Abstract
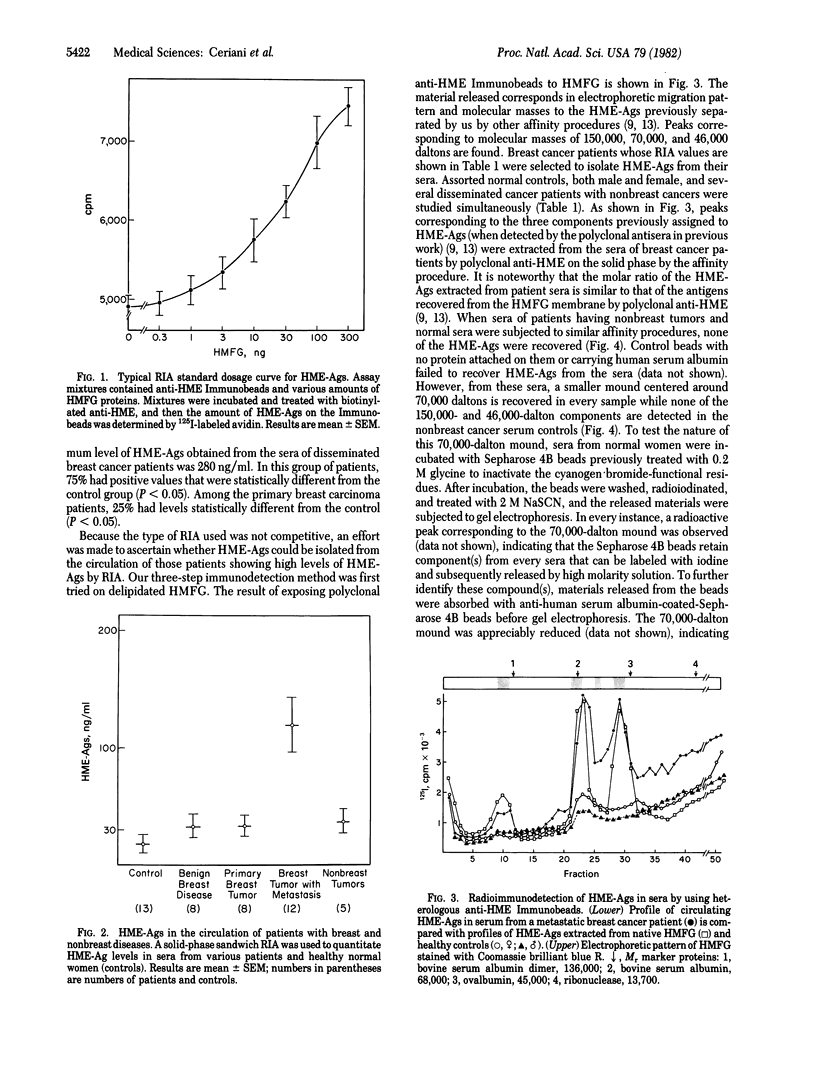
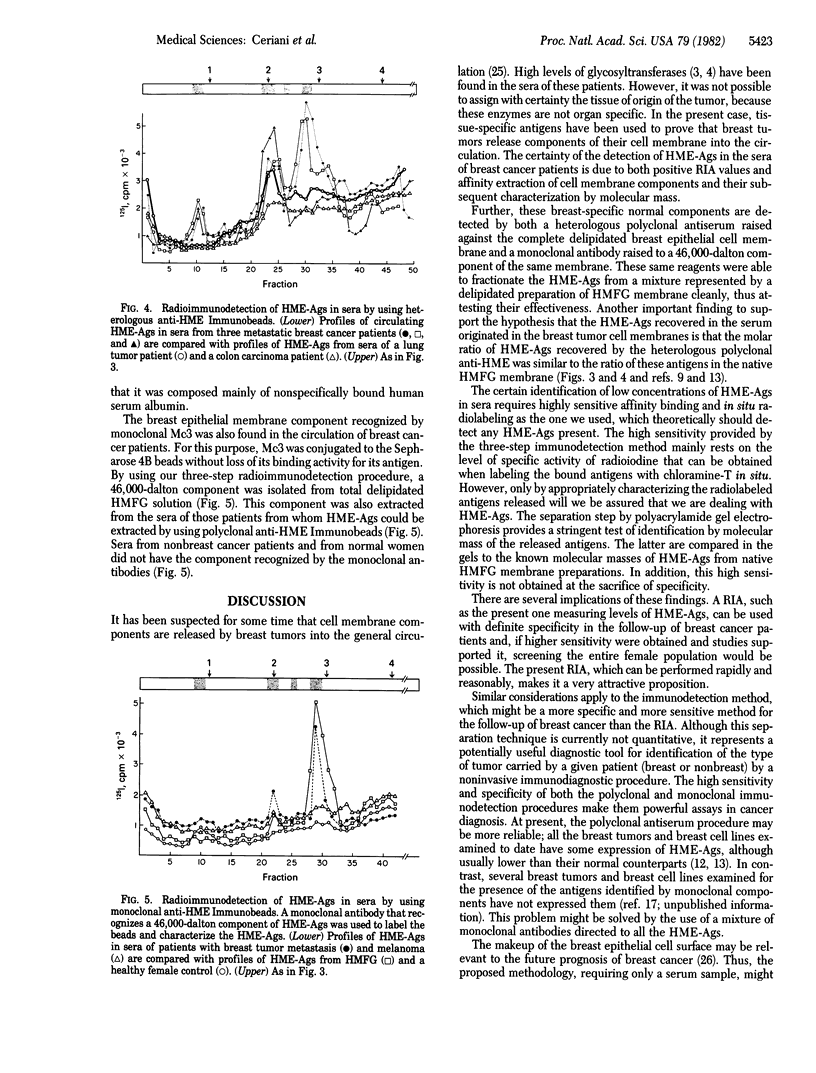
Heterologous specific antisera against human mammary epithelial antigens (HME-Ags), which are present in the human milk fat globule membrane and breast epithelial cells, were used in a solid-phase radioimmunoassay to determine the presence of these antigens in the sera of patients with disseminated cancer of the breast and other organs. Breast cancer patients carry high levels of HME-Ags in their circulation, while patients with disseminated nonbreast cancer, as well as normal female controls, do not. A similar release of HME-Ags in the circulation was shown by us in a model system. To further corroborate these findings, a three-step procedure for the extraction and identification of HME-Ags from the sera was devised. In this analytical procedure, circulating HME-Ags are recovered on a solid phase carrying their corresponding antibody (anti-HME) and radioiodinated in situ. Later, the labeled HME-Ags are released from the solid phase and characterized by NaDodSO4 gel electrophoresis. With this procedure, HME-Ags were isolated from sera of breast cancer patients but not from sera of nonbreast cancer patients or of normal female controls. The extracted HME-Ags had molecular masses of 150,000, 70,000, and 46,000 daltons. To further support these findings, a monoclonal antibody, BLMRL-HMFG-Mc3, directed to the 46,000-dalton HME-Ag was also used to extract its corresponding antigen from sera. Breast cancer patient sera contained such antigen while the sera of the other patients and controls did not. This highly sensitive methodology offers a specific approach to breast cancer diagnosis as well as further insight into the nature of circulating antigens with a view to increasing our understanding of breast cancer biology.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Black P. H. Shedding from the cell surface of normal and cancer cells. Adv Cancer Res. 1980;32:75–199. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60361-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky F. M., Parham P., Barnstable C. J., Crumpton M. J., Bodmer W. F. Monoclonal antibodies for analysis of the HLA system. Immunol Rev. 1979;47:3–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00288.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceriani R. L., Thompson K., Peterson J. A., Abraham S. Surface differentiation antigens of human mammary epithelial cells carried on the human milk fat globule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):582–586. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dao T. L., Ip C., Patel J. Serum sialyltransferase and 5'-nucleotidase as reliable biomarkers in women with breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1980 Sep;65(3):529–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franchimont P., Zangerle P. F., Hendrick J. C., Reuter A., Colin C. Simultaneous assays of cancer associated antigens in benign and malignant breast diseases. Cancer. 1977 Jun;39(6 Suppl):2806–2812. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197706)39:6<2806::aid-cncr2820390668>3.0.co;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furmanski P., Kirkland W. L., Gargala T., Rich M. A. Prognostic value of concanavalin A reactivity of primary human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1981 Oct;41(10):4087–4092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN N. M. AVIDIN. 1. THE USE OF (14-C)BIOTIN FOR KINETIC STUDIES AND FOR ASSAY. Biochem J. 1963 Dec;89:585–591. doi: 10.1042/bj0890585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganzinger U., Deutsch E. Serum sialyltransferase levels as a parameter in the diagnosis and follow-up of gastrointestinal tumors. Cancer Res. 1980 Apr;40(4):1300–1304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S. K., Grossberg A. L., Kim U., Pressman D. Identification and purification of an organ specific, tumor membrane associated antigen from a spontaneously metastasizing rat mammary carcinoma. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jun;15(6):345–352. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90129-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitzmann H., Richards F. M. Use of the avidin-biotin complex for specific staining of biological membranes in electron microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3537–3541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip C., Dao T. Alterations in serum glycosyltransferases and 5'-nucleotidase in breast cancer patients. Cancer Res. 1978 Mar;38(3):723–728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessel D., Shah-Reddy I., Mirchandani I., Khilanani P., Chou T. H. Electrofocusing patterns of fucosyltransferase activity in plasma of patients with chronic granulocytic leukemia. Cancer Res. 1980 Oct;40(10):3576–3578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinberg D. L. Human alpha-lactalbumin: measurement in serum and in breast cancer organ cultures by radioimmunoassay. Science. 