Abstract
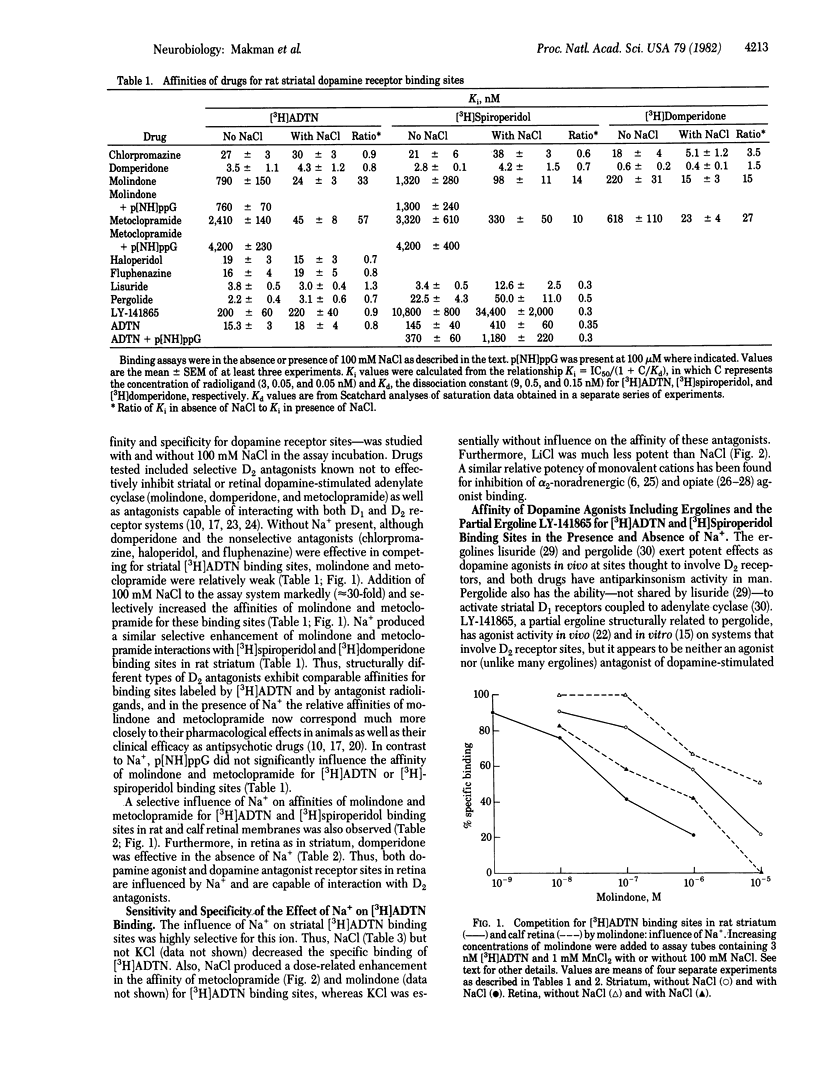
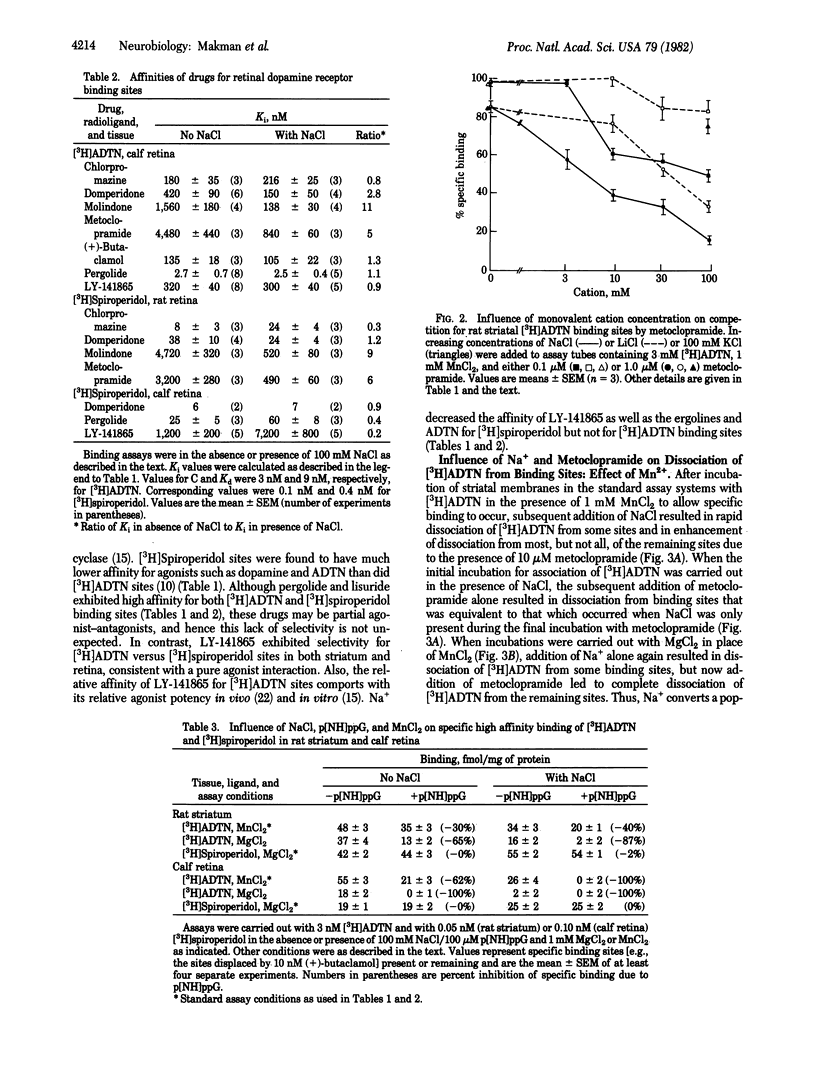
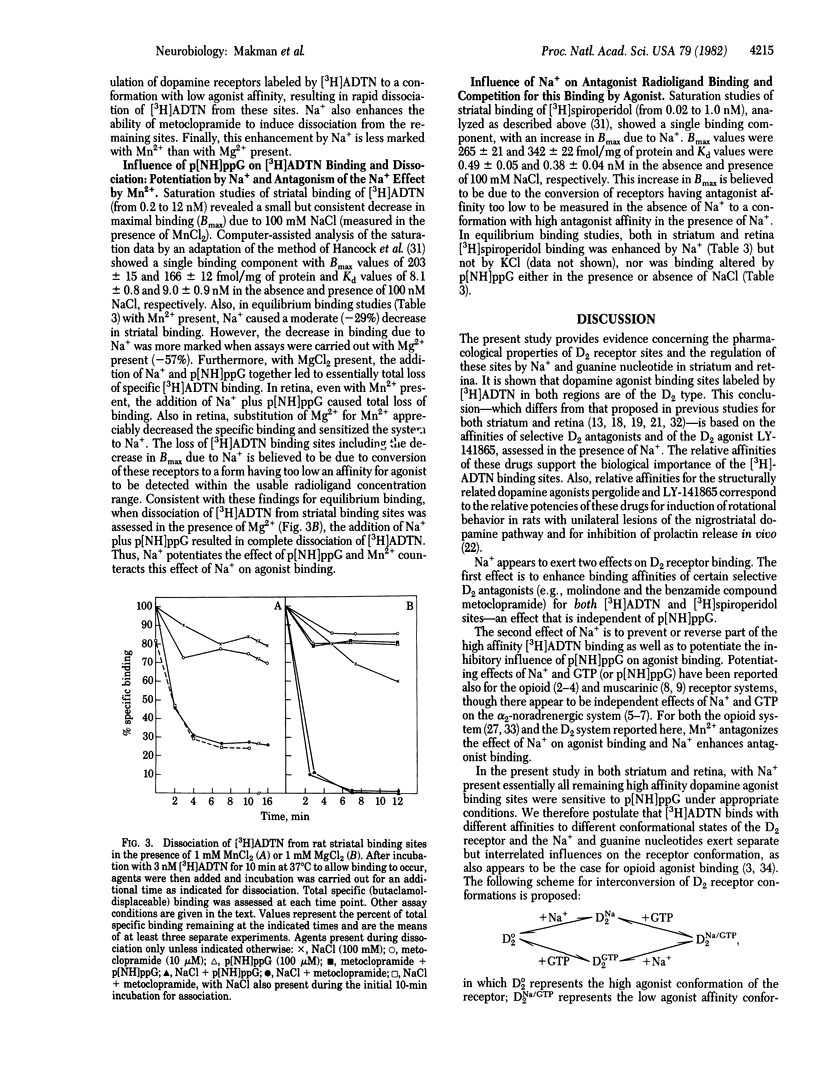
Sodium ion (Na+) influences binding of both dopamine agonists and antagonists to D2 receptors in striatum and retina. Also, Na+ markedly potentiates the loss of high-affinity agonist binding due to the GTP analogue p[NH]ppG. 2-Amino-6, 7-dihydroxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro[5,8-3H]naphthalene ([3H]ADTN) binds exclusively to an agonist conformation of D2 receptor in both striatum and retina, distinct from the antagonist conformation labeled by [3H]spiroperidol or [3H]domperidone in striatum or by [3H]spiroperidol in retina. Na+ is not required for interaction of [3H]ADTN or antagonist radioligand sites with the selective D2 agonist LY-141865, the D2 antagonist domperidone, or nonselective dopamine agonists or antagonists; however, Na+ is necessary for high affinity interaction of those radioligand sites with the D2 antagonists molindone and metoclopramide. With Na+ present, striatal sites for [3H]ADTN, [3H]spiroperidol, and [3H]domperidone have similar affinities for antagonists but only [3H]ADTN sites have high affinity for agonists. Na+ further decreases the low affinity of dopamine agonists for [3H]spiroperidol binding sites. Also, Na+ enhances [3H]spiroperidol and decreases [3H]ADTN binding. Na+ alone causes bound [3H]ADTN to dissociate from at least 30% of striatal and 50% of retinal sites, and with Na+ present [3H]ADTN rapidly dissociates from the remaining sites upon addition of p[NH]ppG. It is proposed that D2 receptors in striatum and retina exist in distinct but interconvertible conformational states, with different properties depending on the presence or absence of Na+ and of guanine nucleotide.
Keywords: adenylate cyclase, antipsychotic drugs, neuroleptic drugs, guanine nucleotide
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach N. J., Kornfeld E. C., Jones N. D., Chaney M. O., Dorman D. E., Paschal J. W., Clemens J. A., Smalstig E. B. Bicyclic and tricyclic ergoline partial structures. Rigid 3-(2-aminoethyl)pyrroles and 3- and 4-(2-aminoethyl)pyrazoles as dopamine agonists. J Med Chem. 1980 May;23(5):481–491. doi: 10.1021/jm00179a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blume A. J., Lichtshtein D., Boone G. Coupling of opiate receptors to adenylate cyclase: requirement for Na+ and GTP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5626–5630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burt D. R., Creese I., Snyder S. H. Properties of [3H]haloperidol and [3H]dopamine binding associated with dopamine receptors in calf brain membranes. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 Sep;12(5):800–812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childers S. R., Snyder S. H. Differential regulation by guanine nucleotides or opiate agonist and antagonist receptor interactions. J Neurochem. 