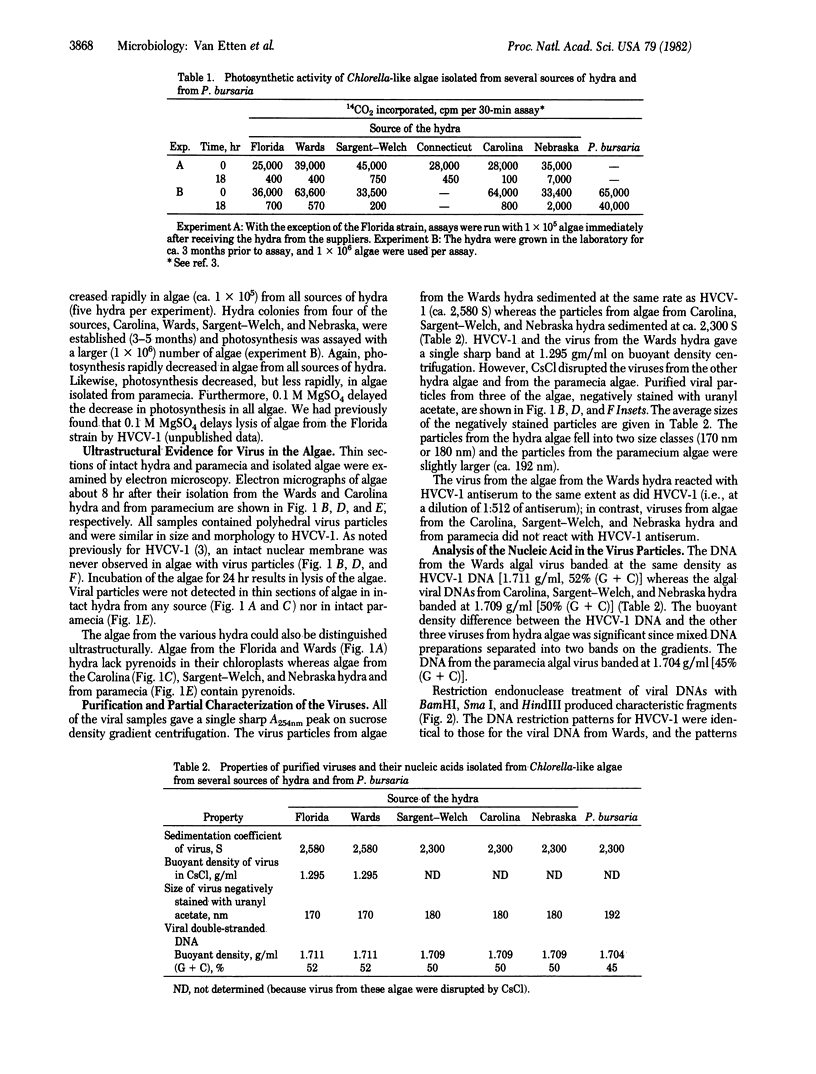
We previously reported that isolation of symbiotic Chlorella-like algae from the Florida strain of Hydra viridis induced replication of a virus (designated HVCV-1) in the algae. We now report that isolation of symbiotic Chlorella-like algae from four other sources of green hydra and one source of the protozoan Paramecium bursaria also induced virus synthesis. Algae from one of these hydra contained a virus identical to HVCV-1 (based on its rate of sedimentation, buoyant density, reaction to HVCV-1 antiserum, and DNA restriction fragments) whereas algae from the other three hydra contained another similar, but distinct, virus (designated HVCV-2). The virus from the paramecium algae (designated PBCV-1) was distinct from both HVCV-1 and HVCV-2. The symbiotic algae in the hydra could also be distinguished ultrastructurally. Chloroplasts of both algae that produced HVCV-1 lacked a pyrenoid whereas chloroplasts of the other three symbiotic algae contained pyrenoids. Since all symbiotic eukaryotic algae we have examined have had virus, a potential viral role in symbiosis is suggested.
Keywords: symbiosis, double-stranded DNA viruses, eukaryotic algae, pyrenoids
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Lemke P. A. Viruses of eucaryotic microorganisms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1976;30:105–145. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.30.100176.000541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenhoff H. M., Brown R. D. Mass culture of hydra: an improved method and its application to other aquatic invertebrates. Lab Anim. 1970 Apr;4(1):139–154. doi: 10.1258/002367770781036463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]