1975 Oct 17;190(4211):276–278. doi: 10.1126/science.1179206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloppel T. M., Keenan T. W., Freeman M. J., Morré D. J. Glycolipid-bound sialic acid in serum: increased levels in mice and humans bearing mammary carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3011–3013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. A., Bartholomew J. C., Stampfer M., Ceriani R. L. Analysis of expression of human mammary epithelial antigens in normal and malignant breast cells at the single cell level by flow cytofluorimetry. Exp Cell Biol. 1981;49(1):1–14. doi: 10.1159/000163773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. A., Buehring G. C., Taylor-Papadimitriou J., Ceriani R. L. Expression of human mammary epithelial (HME) antigens in primary cultures of normal and abnormal breast tissue. Int J Cancer. 1978 Dec;22(6):655–661. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910220603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki M., Peterson J. A., Ceriani R. L. Quantitation of human mammary epithelial antigens in cells cultured from normal and cancerous breast tissues. In Vitro. 1981 Feb;17(2):150–158. doi: 10.1007/BF02618073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki M., Peterson J. A., Wara W. M., Ceriani R. L. Human mammary epithelial antigens (HME-Ags) in the circulation of nude mice implanted with a breast tumor and non-breast tumors. Cancer. 1981 Nov 15;48(10):2204–2210. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19811115)48:10<2204::aid-cncr2820481015>3.0.co;2-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skipski V. P., Barclay M., Archibald F. M., Lynch T. P., Jr, Stock C. C. A new proteolipid apparently associated with cancer. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Apr;136(4):1261–1264. doi: 10.3181/00379727-136-35471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Papadimitriou J., Peterson J. A., Arklie J., Burchell J., Ceriani R. L., Bodmer W. F. Monoclonal antibodies to epithelium-specific components of the human milk fat globule membrane: production and reaction with cells in culture. Int J Cancer. 1981 Jul 15;28(1):17–21. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910280104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kleist S., Chany E., Burtin P., King M., Fogh J. Immunohistology of the antigenic pattern of a continuous cell line from a human colon tumor. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Sep;55(3):555–560. doi: 10.1093/jnci/55.3.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


