Abstract
The state of phosphorylation of proteins I, IIIa, and IIIb--neuron-specific phosphoproteins--was studied in neurosecretory endings of the neurohypophysis in vitro. Brief periods (a few seconds) of electrical stimulation caused large increases in the state of phosphorylation of all three proteins. The three proteins were dephosphorylated within 1 min after termination of the stimulation. High potassium, 8-bromo-cAMP, and dopamine also stimulated the phosphorylation of the three proteins. The effect of dopamine was blocked by the dopamine antagonist fluphenazine. Peptide mapping of protein I revealed that electrical stimulation or high potassium increased the state of phosphorylation of two regions of the molecule, whereas 8-bromo-cAMP and dopamine increased the state of phosphorylation of only one of these regions.
Full text
PDF

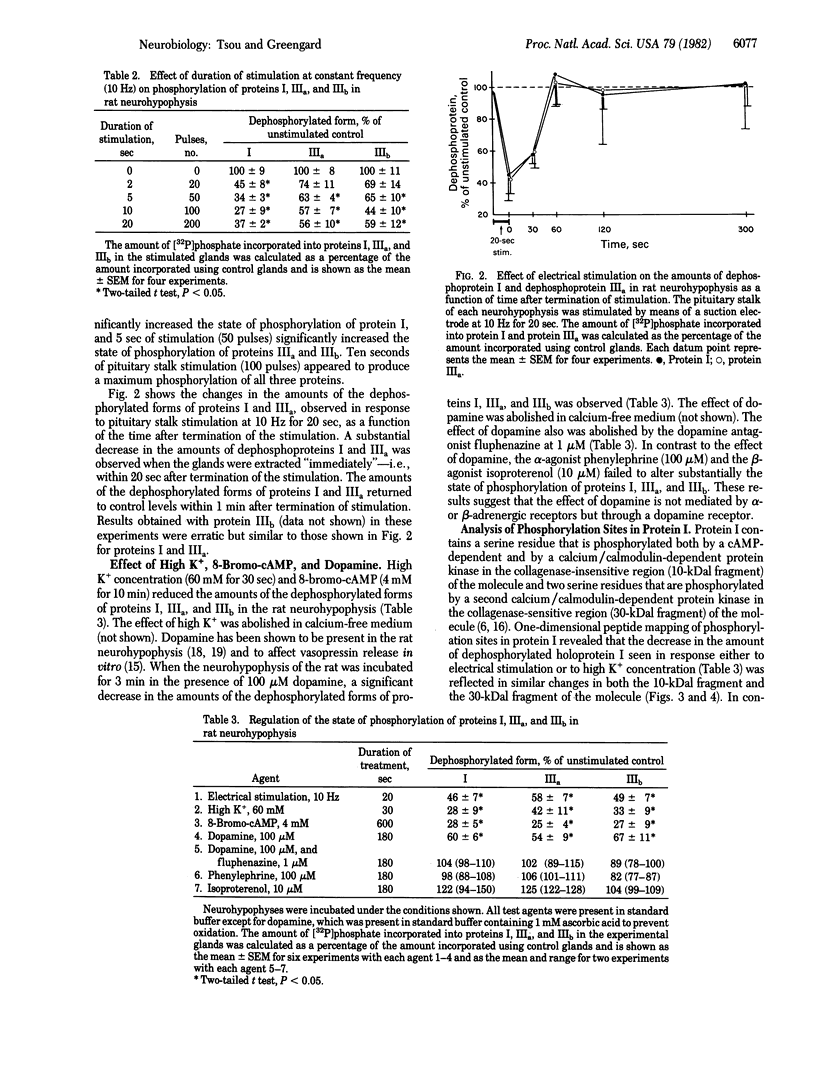
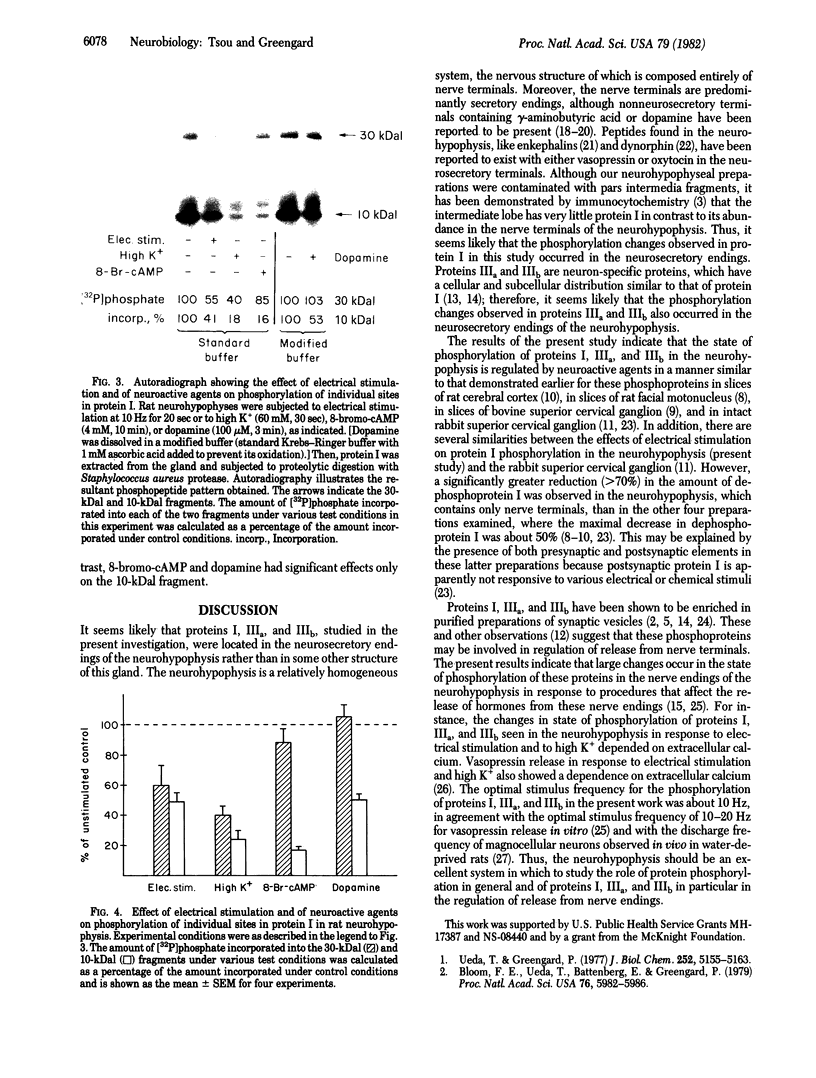

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumgarten H. G., Björklund A., Holstein A. F., Nobin A. Organization and ultrastructural identification of the catecholamine nerve terminals in the neural lobe and pars intermedia of the rat pituitary. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1972;126(4):483–517. doi: 10.1007/BF00306908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björklund A., Moore R. Y., Nobin A., Stenevi U. The organization of tubero-hypophyseal and reticulo-infundibular catecholamine neuron systems in the rat brain. Brain Res. 1973 Mar 15;51:171–191. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90371-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom F. E., Ueda T., Battenberg E., Greengard P. Immunocytochemical localization, in synapses, of protein I, an endogenous substrate for protein kinases in mammalian brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5982–5986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS W. W., POISNER A. M. STIMULUS-SECRETION COUPLING IN A NEUROSECRETORY ORGAN: THE ROLE OF CALCIUM IN THE RELEASE OF VASOPRESSIN FROM THE NEUROHYPOPHYSIS. J Physiol. 1964 Jul;172:1–18. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camilli P., Ueda T., Bloom F. E., Battenberg E., Greengard P. Widespread distribution of protein I in the central and peripheral nervous systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5977–5981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolphin A. C., Greengard P. Neurotransmitter- and neuromodulator-dependent alterations in phosphorylation of protein I in slices of rat facial nucleus. J Neurosci. 1981 Feb;1(2):192–203. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-02-00192.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forn J., Greengard P. Depolarizing agents and cyclic nucleotides regulate the phosphorylation of specific neuronal proteins in rat cerebral cortex slices. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5195–5199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried G., Nestler E. J., De Camilli P., Stjärne L., Olson L., Lundberg J. M., Hökfelt T., Ouimet C. C., Greengard P. Cellular and subcellular localization of protein I in the peripheral nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2717–2721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard P. Intracellular signals in the brain. Harvey Lect. 1979 1980;75:277–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. K., Browning