Abstract
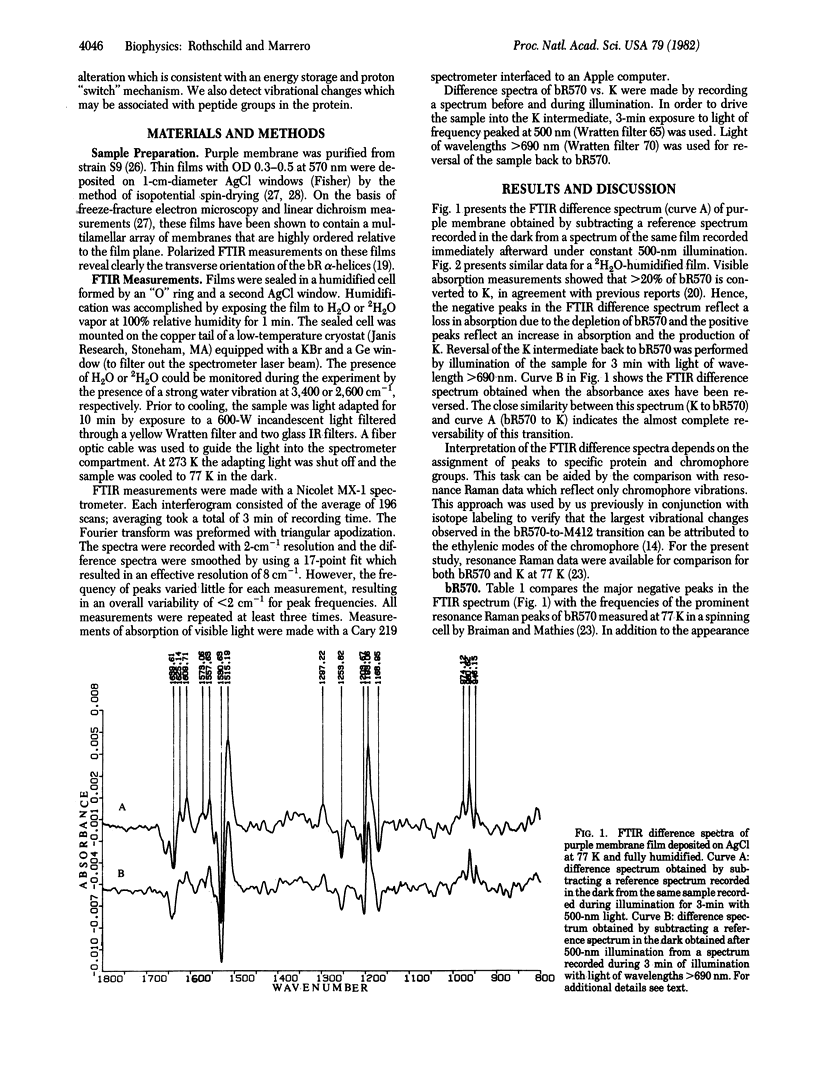
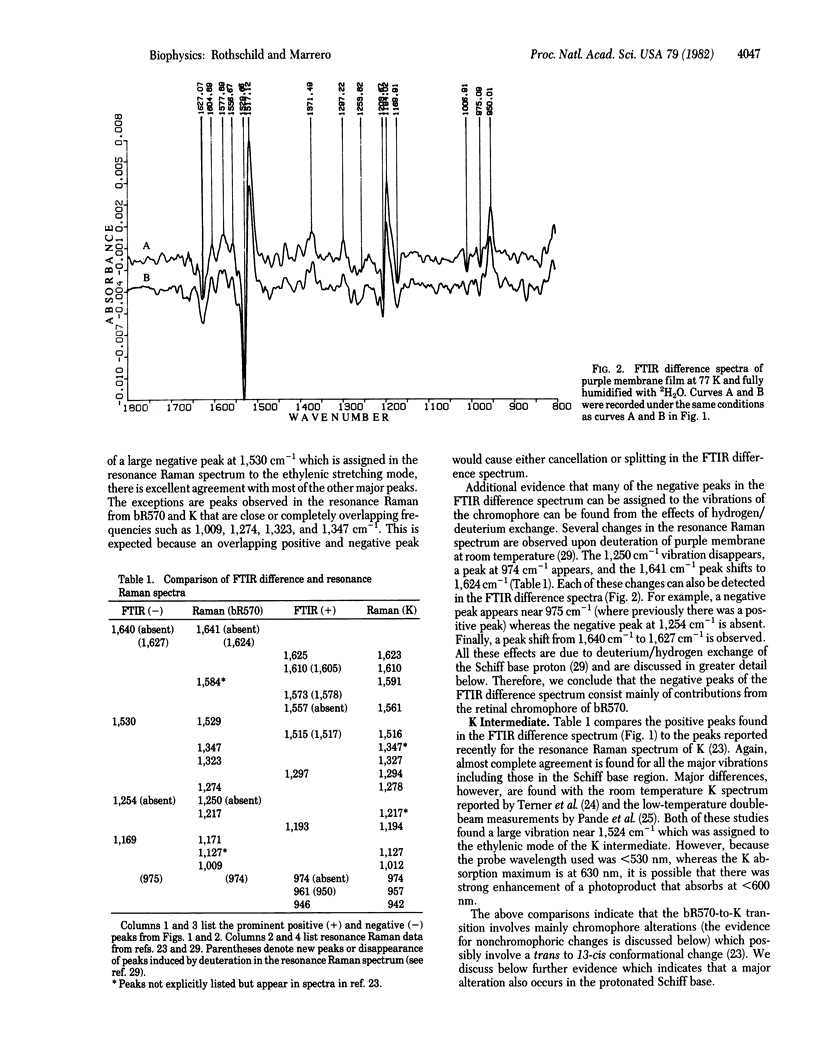
It is possible, by using Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) difference spectroscopy, to detect the conformational changes occurring in both the protein and the chromophore of bacteriorhodopsin during the photocycle. In contrast to Raman spectroscopy, a laser is unnecessary and hence the problem of a perturbing probe beam is eliminated. Furthermore, the relatively high signal-to-noise ratio obtainable with FTIR enables measurements to be made in minutes over a large spectral range. In the study reported in this paper, we used this method to examine the state of protonation of the retinylidene Schiff base in light-adapted bR570 and in K, the first intermediate in the photocycle. Resonance Raman spectroscopy provides evidence that bR570 is protonated, but these results have been questioned on the basis of theoretical and experimental grounds. FTIR difference spectral changes in the bR570-to-K transition clearly indicate that bR570 contains a protonated Schiff base. In contrast, the K intermediate displays a Schiff base that is altered but still is associated to some degree with a proton. Because the low-temperature FTIR difference spectrum of bR570 and K is similar to the recently reported low-temperature resonance Raman spectra of bR570 and K [Braiman, M. & Mathies, R. (1982) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79, 403-407], we can assign most, but not all, vibrational changes in the bR570-to-K transition to the chromophore. These results are consistent with a simple model of the first step in the photocycle which involves a movement of the Schiff base proton away from a counterion.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Applebury M. L., Peters K. S., Rentzepis P. M. Primary intermediates in the photochemical cycle of bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1978 Sep;23(3):375–382. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85456-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argade P. V., Rothschild K. J., Kawamoto A. H., Herzfeld J., Herlihy W. C. Resonance Raman spectroscopy of specifically [epsilon-15N]lysine-labeled bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1643–1646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aton B., Doukas A. G., Callender R. H., Becher B., Ebrey T. G. Resonance Raman studies of the purple membrane. Biochemistry. 1977 Jun 28;16(13):2995–2999. doi: 10.1021/bi00632a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aton B., Doukas A. G., Narva D., Callender R. H., Dinur U., Honig B. Resonance Raman studies of the primary photochemical event in visual pigments. Biophys J. 1980 Jan;29(1):79–94. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85119-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becher B. M., Cassim J. Y. Improved isolation procedures for the purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium. Prep Biochem. 1975;5(2):161–178. doi: 10.1080/00327487508061568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatz P. E., Mohler J. H. Effect of selected anions and solvents on the electron absorption, nuclear magnetic resonance, and infrared spectra of the N-retinylidene-n-butylammonium cation. Biochemistry. 