Abstract
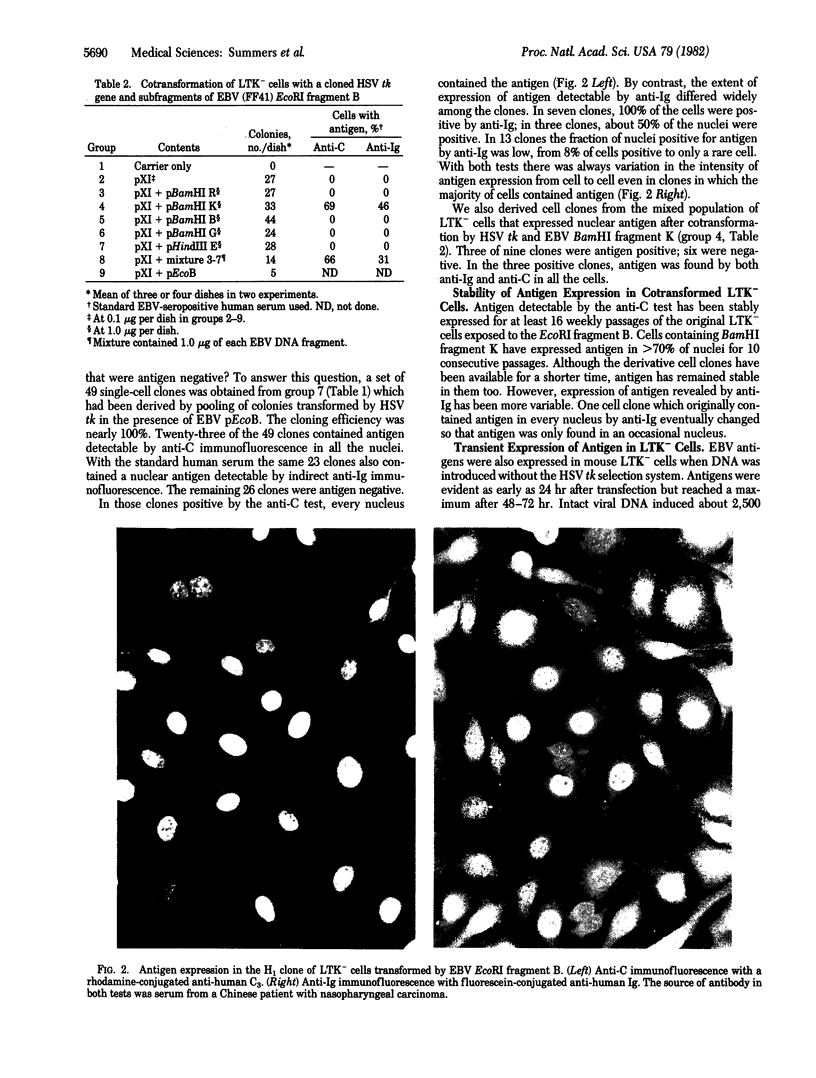
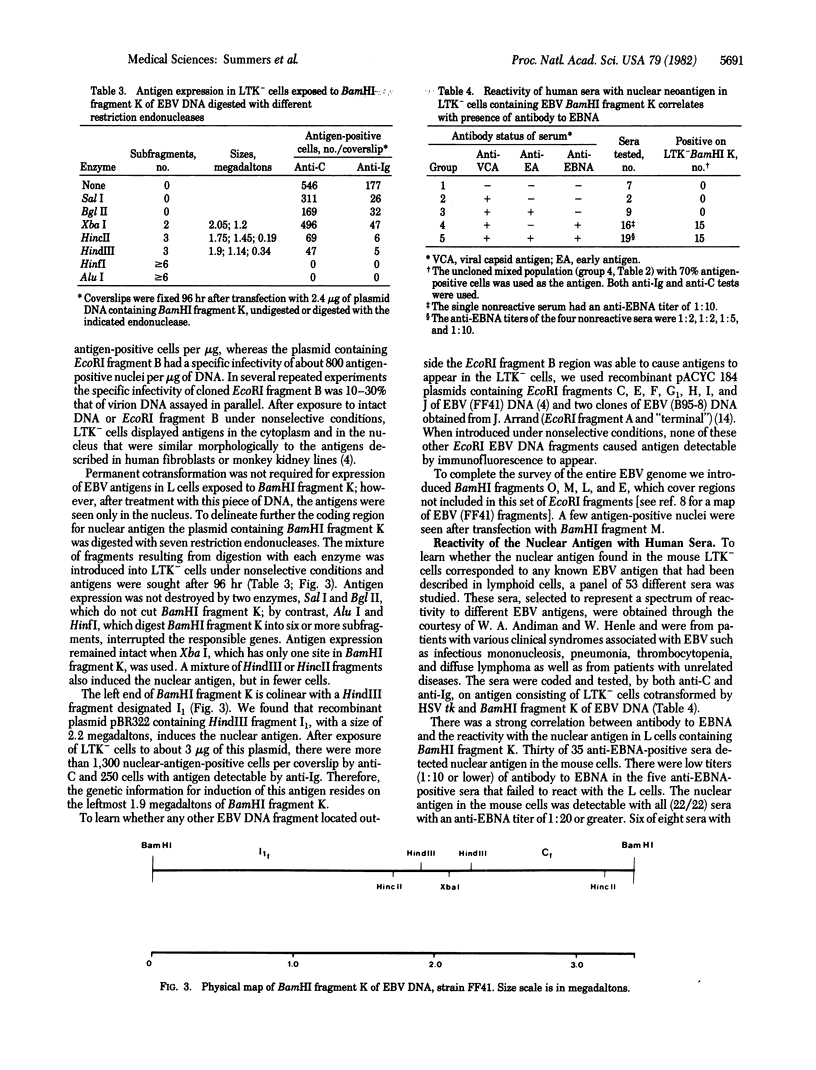
All cells that harbor the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) genome contain a neoantigen in the nucleus (EBNA). By transfection we located a segment of the genome that encodes or induces an antigen serologically related to EBNA. The responsible genes are found in the 3.4-megaldalton BamHI fragment K of EBV DNA, specifically in the left 1.9 megadaltons represented by HindIII fragment I1. Mouse LTK- cells were cotransformed with recombinant plasmids, containing the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene and either EcoRI fragment B or BamHI fragment of K of EBV DNA. The TK+ cells surviving in selective medium were cloned. About 50% of the clones expressed the neoantigen in every nucleus. These mouse cells were used as antigens in immunofluorescence tests. Antibody to the nuclear antigen was found in 30 human sera known to contain antibody to EBNA; it was not detected in 18 sera that did not have antibody to EBNA. Mouse cells expressing EBNA as the result of acquisition of cloned EBV DNA fragments should prove useful in the characterization of the structure of this antigen and as reagents for the diagnosis of EBV infections.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arrand J. R., Rymo L. Characterization of the major Epstein-Barr virus-specific RNA in Burkitt lymphoma-derived cells. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):376–389. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.376-389.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrand J. R., Rymo L., Walsh J. E., Björck E., Lindahl T., Griffin B. E. Molecular cloning of the complete Epstein-Barr virus genome as a set of overlapping restriction endonuclease fragments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):2999–3014. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron D., Strominger J. L. Partial purification and properties of the Epstein-Barr virus-associated nuclear antigen. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2875–2881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enquist L. W., Vande Woude G. F., Wagner M., Smiley J. R., Summers W. C. Construction and characterization of a recombinant plasmid encoding the gene for the thymidine kinase of Herpes simplex type 1 virus. Gene. 1979 Nov;7(3-4):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90052-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer D. K., Miller G., Gradoville L., Heston L., Westrate M. W., Maris W., Wright J., Brandsma J., Summers W. C. Genome of a mononucleosis Epstein-Barr virus contains DNA fragments previously regarded to be unique to Burkitt's lymphoma isolates. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):543–553. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90345-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graessmann A., Wolf H., Bornkamm G. W. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus genes in different cell types after microinjection of viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):433–436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grogan E., Miller G., Henle W., Rabson M., Shedd D., Niederman J. C. Expression of Epstein-Barr viral early antigen in monolayer tissue cultures after transfection with viral DNA and DNA fragments. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):861–869. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.861-869.