1980 Mar;34(3):583–593. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb11184.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. L., Huber W. K., Sakata K., Fowles D. C., Serafetinides E. A. Molindone in chronic schizophrenia. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1970 Sep-Oct;11(5):680–688. doi: 10.1002/cpt1970115680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creese I., Snyder S. H. Dopamine receptor binding of 3H-ADTN (2-amino-6,7-dihydroxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalene) regulated by guanyl nucleotides. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Aug 15;50(4):459–461. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90156-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creese I., Usdin T., Snyder S. H. Guanine nucleotides distinguish between two dopamine receptors. Nature. 1979 Apr 5;278(5704):577–578. doi: 10.1038/278577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuxe K., Hall H., Köhler C. Evidence for an exclusive localization of 3H-ADTN binding sites to postsynaptic nerve cells in the striatum of the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Oct 15;58(4):515–517. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90328-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glossmann H., Presek P. Alpha noradrenergic receptors in brain membranes: sodium, magnesium and guanyl nucleotides modulate agonist binding. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Jan;306(1):67–73. doi: 10.1007/BF00515595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein M., Lieberman A., Lew J. Y., Asano T., Rosenfeld M. R., Makman M. H. Interaction of pergolide with central dopaminergic receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3725–3728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock A. A., DeLean A. L., Lefkowitz R. J. Quantitative resolution of beta-adrenergic receptor subtypes by selective ligand binding: application of a computerized model fitting technique. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Jul;16(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn I. D., Makman M. H., Gardner E. L. Changes in guanine nucleotide sensitive and insensitive 3H-ADTN binding in striatum following substantia nigra lesions. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Mar 7;62(1):123–124. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90490-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn I. D., Makman M. H., Sharpless N. S. Dopamine receptor sensitivity following nigrostriatal lesion in the aged rat. Brain Res. 1982 Feb 25;234(2):357–368. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90875-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman B. B., Yim S., Tsai B. S., Lefkowitz R. J. Preferential uncoupling by manganese of alpha adrenergic receptor mediated inhibition of adenylate cyclase in human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 May 29;100(2):724–731. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80235-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kebabian J. W., Calne D. B. Multiple receptors for dopamine. Nature. 1979 Jan 11;277(5692):93–96. doi: 10.1038/277093a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtshtein D., Boone G., Blume A. Muscarinic receptor regulation of NG108-15 adenylate cyclase: requirement for Na+ and GTP. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979 Oct;5(5):367–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makman M. H., Dvorkin B., Horowitz S. G., Thal L. J. Properties of dopamine agonist and antagonist binding sites in mammalian retina. Brain Res. 1980 Aug 4;194(2):403–418. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)91221-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel T., Hoffman B. B., Lefkowitz R. J. Differential regulation of the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor by Na+ and guanine nucleotides. Nature. 1980 Dec 25;288(5792):709–711. doi: 10.1038/288709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak G. W., Snowman A. M., Snyder S. H. Selective enhancement of [3H]opiate agonist binding by divalent cations. Mol Pharmacol. 1975 Nov;11(6):735–744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peringer E., Jenner P., Marsden C. D. Effect of metoclopramide on turnover of brain dopamine noradrenaline and 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1975 Jun;27(6):442–444. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1975.tb09477.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M. The role of hormone receptors and GTP-regulatory proteins in membrane transduction. Nature. 1980 Mar 6;284(5751):17–22. doi: 10.1038/284017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberger L. B., Yamamura H. I., Roeske W. R. Cardiac muscarinic cholinergic receptor binding is regulated by Na+ and guanyl nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):820–823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. R., Dvorkin B., Klein P. N., Makman M. H. Differential affinities of molindone, metoclopramide and domperidone for classes of [3H]spiroperidol binding sites in rat striatum: evidence for pharmacologically distinct classes of receptors. Brain Res. 1982 Mar 4;235(1):205–211. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90214-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. R., Makman M. H. The interaction of lisuride, an ergot derivative, with serotonergic and dopaminergic receptors in rabbit brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Mar;216(3):526–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarcz R., Creese I., Coyle J. T., Snyder S. H. Dopamine receptors localised on cerebral cortical afferents to rat corpus striatum. Nature. 