1975 Jun 3;14(11):2304–2309. doi: 10.1021/bi00682a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braiman M., Mathies R. Resonance Raman spectra of bacteriorhodopsin's primary photoproduct: evidence for a distorted 13-cis retinal chromophore. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):403–407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridgen J., Walker I. D. Photoreceptor protein from the purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium. Molecular weight and retinal binding site. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 24;15(4):792–798. doi: 10.1021/bi00649a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark N. A., Rothschild K. J., Luippold D. A., Simon B. A. Surface-induced lamellar orientation of multilayer membrane arrays. Theoretical analysis and a new method with application to purple membrane fragments. Biophys J. 1980 Jul;31(1):65–96. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85041-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupuis P., Hárosi F. I., Sándorfy C., Leclercq J. M., Vocelle D. First step in vision: proton transfer or isomerization? Rev Can Biol. 1980 Dec;39(4):247–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillbro T., Kriebel A. N., Wild U. P. On the origin of the red emission of light adapted purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium. FEBS Lett. 1977;78(1):57–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80272-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Unwin P. N. Three-dimensional model of purple membrane obtained by electron microscopy. Nature. 1975 Sep 4;257(5521):28–32. doi: 10.1038/257028a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honig B., Ebrey T., Callender R. H., Dinur U., Ottolenghi M. Photoisomerization, energy storage, and charge separation: a model for light energy transduction in visual pigments and bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2503–2507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honig B., Greenberg A. D., Dinur U., Ebrey T. G. Visual-pigment spectra: implications of the protonation of the retinal Schiff base. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 19;15(21):4593–4599. doi: 10.1021/bi00666a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. B., Ebrey T. G. Energy transfer in the purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium. Biophys J. 1978 Apr;22(1):49–66. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85470-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hárosi F. I., Favrot J., Leclercq J. M., Vocelle D., Sándorfy C. Photochemistry of visual pigments: an interpretation of spectral changes in terms of molecular associations and isomerization. Rev Can Biol. 1978 Dec;37(4):257–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KROPF A., HUBBARD R. The mechanism of bleaching rhodopsin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Nov 12;74(2):266–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1958.tb39550.