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Henle G., Zajac B. A., Pearson G., Waubke R., Scriba M. Differential reactivity of human serums with early antigens induced by Epstein-Barr virus. Science. 1970 Jul 10;169(3941):188–190. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3941.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIT S., DUBBS D. R., PIEKARSKI L. J., HSU T. C. DELETION OF THYMIDINE KINASE ACTIVITY FROM L CELLS RESISTANT TO BROMODEOXYURIDINE. Exp Cell Res. 1963 Aug;31:297–312. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(63)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Klein G., Reedman B. M., Johansson B., Singh S. Relationship between Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA and the EBV-determined nuclear antigen (EBNA) in Burkitt lymphoma biopsies and other lymphoproliferative malignancies. Int J Cancer. 1974 Jun 15;13(6):764–772. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910130605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luka J., Siegert W., Klein G. Solubilization of the Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen and its characterization as a DNA-binding protein. J Virol. 1977 Apr;22(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.1.1-8.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Grogan E., Heston L., Robinson J., Smith D. Epstein-Barr viral DNA: infectivity for human placental cells. Science. 1981 Apr 24;212(4493):452–455. doi: 10.1126/science.6259735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munyon W., Kraiselburd E., Davis D., Mann J. Transfer of thymidine kinase to thymidine kinaseless L cells by infection with ultraviolet-irradiated herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1971 Jun;7(6):813–820. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.6.813-820.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedman B. M., Klein G. Cellular localization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated complement-fixing antigen in producer and non-producer lymphoblastoid cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1973 May;11(3):499–520. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J., Smith D. Infection of human B lymphocytes with high multiplicities of Epstein-Barr virus: kinetics of EBNA expression, cellular DNA synthesis, and mitosis. Virology. 1981 Mar;109(2):336–343. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90504-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoerker J., Parris D., Yajima Y., Glaser R. Pleiotropic expression of Epstein--Barr virus DNA in human epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5852–5855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volsky D. J., Shapiro I. M., Klein G. Transfer of Epstein-Barr virus receptors to receptor-negative cells permits virus penetration and antigen expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5453–5457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Sweet R., Sim G. K., Wold B., Pellicer A., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Transformation of mammalian cells with genes from procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Santen V., Cheung A., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus RNA VII: size and direction of transcription of virus-specified cytoplasmic RNAs in a transformed cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1930–1934. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]