Abstract
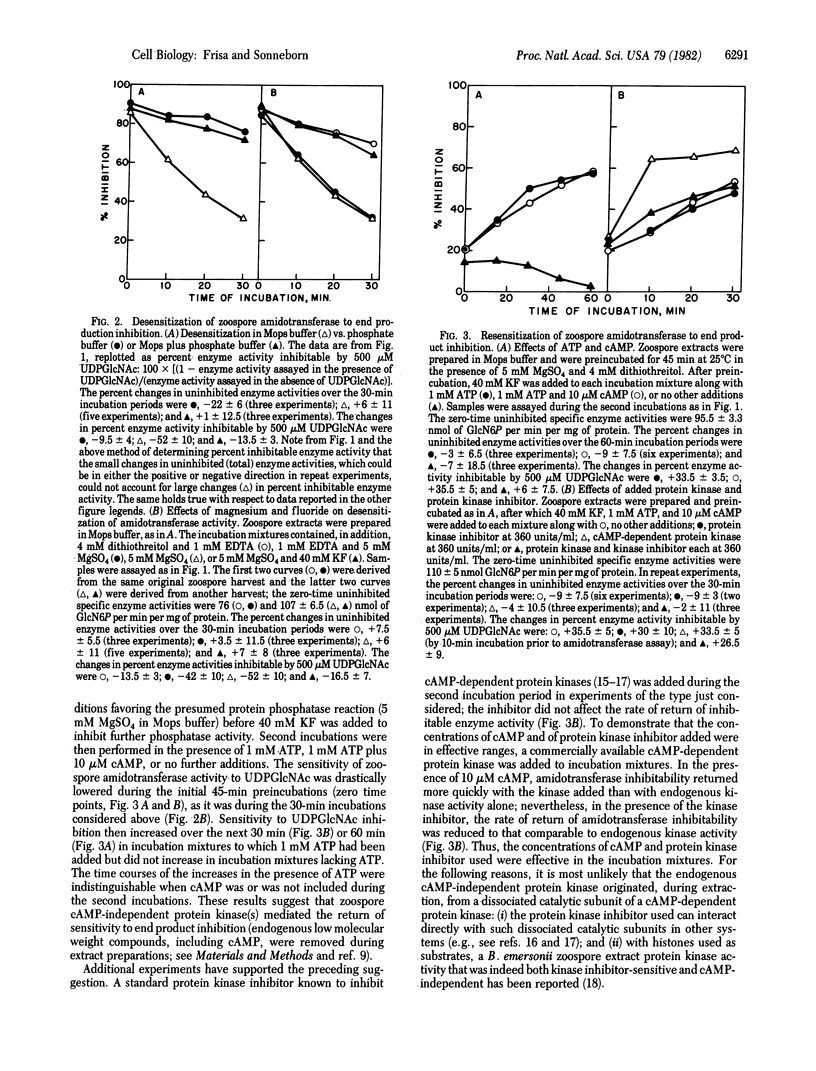
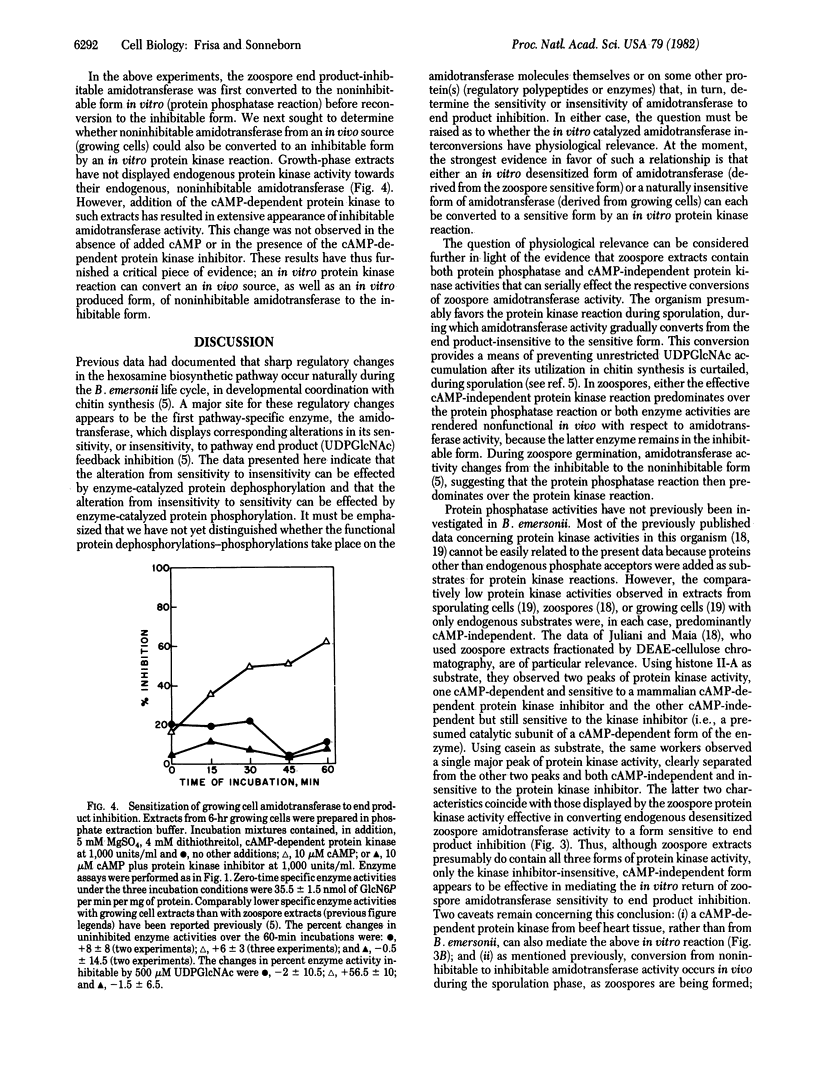
During the life cycle of Blastocladiella emersonii, dramatic shifts occur in the sensitivity of the first hexosamine biosynthetic pathway-specific enzyme [amidotransferase; 2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose-6-phosphate ketol-isomerase (amino-transferring), EC 5.3.1.19] to end product inhibition. These shifts are developmentally correlated with changes in the utilization of the end product (uridine-5'-diphospho-N-acetylglucosamine) for chitin synthesis [Selitrennikoff, C. P., Dalley, N. E. & Sonneborn, D. R. (1980) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77, 5998-6002]. Alterations in amidotransferase sensitivity to end product inhibition can be mimicked by in vitro protein dephosphorylation-phosphorylation reactions, as follows: (i) Zoospore end product-inhibitable amidotransferase activity can be converted to a noninhibitable form by an endogenous (zoospore) protein phosphatase (phosphoprotein phosphohydrolase EC 3.1.3.16) reaction; this noninhibitable form can be converted back to an inhibitable form either by an endogenous cAMP-independent protein kinase (ATP:protein phosphotransferase, EC 2.7.1.37) reaction or with an added cAMP-dependent protein kinase. (ii) Noninhibitable amidotransferase activity from growing cells can also be converted to the inhibitable form with added protein kinase.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashby C. D., Walsh D. A. Characterization of the interaction of a protein inhibitor with adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. I. Interaction with the catalytic subunit of the protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 25;247(20):6637–6642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashby C. D., Walsh D. A. Characterization of the interaction of a protein inhibitor with adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. II. Mechanism of action with the holoenzyme. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 25;248(4):1255–1261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juliani M. H., Da Costa Maia J. C. Cyclic AMP-dependent and -independent protein kinases of the water mold, Blastocladiella emersonii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Apr 12;567(2):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90121-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G., Beavo J. A. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:923–959. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett J. S. Growth and differentiation of the water mold Blastocladiella emersonii: cytodifferentiation and the role of ribonucleic acid and protein synthesis. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Dec;39(4):345–404. doi: 10.1128/br.39.4.345-404.