Abstract
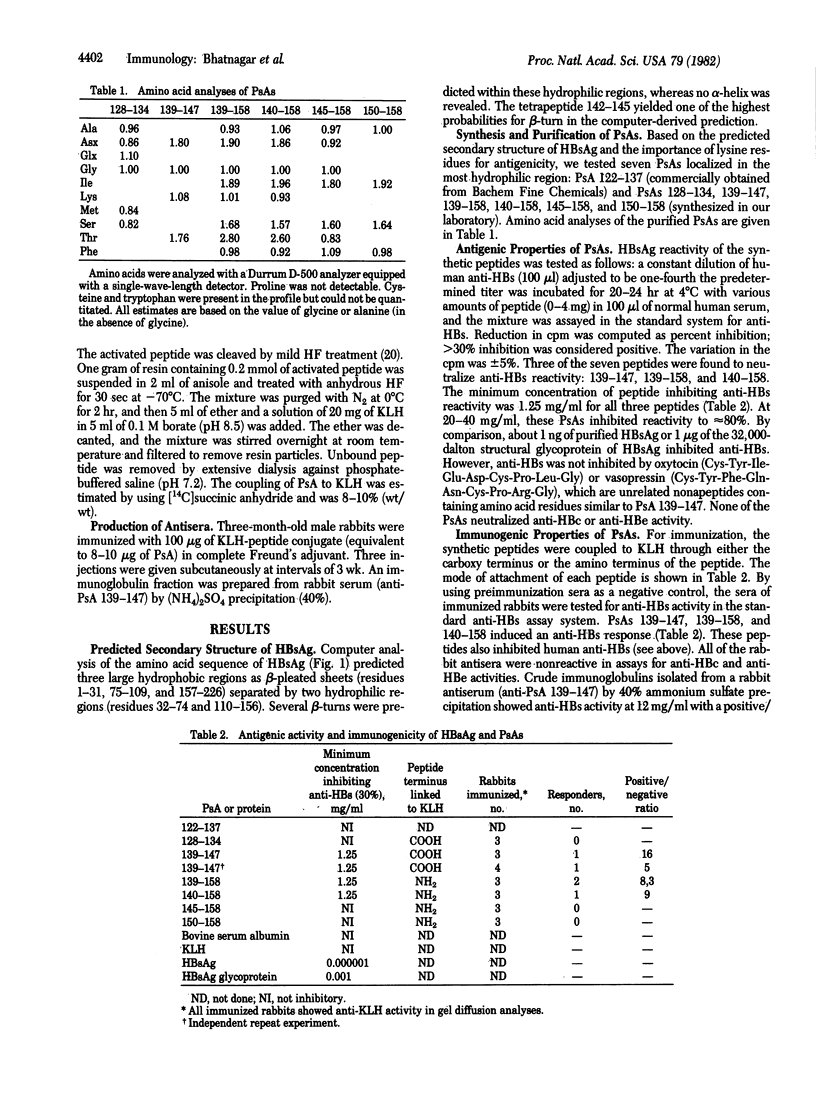
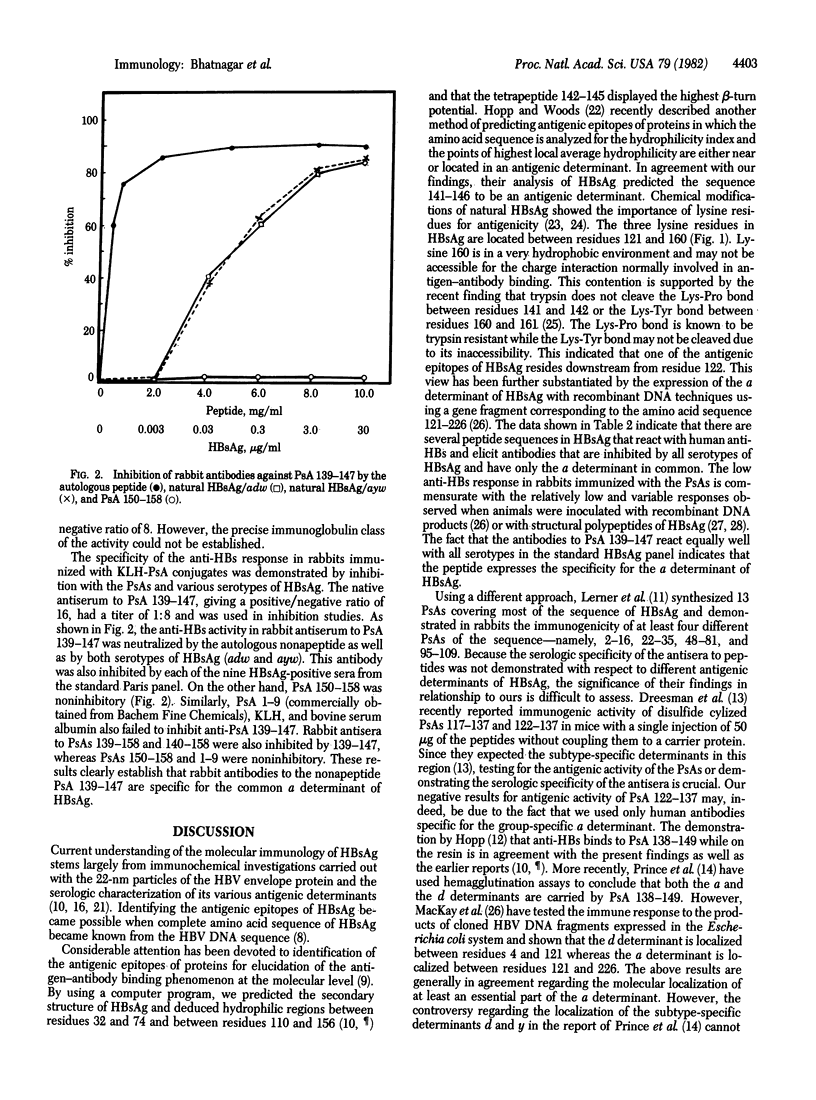
Recovery from a natural infection with hepatitis B virus or vaccination with purified envelope protein leads to production of antibodies against the hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg). Such physiologic response in man is generally directed against the a determinant of HBsAg common to all serotypes of the virus. To define the immunochemical specificity of this determinant, the secondary structure of HBsAg was derived from its sequence of 226 amino acids. Hydrophilic stretches expected to contain the antigenic determinants were located between residues 32 and 76 and between residues 110 and 156. Loss of the antigenic activity after chemical modification of lysine residues of HBsAg indicated their critical importance in antigenicity. Because all lysines are located between residues 121 and 160, we selected this region for localization of HbsAg determinants. Solid-phase synthesis was used to prepare seven peptide analogues of HBsAg (PsAs): 122-137, 128-134, 139-147, 139-158, 140-158, 145-158, and 150-158. For experimental immunization of rabbits the synthetic peptides were coupled to keyhole limpet hemocyanin. We studied the antigenicity of each peptide analogue by serologic neutralization of human antibodies specific for the a determinant of HBsAg. Analogues 139-147, 139-158, and 140-158 showed antigenicity as well as function of anti-HBsAg. The rabbit antibodies were inhibited with each of the three peptide analogues and all serotypes of natural HbSag, having only the a determinant in common. These results indicate that the nonapeptide sequence 139-147 represents the total or an essential part of the a determinant of HBsAg.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atassi M. Z. Precise determination of protein antigenic structures has unravelled the molecular immune recognition of proteins and provided a prototype for synthetic mimicking of other protein binding sites. Mol Cell Biochem. 1980 Aug 29;32(1):21–43. doi: 10.1007/BF00421293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvier G. L., Williams A. Serotypes of hepatitis B antigen (HBs Ag): the problem of "new" determinants, as exemplified by "t". Am J Med Sci. 1975 Jul-Aug;270(1):165–171. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197507000-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabral G. A., Marciano-Cabral F., Funk G. A., Sanchez Y., Hollinger F. B., Melnick J. L., Dreesman G. R. Cellular and humoral immunity in guinea pigs to two major polypeptides derived from hepatitis B surface antigen. J Gen Virol. 