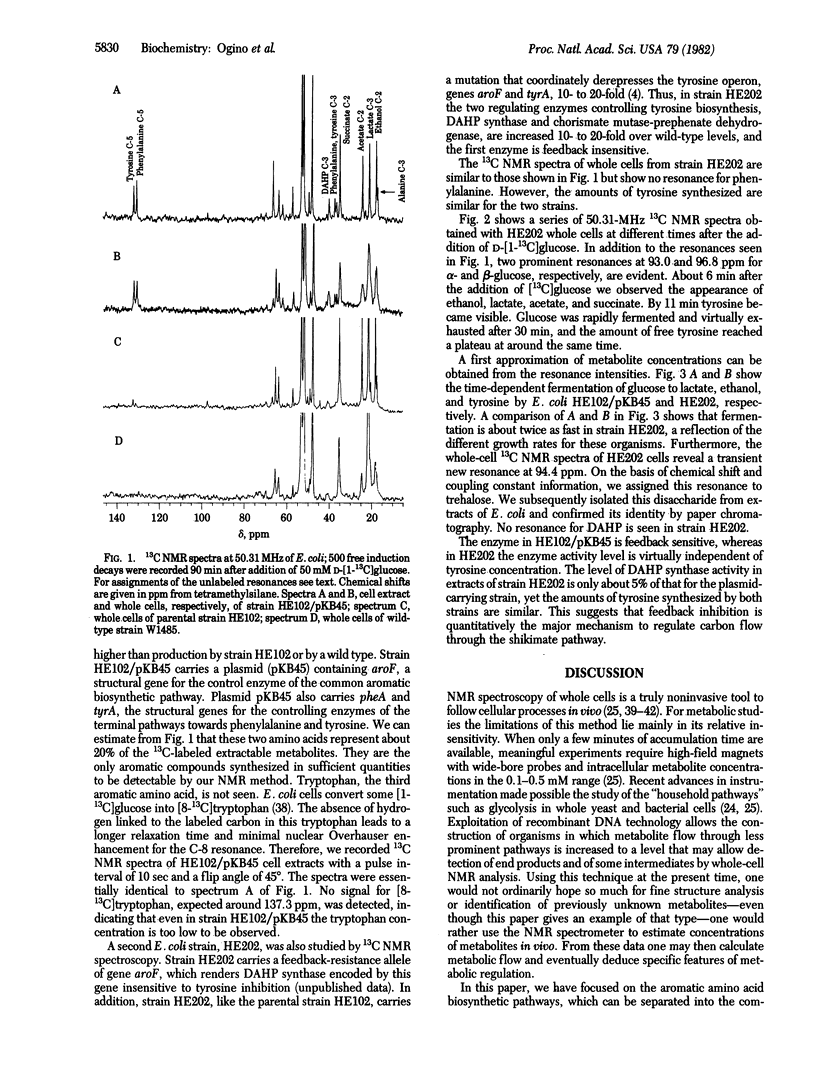
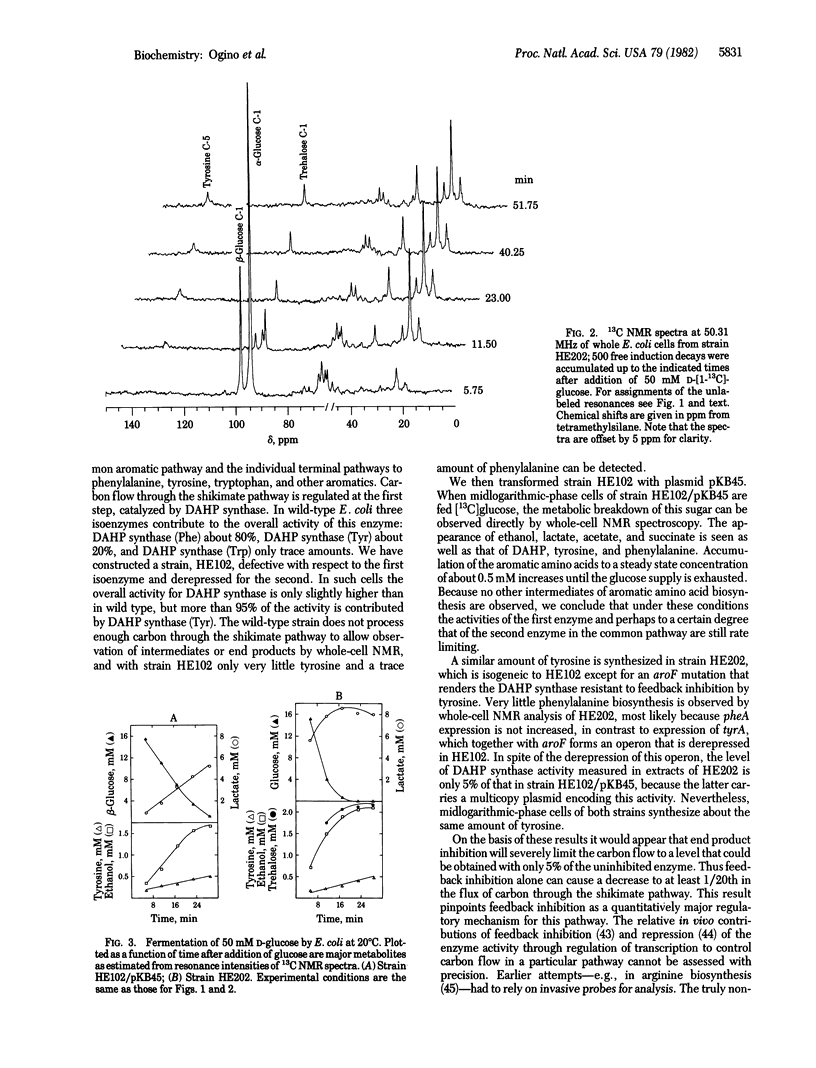
Abstract
13C and 31P NMR spectra of wild-type Escherichia coli showed resonances from metabolic intermediates of glycolysis and ATP formation but no detectable signals from aromatic amino acids. However, tyrosine biosynthesis from D-[l-13C]glucose was observed in cells harboring a feedback-resistant allele of aroF, the gene encoding tyrosine-sensitive 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase [7-phospho-2-keto-3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptonate D-erythrose-4-phosphate-lyase (pyruvate-phosphorylating), EC4.1.2.15], one of the isoenzymes that control carbon flow through the common aromatic biosynthetic pathway. A similar accumulation of tyrosine and phenylalanine is seen in cells carrying a multiple-copy plasmid that carries a wild-type aroF allele in addition to pheA and tyrA, the structural genes for controlling enzymes of the terminal pathways to phenylalanine and tyrosine biosynthesis. These in vivo measurements by a noninvasive probe suggest feedback inhibition as the quantitatively major mechanism controlling carbon flow in the common aromatic compound biosynthetic pathway. In strains accumulating aromatic amino acids, a transient accumulation of trehalose was detected, indicating that previously unknown changes in Escherichia coli metabolism accompany overproduction of aromatic compounds.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J., Low K. B. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 6. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Mar;44(1):1–56. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.1.1-56.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown F. F., Campbell I. D., Kuchel P. W., Rabenstein D. C. Human erythrocyte metabolism studies by 1H spin echo NMR. FEBS Lett. 1977 Oct 1;82(1):12–16. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80875-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burt C. T., Glonek T., Bárány M. Analysis of phosphate metabolites, the intracellular pH, and the state of adenosine triphosphate in intact muscle by phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 10;251(9):2584–2591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eakin R. T., Morgan L. O., Gregg C. T., Matwiyoff N. A. Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of living cells and their metabolism of a specifically labeled 13C substrate. FEBS Lett. 1972 Dec 15;28(3):259–264. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80726-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbein A. D. The metabolism of alpha,alpha-trehalose. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 1974;30:227–256. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2318(08)60266-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORINI L. Regulation en retour (feedback control) de la synthèse de l'arginine chez Escherichia coli. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1958;40(12):1939–1952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gachelin G. An investigation on the mode of action of sodium azide on the glucose permease of "Escherichia coli" K12. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1972 Jun;122(6):1099–1116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadian D. G., Hoult D. I., Radda G. K., Seeley P. J., Chance B., Barlow C. Phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance studies on normoxic and ischemic cardiac tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4446–4448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadian D. G., Radda G. K. NMR studies of tissue metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:69–83. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann K. M., Poling M. D. The synthesis of 3-deoxyheptulosonic acid 7-phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):6817–6821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann K. M., Shultz J., Hermodson M. A. Sequence homology between the tyrosine-sensitive 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate 7-phosphate synthase from Escherichia coli and hemerythrin from Sipunculida. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7079–7081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollis D. P., Nunnally R. L., Jacobus W. E., Taylor G. J., 4th Detection of regional ischemia in perfused beating hearts by phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Apr 25;75(4):1086–1091. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91493-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoult D. I., Busby S. J., Gadian D. G., Radda G. K., Richards R. E., Seeley P. J. Observation of tissue metabolites using 31P nuclear magnetic resonance. Nature. 1974 Nov 22;252(5481):285–287. doi: 10.1038/252285a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kainosho M., Ajisaka K., Nakazawa H. In situ analysis of the microbial fermentation process by natural abundance 13C and 31P NMR spectroscopy. Production of adenosine-5'-triphosphate from adenosine. FEBS Lett. 1977 Aug 15;80(2):385–389. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80482-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maréchal L. R., Belocopitow E. Metabolism of trehalose in Euglena gracilis. I. Partial purification and some properties of trehalose phosphorylase. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 25;247(10):3223–3228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCandliss R. J., Herrmann K. M. Immunological studies on 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase isoenzymes. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):3761–3764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCandliss R. J., Herrmann K. M. Iron, an essential element for biosynthesis of aromatic compounds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4810–4813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCandliss R. J., Poling M. D., Herrmann K. M. 3-Deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate 7-phosphate synthase. Purification and molecular characterization of the phenylalanine-sensitive isoenzyme from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4259–4265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCray J. W., Jr, Herrmann K. M. Derepression of certain aromatic amino acid biosynthetic enzymes of Escherichia coli K-12 by growth in Fe3+-deficient medium. J Bacteriol. 1976 Feb;125(2):608–615. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.2.608-615.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon R. B., Richards J. H. Determination of intracellular pH by 31P magnetic resonance. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):7276–7278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navon G., Ogawa S., Shulman R. G., Yamane T. High-resolution 31P nuclear magnetic resonance studies of metabolism in aerobic Escherichia coli cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):888–891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., Bloch P. L., Smith D. F. Culture medium for enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):736–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.736-747.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogino T., Arata Y., Fujiwara S. Proton correlation nuclear magnetic resonance study of metabolic regulations and pyruvate transport in anaerobic Escherichia coli cells. Biochemistry. 1980 Aug 5;19(16):3684–3691. doi: 10.1021/bi00557a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogino T., Arata Y., Fujiwara S., Shoun H., Beppu T. Proton correlation nuclear magnetic resonance study of anaerobic metabolism of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4742–4745. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postma P. W., Roseman S. The bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 14;457(3-4):213–257. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radda G. K., Seeley P. J. Recent studies on cellular metabolism by nuclear magnetic resonance. Annu Rev Physiol. 