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khorana H. G., Gerber G. E., Herlihy W. C., Gray C. P., Anderegg R. J., Nihei K., Biemann K. Amino acid sequence of bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5046–5050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A., Spoonhower J., Bogomolni R. A., Lozier R. H., Stoeckenius W. Tunable laser resonance raman spectroscopy of bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4462–4466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier R. H., Niederberger W., Bogomolni R. A., Hwang S., Stoeckenius W. Kinetics and stoichiometry of light-induced proton release and uptake from purple membrane fragments, Halobacterium halobium cell envelopes, and phospholipid vesicles containing oriented purple membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 13;440(3):545–556. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(76)90041-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Rhodopsin-like protein from the purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 29;233(39):149–152. doi: 10.1038/newbio233149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oseroff A. R., Callender R. H. Resonance Raman spectroscopy of rhodopsin in retinal disk membranes. Biochemistry. 1974 Sep 24;13(20):4243–4248. doi: 10.1021/bi00717a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pande J., Callender R. H., Ebrey T. G. Resonance Raman study of the primary photochemistry of bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7379–7382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothschild K. J., Sanches R., Hsiao T. L., Clark N. A. A spectroscopic study of rhodopsin alpha-helix orientation. Biophys J. 1980 Jul;31(1):53–64. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85040-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothschild K. J., Zagaeski M., Cantore W. A. Conformational changes of bacteriorhodopsin detected by Fourier transform infrared difference spectroscopy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Nov 30;103(2):483–489. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90478-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shriver J., Mateescu G., Fager R., Toricha D., Abrahamson E. W. Unprotonated chromophore-protein bond in visual pigments from 13C-NMR spectra. Nature. 1977 Nov 17;270(5634):271–274. doi: 10.1038/270271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebert F., Mäntele W. Investigations of the rhodopsin/Meta I and rhodopsin/Meta II transitions of bovine rod outer segments by means of kinetic infrared spectroscopy. Biophys Struct Mech. 1980;6(2):147–164. doi: 10.1007/BF00535751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Lozier R. H., Bogomolni R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin and the purple membrane of halobacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 14;505(3-4):215–278. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(79)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terner J., Hsieh C. L., Burns A. R., El-Sayed M. A. Time-resolved resonance Raman spectroscopy of intermediates of bacteriorhodopsin: The bK(590) intermediate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3046–3050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOSHIZAWA T., WALD G. Pre-lumirhodopsin and the bleaching of visual pigments. Nature. 1963 Mar 30;197:1279–1286. doi: 10.1038/1971279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


