Abstract
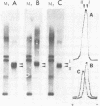
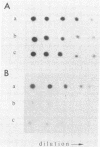
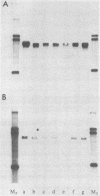
Sequence analysis of mouse H-2 cDNA clones has suggested the existence of an unusual class of H-2 (class I)-related antigens that, unlike the classical membrane-associated molecules, retains only the extracellular portion and is likely to be secreted. The expression of this class of H-2-related mRNA is tissue restricted; it is detectable in liver but not in brain, kidney, testis, thymus, or spleen. In the liver, its accumulation represents about one-fourth of all the H-2 (class I)-specific transcripts. This class of transcripts is present in mice of different inbred strains, but the level of expression differs markedly among them. A model is presented in which such a soluble form of the H-2 antigen would play the role of a blocking factor in maintaining peripheral inhibition of H-2 recognition. This would ensure tolerance of the H-2 molecule as a self antigen while permitting it to act as a guidance molecule for the associative recognition of viral and tumor antigens by cytotoxic T cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calne R. Y., Davis D. R., Hadjiyannakis E., Sells R. A., White D., Herbertson B. M., Millard P. R., Joysey V. C., Davies D. A., Binns R. M. Immunosuppressive effects of soluble cell membrane fractions, donor blood and serum on renal allograft survival. Nature. 1970 Aug 29;227(5261):903–906. doi: 10.1038/227903a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calne R. Y., Sells R. A., Pena J. R., Davis D. R., Millard P. R., Herbertson B. M., Binns R. M., Davies D. A. Induction of immunological tolerance by porcine liver allografts. Nature. 1969 Aug 2;223(5205):472–476. doi: 10.1038/223472a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosman D., Khoury G., Jay G. Three classes of mouse H-2 messenger RNA distinguished by analysis of cDNA clones. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):73–76. doi: 10.1038/295073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamada N., Davies H. S., Roser B. Reversal of transplantation immunity by liver grafting. Nature. 1981 Aug 27;292(5826):840–842. doi: 10.1038/292840a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J. The major histocompatibility complex of the mouse. Science. 1979 Feb 9;203(4380):516–521. doi: 10.1126/science.104386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalanne J. L., Bregegere F., Delarbre C., Abastado J. P., Gachelin G., Kourilsky P. Comparison of nucleotide sequences of mRNAs belonging to the mouse H-2 multigene family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 11;10(3):1039–1049. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.3.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margulies D. H., Evans G. A., Flaherty L., Seidman J. G. H-2-like genes in the Tla region of mouse chromosome 17. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):168–170. doi: 10.1038/295168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathenson S. G., Uehara H., Ewenstein B. M., Kindt T. J., Coligan J. E. Primary structural: analysis of the transplantation antigens of the murine H-2 major histocompatibility complex. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:1025–1052. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.005113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploegh H. L., Orr H. T., Strominger J. L. Major histocompatibility antigens: the human (HLA-A, -B, -C) and murine (H-2K, H-2D) class I molecules. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):287–299. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90318-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Frelinger J. G., Fisher D., Hunkapiller T., Pereira D., Weissman S. M., Uehara H., Nathenson S., Hood L. Three cDNA clones encoding mouse transplantation antigens: homology to immunoglobulin genes. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90508-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Moore K. W., Frelinger J. G., Sher B. T., Shen F. W., Boyse E. A., Hood L. A pseudogene homologous to mouse transplantation antigens: transplantation antigens are encoded by eight exons that correlate with protein domains. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):683–692. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Winoto A., Minard K., Hood L. Clusters of genes encoding mouse transplantation antigens. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):489–498. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90203-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strohman R. C., Moss P. S., Micou-Eastwood J., Spector D., Przybyla A., Paterson B. Messenger RNA for myosin polypeptides: isolation from single myogenic cell cultures. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90220-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. MHC-restricted cytotoxic T cells: studies on the biological role of polymorphic major transplantation antigens determining T-cell restriction-specificity, function, and responsiveness. Adv Immunol. 1979;27:51–177. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]