1978 Feb;38(2):339–350. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-38-2-339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dane D. S., Cameron C. H., Briggs M. Virus-like particles in serum of patients with Australia-antigen-associated hepatitis. Lancet. 1970 Apr 4;1(7649):695–698. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90926-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreesman G. R., Sanchez Y., Ionescu-Matiu I., Sparrow J. T., Six H. R., Peterson D. L., Hollinger F. B., Melnick J. L. Antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen after a single inoculation of uncoupled synthetic HBsAg peptides. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):158–160. doi: 10.1038/295158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold J. W., Shih J. W., Purcell R. H., Gerin J. L. Characterization of antibodies to the structural polypeptides of HGSAg: evidence for subtype-specific determinants. J Immunol. 1976 Oct;117(4):1404–1406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P. A synthetic peptide with hepatitis B surface antigen reactivity. Mol Immunol. 1981 Sep;18(9):869–872. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(81)90009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. A., Green N., Alexander H., Liu F. T., Sutcliffe J. G., Shinnick T. M. Chemically synthesized peptides predicted from the nucleotide sequence of the hepatitis B virus genome elicit antibodies reactive with the native envelope protein of Dane particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3403–3407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay P., Pasek M., Magazin M., Kovacic R. T., Allet B., Stahl S., Gilbert W., Schaller H., Bruce S. A., Murray K. Production of immunologically active surface antigens of hepatitis B virus by Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4510–4514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrifield R. B. Solid-phase peptide synthesis. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1969;32:221–296. doi: 10.1002/9780470122778.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Strick N., Oleszko W. R. Localization of a hepatitis B surface antigen determinant deduced from results of chemical modifications. J Virol Methods. 1981 Sep;3(2):115–125. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(81)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. L. Isolation and characterization of the major protein and glycoprotein of hepatitis B surface antigen. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6975–6983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. L., Roberts I. M., Vyas G. N. Partial amino acid sequence of two major component polypeptides of hepatitis B surface antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1530–1534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince A. M., Ikram H., Hopp T. P. Hepatitis B virus vaccine: identification of HBsAg/a and HBsAg/d but not HBsAg/y subtype antigenic determinants on a synthetic immunogenic peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):579–582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao K. R., Vyas G. N. Structure and activity of hepatitis B antigen (HBAg). 1. Studies on some conformational aspects and chemical modification of hepatitis B antigen. Microbios. 1974 Mar-Apr;9(36):239–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. S. The genome of hepatitis B virus. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:357–377. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.002041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparrow J. T. An improved polystyrene support for solid phase peptide synthesis. J Org Chem. 1976 Apr 16;41(8):1350–1353. doi: 10.1021/jo00870a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szmuness W., Stevens C. E., Harley E. J., Zang E. A., Oleszko W. R., William D. C., Sadovsky R., Morrison J. M., Kellner A. Hepatitis B vaccine: demonstration of efficacy in a controlled clinical trial in a high-risk population in the United States. N Engl J Med. 1980 Oct 9;303(15):833–841. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198010093031501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiollais P., Charnay P., Vyas G. N. Biology of hepatitis B virus. Science. 1981 Jul 24;213(4506):406–411. doi: 10.1126/science.6264599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela P., Gray P., Quiroga M., Zaldivar J., Goodman H. M., Rutter W. J. Nucleotide sequence of the gene coding for the major protein of hepatitis B virus surface antigen. Nature. 1979 Aug 30;280(5725):815–819. doi: 10.1038/280815a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyas G. N., Rao K. R., Ibrahim A. B. Australia antigen (hepatitis B antigen): a conformational antigen dependent on disulfide bonds. Science. 1972 Dec 22;178(4067):1300–1301. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4067.1300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyas G. N., Williams E. W., Klaus G. G., Bond H. E. Hepatitis-associated Australia antigen. Protein, peptides and amine acid composition of purified antigen with its use in determining sensitivity of the hemagglutination test. J Immunol. 1972 Apr;108(4):1114–1118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


