Abstract
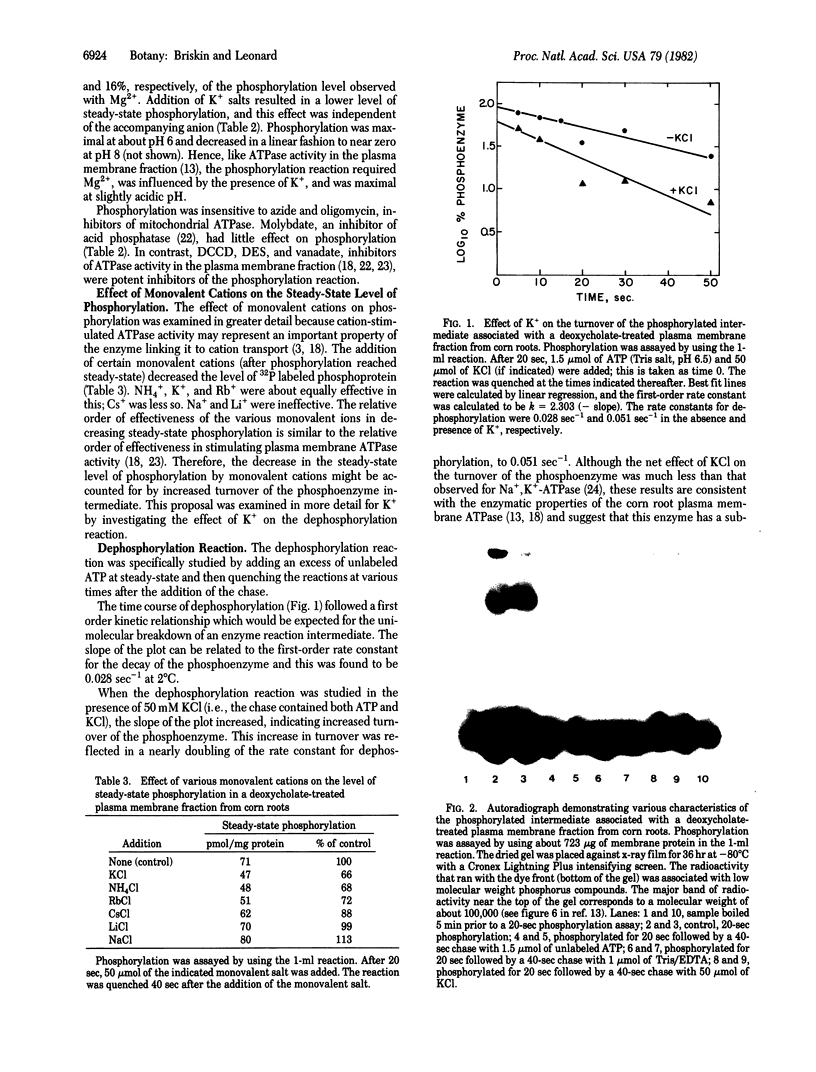
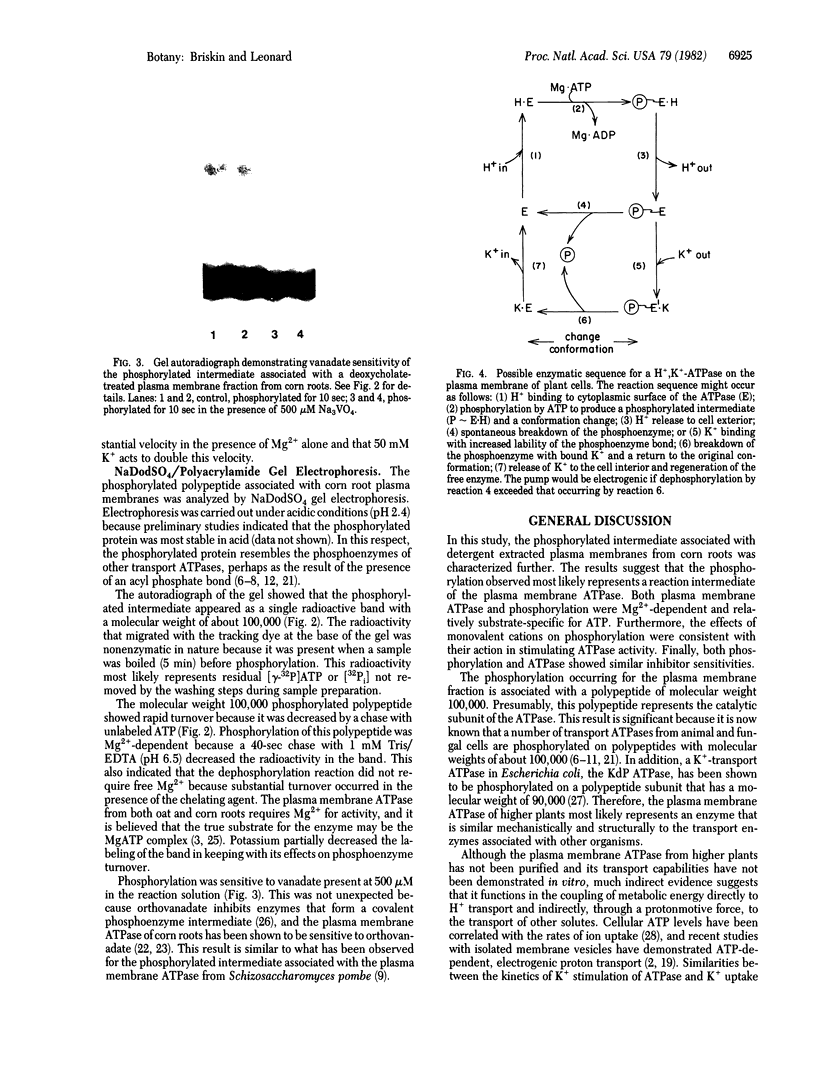
The phosphorylated protein associated with a deoxycholate-extracted plasma membrane fraction from corn (Zea mays L. var WF9 × Mol7) roots was characterized in order to correlate its properties with those of plasma membrane ATPase. Its phosphorylation, like that of plasma membrane ATPase, was dependent on Mg2+, substrate specific for ATP, insensitive to azide, oligomycin, or molybdate, and sensitive to N,N′-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, diethylstilbestrol, or vanadate. Monovalent cations affected the phosphorylation of the protein in a manner consistent with their stimulatory effects on ATPase. For K+, this was shown to occur through an increase in the turnover of the phosphoenzyme. Analysis of the phosphorylated protein by NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis revealed the presence of a single labeled polypeptide with a molecular weight of about 100,000. Phosphorylation of this polypeptide was dependent on Mg2+, sensitive to K+, and inhibited by vanadate. It is concluded that this polypeptide represents the catalytic subunit of the plasma membrane ATPase. These results are discussed in terms of a model for the coupling of metabolic energy to H+ and K+ transport in higher plants.
Keywords: ion transport, energy coupling, transport reaction mechanism
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balke N. E., Hodges T. K. Plasma membrane adenosine triphosphatase of oat roots: activation and inhibition by mg and ATP. Plant Physiol. 1975 Jan;55(1):83–86. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Jr, Cantley L. G., Josephson L. A characterization of vanadate interactions with the (Na,K)-ATPase. Mechanistic and regulatory implications. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7361–7368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dame J. B., Scarborough G. A. Identification of the hydrolytic moiety of the Neurospora plasma membrane H+-ATPase and demonstration of a phosphoryl-enzyme intermediate in its catalytic mechanism. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 24;19(13):2931–2937. doi: 10.1021/bi00554a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont F. M., Burke L. L., Spanswick R. M. Characterization of a partially purified adenosine triphosphatase from a corn root plasma membrane fraction. Plant Physiol. 1981 Jan;67(1):59–63. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont F. M., Leonard R. T. Solubilization and partial purification of the adenosine triphosphatase from a corn root plasma membrane fraction. Plant Physiol. 1980 May;65(5):931–938. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.5.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Avruch J. Four gel systems for electrophoretic fractionation of membrane proteins using ionic detergents. J Supramol Struct. 1972;1(1):66–75. doi: 10.1002/jss.400010110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foury F., Amory A., Goffeau A. Large-scale purification and phosphorylation of a detergent-treated adenosine triphosphatase complex from plasma membrane of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Oct;119(2):395–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05621.