1978 Feb 23;271(5647):766–768. doi: 10.1038/271766a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P. Brain dopamine receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 1980 Sep;32(3):229–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon E. J., Groth J. Kinetics of opiate receptor inactivation by sulfhydryl reagents: evidence for conformational change in presence of sodium ions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2404–2407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon E. J., Hiller J. M., Groth J., Edelman I. Further properties of stereospecific opiate binding sites in rat brain: on the nature of the sodium effect. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Mar;192(3):531–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon E. J., Hiller J. M. The opiate receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1978;18:371–394. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.18.040178.002103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokoloff P., Martres M. P., Schwartz J. C. Three classes of dopamine receptor (D-2, D-3, D-4) identified by binding studies with 3H-apomorphine and 3H-domperidone. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980;315(2):89–102. doi: 10.1007/BF00499251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanini E., Marchisio A. M., Devoto P., Vernaleone F., Collu R., Spano P. F. Sodium-dependent interaction of benzamides with dopamine receptors. Brain Res. 1980 Sep 29;198(1):229–233. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90360-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai B. S., Lefkowitz R. J. Agonist-specific effects of monovalent and divalent cations on adenylate cyclase-coupled alpha adrenergic receptors in rabbit platelets. Mol Pharmacol. 1978 Jul;14(4):540–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuruta K., Frey E. A., Grewe C. W., Cote T. E., Eskay R. L., Kebabian J. W. Evidence that LY-141865 specifically stimulates the D-2 dopamine receptor. Nature. 1981 Jul 30;292(5822):463–465. doi: 10.1038/292463a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- U'Prichard D. C., Snyder S. H. Guanyl nucleotide influences on 3H-ligand binding to alpha-noradrenergic receptors in calf brain membranes. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 25;253(10):3444–3452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zukin R. S., Walczak S., Makman M. H. GTP modulation of opiate receptors in regions of rat brain and possible mechanism of GTP action. Brain Res. 1980 Mar 17;186(1):238–244. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90273-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


