Abstract
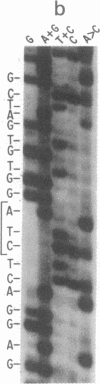
We describe the synthesis, cloning, expression, and in vivo function of a suppressor tRNA gene in mammalian cells. By using "primer-directed mutagenesis" on a Xenopus laevis tyrosine tRNA gene cloned into the recombinant single-strand phage M13mp5, we have generated an amber suppressor tRNA gene that has a nucleotide change--GTA leads to CTA--in the anticodon sequence. The suppressor (Su) tRNA gene was introduced into monkey kidney cells (CV-1) by using simian virus 40 (SV40) DNA as vector (SV40-tRNATyrSu+). CV-1 cells infected with virus containing the mutant, but not the wild-type, tRNA gene produce a functional amber suppressor tRNA as indicated by suppression of amber mutations in co-infecting adenovirus serotype 2-SV40 hybrids. Further evidence that suppression of these amber mutations is tRNA mediated was derived by isolation of total tRNA from CV-1 cells infected with the SV40-tRNATyr (Su+) recombinant and its use in demonstration of read through of an amber codon during in vitro translation of tobacco mosaic virus RNA in reticulocyte extracts. Interestingly, the amplification of an amber suppressor gene in CV-1 cells does not interfere with SV40 production, suggesting that suppression of amber codons may not be very deleterious to mammalian cell metabolism.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cepko C. L., Changelian P. S., Sharp P. A. Immunoprecipitation with two-dimensional pools as a hybridoma screening technique: production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against adenovirus 2 proteins. Virology. 1981 Apr 30;110(2):385–401. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J. C., Kan Y. W. beta 0 thalassemia, a nonsense mutation in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2886–2889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer K. J., Bodemer M., Summers W. P., Summers W. C., Gesteland R. F. In vitro suppression of UAG and UGA mutants in the thymidine kinase gene of herpes simplex virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):430–434. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gesteland R. F., Wills N., Lewis J. B., Grodzicker T. Identification of amber and ochre mutants of the human virus Ad2+ND1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4567–4571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodzicker T., Lewis J. B., Anderson C. W. Conditional lethal mutants of adenovirus type 2-simian virus 40 hybrids. II. Ad2+ND1 host-range mutants that synthesize fragments of the Ad2+ND1 30K protein. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):559–571. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.559-571.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronenborn B., Messing J. Methylation of single-stranded DNA in vitro introduces new restriction endonuclease cleavage sites. Nature. 1978 Mar 23;272(5651):375–377. doi: 10.1038/272375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney E. G., Harrison R. O., Fenno J. Monoclonal antibodies against simian virus 40 T antigens: evidence for distinct sublcasses of large T antigen and for similarities among nonviral T antigens. J Virol. 1980 Jun;34(3):752–763. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.3.752-763.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Phillips S., Edgell M. H., Gillam S., Jahnke P., Smith M. Mutagenesis at a specific position in a DNA sequence. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 25;253(18):6551–6560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo I., Leineweber M., RajBhandary U. L. Site-specific mutagenesis on cloned DNAs: generation of a mutant of Escherichia coli tyrosine suppressor tRNA in which the sequence G-T-T-C corresponding to the universal G-T-pseudouracil-C sequence of tRNAs is changed to G-A-T-C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4753–4757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A. M., Jr, Levine A. S., Crumpacker C. S., Levin M. J., Samaha R. J., Henry P. H. Studies of nondefective adenovirus 2-simian virus 40 hybrid viruses. V. Isolation of additional hybrids which differ in their simian virus 40-specific biological properties. J Virol. 1973 May;11(5):655–664. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.5.655-664.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller F., Clarkson S. G. Nucleotide sequence of genes coding for tRNAPhe and tRNATyr from a repeating unit of X. laevis DNA. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):345–353. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90509-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narang S. A., Hsiung H. M., Brousseau R. Improved phosphotriester method for the synthesis of gene fragments. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:90–98. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Leaky UAG termination codon in tobacco mosaic virus RNA. Nature. 1978 Mar 30;272(5652):469–471. doi: 10.1038/272469a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipson L., Andersson P., Olshevsky U., Weinberg R., Baltimore D., Gesteland R. Translation of MuLV and MSV RNAs in nuclease-treated reticulocyte extracts: enhancement of the gag-pol polypeptide with yeast suppressor tRNA. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):189–199. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90149-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlins D. R., Muzyczka N. Construction of a specific amber codon in the simian virus 40 T-antigen gene by site-directed mutagenesis. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):611–616. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.611-616.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A., Hirose T., Itakura K., Riggs A. D. Efficient correction of a mutation by use of chemically synthesized DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4268–4270. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompayrac L. M., Danna K. J. Efficient infection of monkey cells with DNA of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7575–7578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temple G. F., Dozy A. M., Roy K. L., Kan Y. W. Construction of a functional human suppressor tRNA gene: an approach to gene therapy for beta-thalassaemia. Nature. 1982 Apr 8;296(5857):537–540. doi: 10.1038/296537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterston R. H. A second informational suppressor, SUP-7 X, in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1981 Feb;97(2):307–325. doi: 10.1093/genetics/97.2.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]