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. B., Cantino E. C. The gamma particle. A study of cell-organelle interactions in the development of the water mold Blastocladiella emersonii. Monogr Dev Biol. 1974;8:1–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selitrennikoff C. P., Allin D., Sonneborn D. R. Chitin biosynthesis during Blastocladiella zoospore germination: evidence that the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway is post-translationally activated during cell differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):534–538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selitrennikoff C. P., Dalley N. E., Sonneborn D. R. Regulation of the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway in the water mold Blastocladiella emersonii: Sensitivity to endproduct inhibition is dependent upon the life cycle phase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5998–6002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selitrennikoff C. P., Sonneborn D. R. Alkaline phosphatase of Blastocladiella emersonii: partial purification and characterization. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):249–256. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.249-256.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selitrennikoff C. P., Sonneborn D. R. Post-translational control of de novo cell wall formation during Blastocladiella emersonii zoospore germination: feedback regulation of hexosamine biosynthesis. Dev Biol. 1976 Nov;54(1):37–51. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90284-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman P. M. Cyclic AMP binding proteins and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase from Blastocladiella emersonii. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):976–980. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.976-980.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soll D. R., Bromberg R., Sonneborn D. R. Zoospore germination in the water mold. Blastocladiella emersonii. I. Measurement of germination and sequence of subcellular morphological changes. Dev Biol. 1969 Sep;20(3):183–217. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(69)90012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szmigielski A., Guidotti A., Costa E. Endogenous protein kinase inhibitors. Purification, characterization, and distribution in different tissues. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3848–3853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Brunt J., Harold F. M. Ionic control of germination of Blastocladiella emersonii zoospores. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):735–744. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.735-744.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh D. A., Ashby C. D., Gonzalez C., Calkins D., Fischer E. H. Krebs EG: Purification and characterization of a protein inhibitor of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):1977–1985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. Y., Koshland D. E., Jr The identification of distinct protein kinases and phosphatases in the prokaryote Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4640–4648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


