Abstract
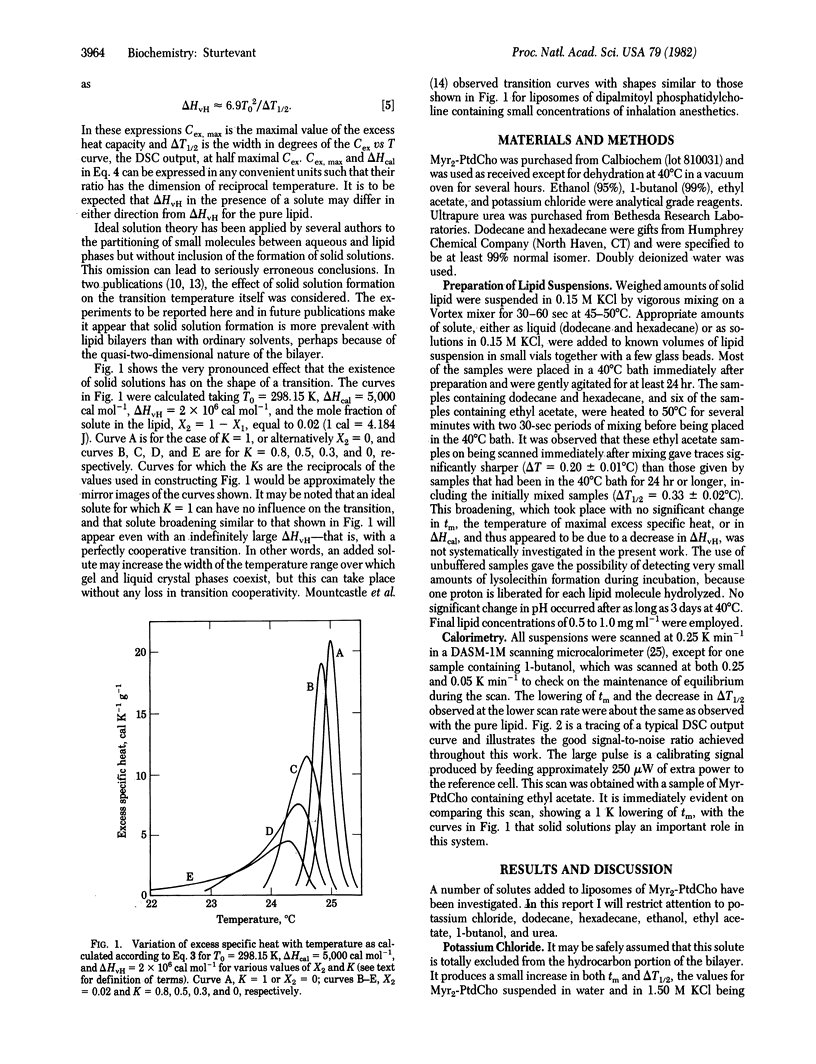
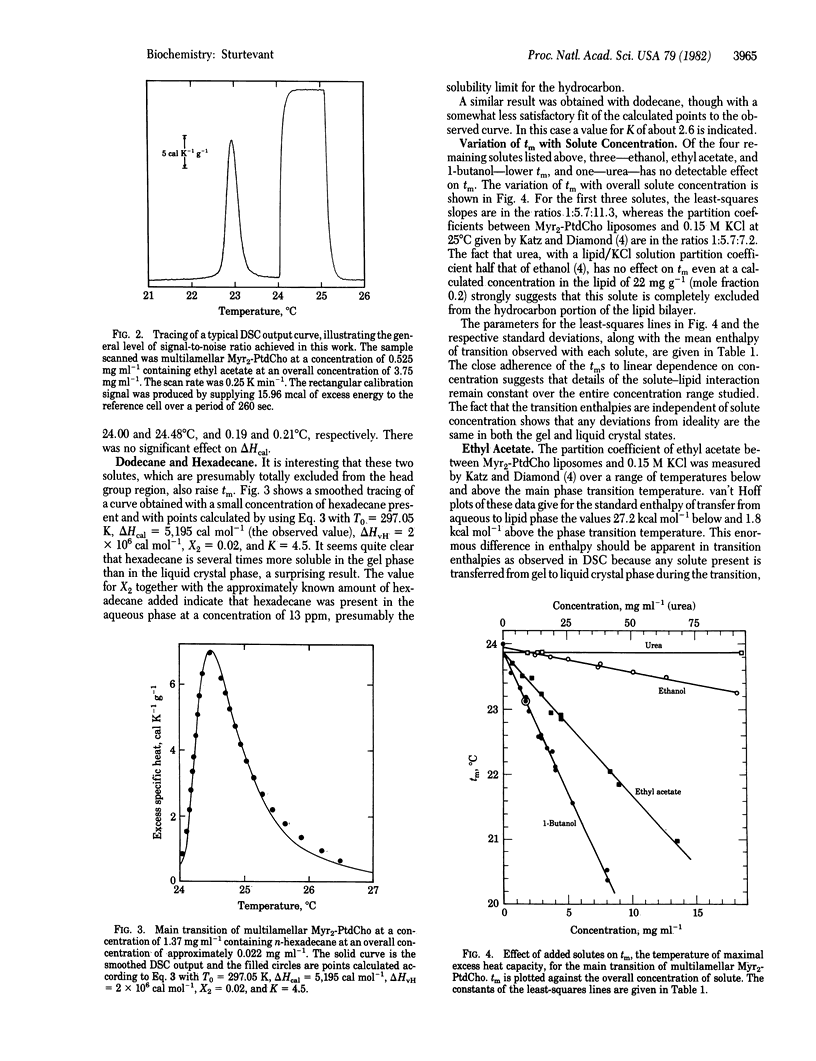
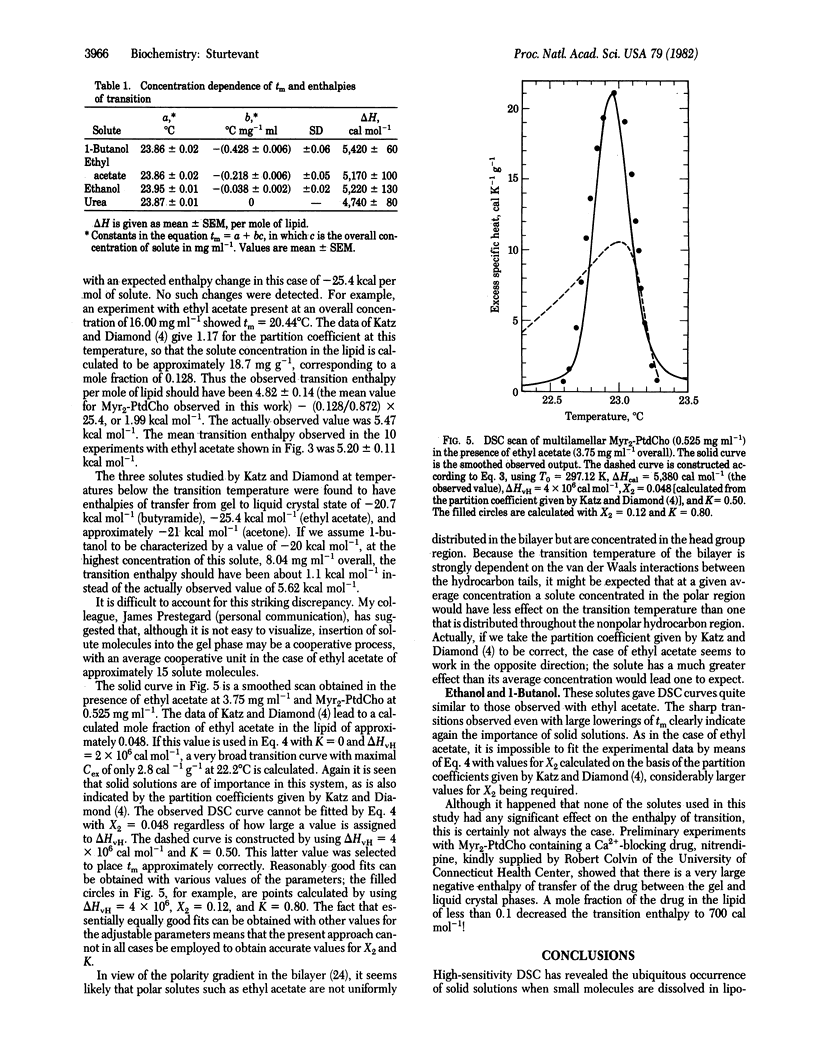
The influence of small molecules on the main phase transition of dimyristoyl phosphatidylcholine was observed by high-sensitivity differential scanning calorimetry. The variation with temperature of the excess heat capacity is markedly affected by solid solution formation, which appears to be of frequent occurrence in solutions in lipid bilayers. The experimental results are in some cases in reasonable agreement with ideal solution theory.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed M., Burton J. S., Hadgraft J., Kellaway I. W. Thermodynamics of partitioning and efflux of phenothiazines from liposomes. J Membr Biol. 1981 Feb 28;58(3):181–189. doi: 10.1007/BF01870904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albon N., Sturtevant J. M. Nature of the gel to liquid crystal transition of synthetic phosphatidylcholines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2258–2260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad M. J., Singer S. J. The solubility of amphipathic molecules in biological membranes and lipid bilayers and its implications for membrane structure. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):808–818. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. M., Katz Y. Interpretation of nonelectrolyte partition coefficients between dimyristoyl lecithin and water. J Membr Biol. 1974;17(2):121–154. doi: 10.1007/BF01870176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliasz A. W., Chapman D., Ewing D. F. Phospholipid phase transitions. Effects of n-alcohols, n-monocarboxylic acids, phenylalkyl alcohols and quaternary ammonium compounds. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 5;448(2):220–230. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90238-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith O. H., Dehlinger P. J., Van S. P. Shape of the hydrophobic barrier of phospholipid bilayers (evidence for water penetration in biological membranes). J Membr Biol. 1974;15(2):159–192. doi: 10.1007/BF01870086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill M. W. The effect of anaesthetic-like molecules on the phase transition in smectic mesophases of dipalmitoyllecithin. I. The normal alcohol up to C equals 9 and three inhalation anaesthetics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 12;356(1):117–124. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90299-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain M. K., Wu N. Y., Wray L. V. Drug-induced phase change in bilayer as possible mode of action of membrane expanding drugs. Nature. 1975 Jun 5;255(5508):494–496. doi: 10.1038/255494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz Y., Diamond J. M. A method for measuring nonelectrolyte partition coefficients between liposomes and water. J Membr Biol. 1974;17(1):69–86. doi: 10.1007/BF01870173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz Y., Diamond J. M. Nonsolvent water in liposomes. J Membr Biol. 1974;17(1):87–100. doi: 10.1007/BF01870174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz Y., Diamond J. M. Thermodynamic constants for nonelectrolyte partition between dimyristoyl lecithin and water. J Membr Biol. 1974;17(2):101–120. doi: 10.1007/BF01870175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. G. Analysis of the defect structure of gel-phase lipid. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 8;16(5):835–841. doi: 10.1021/bi00624a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. G. Interactions between anesthetics and lipid mixtures. Normal alcohols. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 1;15(11):2448–2454. doi: 10.1021/bi00656a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald A. G. A dilatometric investigation of the effects of general anaesthetics, alcohols and hydrostatic pressure on the phase transition in smectic mesophases of dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 2;507(1):26–37. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90371-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milgram J. H., Solomon A. K. Membrane permeability equations and their solutions for red cells. J Membr Biol. 1977 Jun 6;34(2-3):103–144. doi: 10.1007/BF01870297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mountcastle D. B., Biltonen R. L., Halsey M. J. Effect of anesthetics and pressure on the thermotropic behavior of multilamellar dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine liposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4906–4910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papahadjopoulos D., Jacobson K., Poste G., Shepherd G. Effects of local anesthetics on membrane properties. I. Changes in the fluidity of phospholipid bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 18;394(4):504–519. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90137-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle M. J., Miller K. W. Differential effects on phospholipid phase transitions produced by structurally related long-chain alcohols. Biochemistry. 1979 Jul 24;18(15):3314–3320. doi: 10.1021/bi00582a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe E. S. Membrane:buffer partition coefficient for ethanol in dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1981 Spring;5(2):259–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1981.tb04899.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P., Roth S., Schneider H. The membrane concentrations of alcohol anesthetics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 2;225(2):171–184. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90210-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon S. A., Stone W. L., Bennett P. B. Can regular solution theory be applied to lipid bilayer membranes? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jan 5;550(1):38–47. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90113-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderkooi J. M., Landesberg R., Selick H., 2nd, McDonald G. G. Interaction of general anesthetics with phospholipid vesicles and biological membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 4;464(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90366-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


