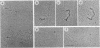
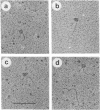
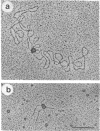
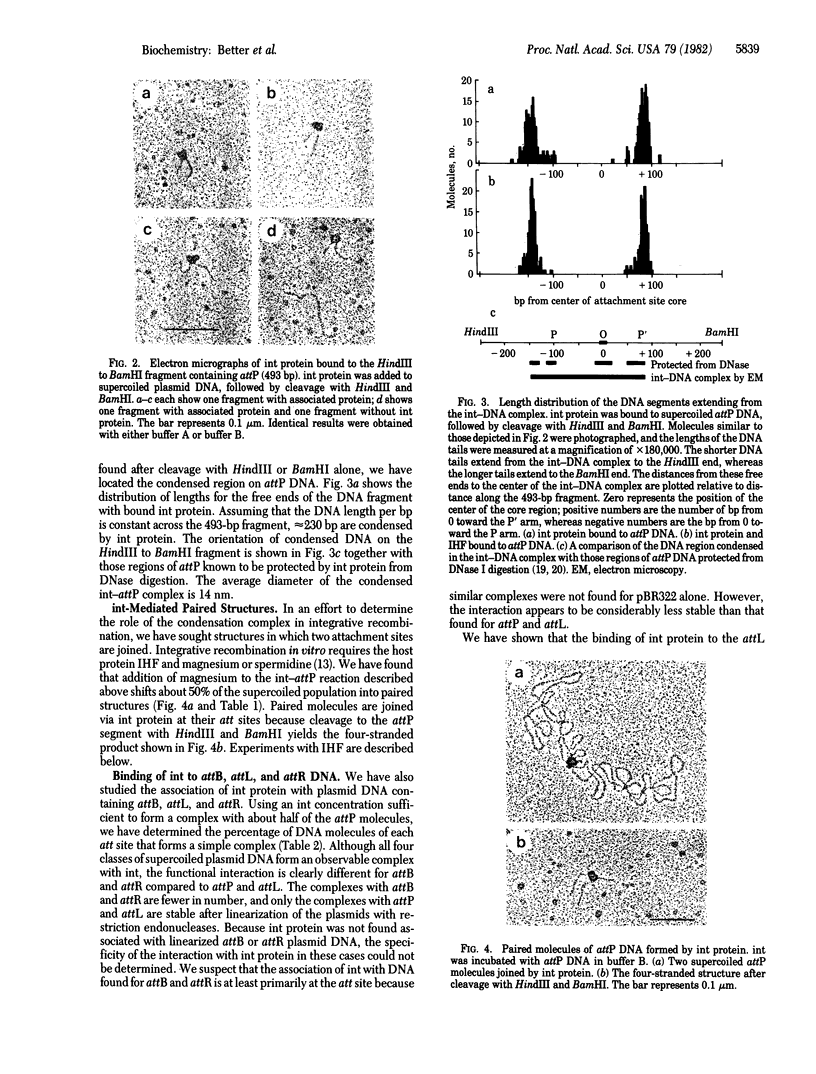
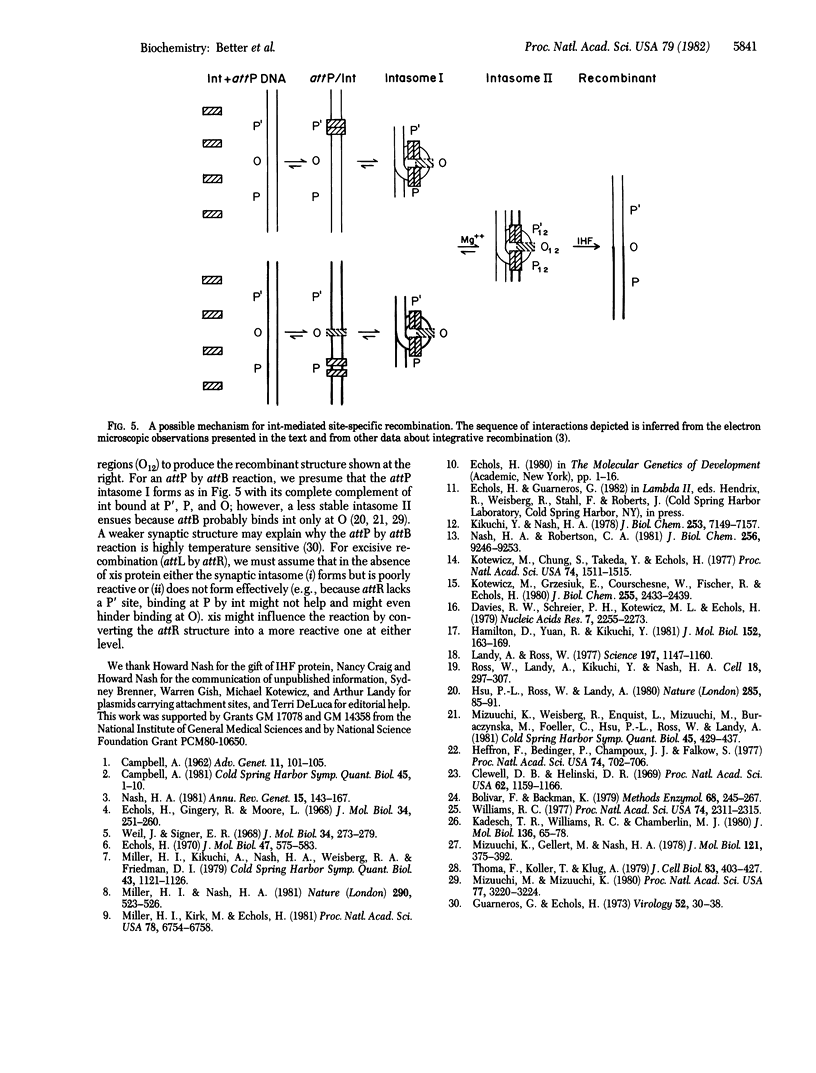
Abstract
The int protein of bacteriophage lambda catalyzes the site-specific integrative recombination that inserts lambda DNA into the host chromosome. The attachment site region of lambda DNA required for this reaction spans 230 base pairs and includes four separable binding sites for int protein. We have used the electron microscope to determine the functional consequences of the interaction of int with its multiple binding sites. We find that int condenses a 230-base pair segment of DNA into a compact structure about 14 nm in diameter; the condensed region includes all of the four binding sites for int. Condensed segments will form paired structures between attachments sites. We suggest that a sequential cooperative interaction between bound int molecules provides for a distinct reactive DNA conformation and for pairing between substrate sites.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolivar F., Backman K. Plasmids of Escherichia coli as cloning vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:245–267. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell A. Some general questions about movable elements and their implications. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):1–9. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. W., Schreier P. H., Kotewicz M. L., Echols H. Studies on the binding of lambda Int protein to attachment site DNA: identification of a tight-binding site in the P' region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 20;7(8):2255–2273. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.8.2255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echols H., Gingery R., Moore L. Integrative recombination function of bacteriophage lambda: evidence for a site-specific recombination enzyme. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 14;34(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90250-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echols H. Integrative and excisive recombination by bacteriophage lambda: evidence for an excision-specific recombination protein. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 14;47(3):575–583. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90324-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarneros G., Echols H. Thermal asymmetry of site-specific recombination by bacteriophage lambda. Virology. 1973 Mar;52(1):30–38. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90395-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton D., Yuan R., Kikuchi Y. The nature of the complexes formed between the int protein and DNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 Oct 15;152(1):163–169. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90100-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffron F., Bedinger P., Champoux J. J., Falkow S. Deletions affecting the transposition of an antibiotic resistance gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):702–706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu P. L., Ross W., Landy A. The lambda phage att site: functional limits and interaction with Int protein. Nature. 1980 May 8;285(5760):85–91. doi: 10.1038/285085a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadesch T. R., Williams R. C., Chamberlin M. J. Electron microscopic studies of the binding of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase to DNA. I. Characterization of the non-specific interactions of holoenzyme with a restriction fragment of bacteriophage T7 DNA. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jan 5;136(1):65–78. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90366-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi Y., Nash H. A. The bacteriophage lambda int gene product. A filter assay for genetic recombination, purification of int, and specific binding to DNA. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7149–7157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotewicz M., Chung S., Takeda Y., Echols H. Characterization of the integration protein of bacteriophage lambda as a site-specific DNA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1511–1515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotewicz M., Grzesiuk E., Courschesne W., Fischer R., Echols H. Purification and characterization of the integration protein specified by bacteriophage lambda. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2433–2439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landy A., Ross W. Viral integration and excision: structure of the lambda att sites. Science. 1977 Sep 16;197(4309):1147–1160. doi: 10.1126/science.331474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. I., Kikuchi A., Nash H. A., Weisberg R. A., Friedman D. I. Site-specific recombination of bacteriophage lambda: the role of host gene products. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):1121–1126. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. I., Kirk M., Echols H. SOS induction and autoregulation of the himA gene for site-specific recombination in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6754–6758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. I., Nash H. A. Direct role of the himA gene product in phage lambda integration. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):523–526. doi: 10.1038/290523a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Gellert M., Nash H. A. Involement of supertwisted DNA in integrative recombination of bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1978 May 25;121(3):375–392. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90370-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Weisberg R., Enquist L., Mizuuchi M., Buraczynska M., Foeller C., Hsu P. L., Ross W., Landy A. Structure and function of the phage lambda att site: size, int-binding sites, and location of the crossover point. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):429–437. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi M., Mizuuchi K. Integrative recombination of bacteriophage lambda: extent of the DNA sequence involved in attachment site function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3220–3224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A. Integration and excision of bacteriophage lambda: the mechanism of conservation site specific recombination. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:143–167. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.001043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A., Robertson C. A. Purification and properties of the Escherichia coli protein factor required for lambda integrative recombination. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9246–9253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma F., Koller T., Klug A. Involvement of histone H1 in the organization of the nucleosome and of the salt-dependent superstructures of chromatin. J Cell Biol. 1979 Nov;83(2 Pt 1):403–427. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.2.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil J., Signer E. R. Recombination in bacteriophage lambda. II. Site-specific recombination promoted by the integration system. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 14;34(2):273–279. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90252-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C. Use of polylysine for adsorption of nuclei acids and enzymes to electron microscope specimen films. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2311–2315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]