1979;41:749–769. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.41.030179.003533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SRINIVASAN P. R., SPRINSON D. B. 2-Keto-3-deoxy-D-arabo-heptonic acid 7-phosphate synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1959 Apr;234(4):716–722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Feucht B. U., Hofstadter L. J. Regulation of carbohydrate uptake and adenylate cyclase activity mediated by the enzymes II of the phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 10;251(3):883–892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoner R., Herrmann K. M. 3-Deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate 7-phosphate synthase. Purification, properties, and kinetics of the tyrosine-sensitive isoenzyme from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 25;251(18):5440–5447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott A. I., Baxter R. L. Applications of 13C NMR to metabolic studies. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1981;10:151–174. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.10.060181.001055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman R. G., Brown T. R., Ugurbil K., Ogawa S., Cohen S. M., den Hollander J. A. Cellular applications of 31P and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance. Science. 1979 Jul 13;205(4402):160–166. doi: 10.1126/science.36664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieben A. S., Perlin A. S., Simpson F. J. An improved preparative method for D-erythrose 4-phosphate. Can J Biochem. 1966 Jun;44(6):663–669. doi: 10.1139/o66-083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan P. R. The biosynthesis of anthranilate from [3,4-'+C]glucose in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1965 Dec;4(12):2860–2865. doi: 10.1021/bi00888a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UMBARGER H. E. Evidence for a negative-feedback mechanism in the biosynthesis of isoleucine. Science. 1956 May 11;123(3202):848–848. doi: 10.1126/science.123.3202.848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ugurbil K., Brown T. R., den Hollander J. A., Glynn P., Shulman R. G. High-resolution 13C nuclear magnetic resonance studies of glucose metabolism in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3742–3746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ugurbil K., Rottenberg H., Glynn P., Shulman R. G. 31P nuclear magnetic resonance studies of bioenergetics and glycolysis in anaerobic Escherichia coli cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2244–2248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel H. J. REPRESSED AND INDUCED ENZYME FORMATION: A UNIFIED HYPOTHESIS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1957 Jun 15;43(6):491–496. doi: 10.1073/pnas.43.6.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski G., Brown K., Killingly D., Yanofsky C. Nucleotide sequence of the leader region of the phenylalanine operon of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4271–4275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski G., Gunsalus R. P., Brown K. D., Yanofsky C. Structure and regulation of aroH, the structural gene for the tryptophan-repressible 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonic acid-7-phosphate synthetase of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jan 5;145(1):47–73. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90334-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lares L. B., Ratouchniak J., Casse F. Chromosomal location of gene governing the trehalose utilization in Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Mar 28;152(1):105–108. doi: 10.1007/BF00264946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Hollander J. A., Behar K. L., Shulman R. G. 13C NMR study of transamination during acetate utilization by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2693–2697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