M. D., Greengard P. Purification and characterization of protein IIIb, a mammalian brain phosphoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6524–6528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B., DeGennaro L. J., Greengard P. Differential phosphorylation of multiple sites in purified protein I by cyclic AMP-dependent and calcium-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 10;256(3):1482–1488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B., Greengard P. Multiple phosphorylation sites in protein I and their differential regulation by cyclic AMP and calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5402–5406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. B., Greengard P. Two calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases, which are highly concentrated in brain, phosphorylate protein I at distinct sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1293–1297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightman S. L., Iversen L. L., Forsling M. L. Dopamine and [D-ALA2, D-Leu5]enkephalin inhibit the electrically stimulated neurohypophyseal release of vasopressin in vitro: evidence for calcium-dependent opiate action. J Neurosci. 1982 Jan;2(1):78–81. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-01-00078.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R., Voigt K. H. Enkephalins co-exist with oxytocin and vasopressin in nerve terminals of rat neurohypophysis. Nature. 1981 Feb 5;289(5797):502–504. doi: 10.1038/289502a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestler E. J., Greengard P. Dopamine and depolarizing agents regulate the state of phosphorylation of protein I in the mammalian superior cervical sympathetic ganglion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7479–7483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestler E. J., Greengard P. Nerve impulses increase the phosphorylation state of protein I in rabbit superior cervical ganglion. Nature. 1982 Apr 1;296(5856):452–454. doi: 10.1038/296452a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oertel W. H., Mugnaini E., Tappaz M. L., Weise V. K., Dahl A. L., Schmechel D. E., Kopin I. J. Central GABAergic innervation of neurointermediate pituitary lobe: biochemical and immunocytochemical study in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):675–679. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Greengard P. Adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-regulated phosphoprotein system of neuronal membranes. I. Solubilization, purification, and some properties of an endogenous phosphoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):5155–5163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Greengard P., Berzins K., Cohen R. S., Blomberg F., Grab D. J., Siekevitz P. Subcellular distribution in cerebral cortex of two proteins phosphorylated by a cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Cell Biol. 1979 Nov;83(2 Pt 1):308–319. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.2.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. J., Akil H., Fischli W., Goldstein A., Zimmerman E., Nilaver G., van wimersma Griedanus T. B. Dynorphin and vasopressin: common localization in magnocellular neurons. Science. 1982 Apr 2;216(4541):85–87. doi: 10.1126/science.6121376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]