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunn R. B. Co- and counter-transport mechanisms in cell membranes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1980;42:249–259. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.42.030180.001341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs A. S., Albers R. W. The structure of proteins involved in active membrane transport. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1980;9:259–291. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.09.060180.001355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard R. T., Hotchkiss C. W. Plasma Membrane-associated Adenosine Triphosphatase Activity of Isolated Cortex and Stele from Corn Roots. Plant Physiol. 1978 Feb;61(2):175–179. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.2.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malpartida F., Serrano R. Phosphorylated intermediate of the ATPase from the plasma membrane of yeast. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May 15;116(2):413–417. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05350.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POST R. L., SEN A. K., ROSENTHAL A. S. A PHOSPHORYLATED INTERMEDIATE IN ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE-DEPENDENT SODIUM AND POTASSIUM TRANSPORT ACROSS KIDNEY MEMBRANES. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1437–1445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petraglia T., Poole R. J. ATP Levels and their Effects on Plasmalemma Influxes of Potassium Chloride in Red Beet. Plant Physiol. 1980 May;65(5):969–972. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.5.969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post R. L., Hegyvary C., Kume S. Activation by adenosine triphosphate in the phosphorylation kinetics of sodium and potassium ion transport adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 25;247(20):6530–6540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasi-Caldogno F., de Michelis M. I., Pugliarello M. C. Evidence for an electrogenic ATPase in microsomal vesicles from pea internodes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Mar 20;642(1):37–45. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90135-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs G., Berglindh T., Rabon E., Wallmark B., Barcellona M. L., Stewart H. B., Saccomani G. The interaction of K+ with gastric parietal cells and gastric ATPase. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;358:118–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb15391.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkadi B. Active calcium transport in human red cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Sep 30;604(2):159–190. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90573-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sze H., Churchill K. A. Mg/KCl-ATPase of plant plasma membranes is an electrogenic pump. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5578–5582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Meis L., Vianna A. L. Energy interconversion by the Ca2+-dependent ATPase of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:275–292. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]