Abstract
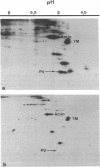
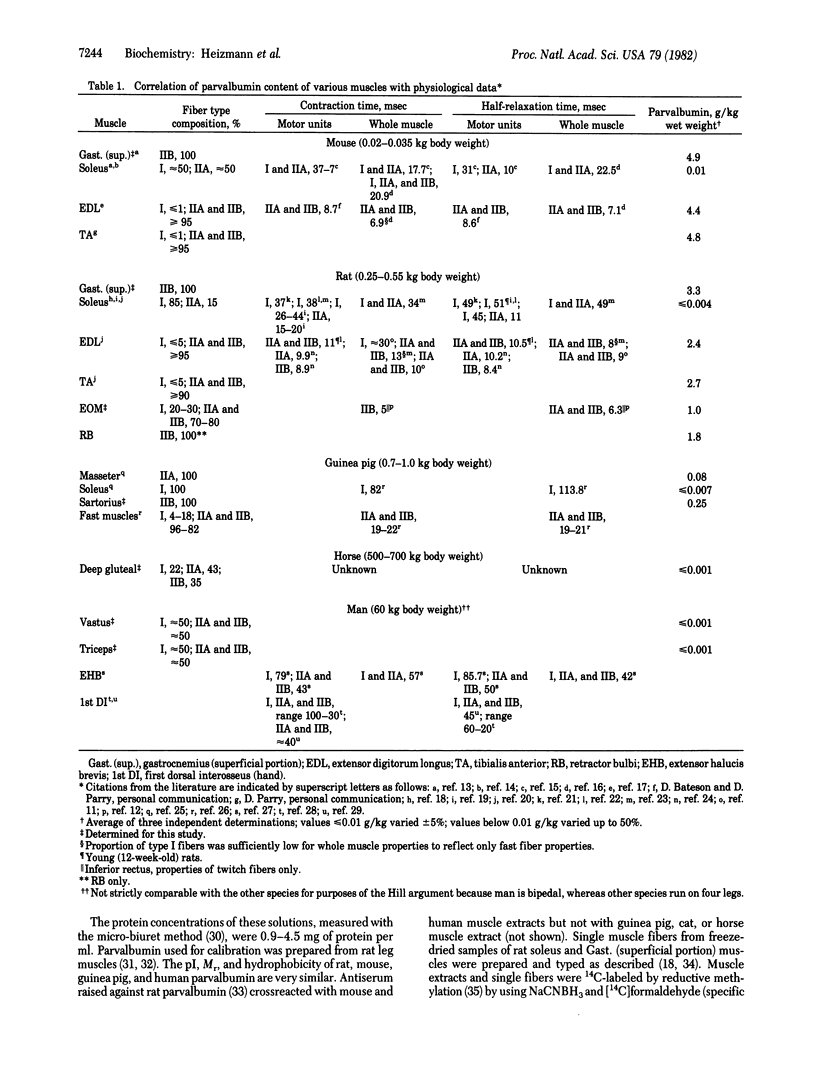
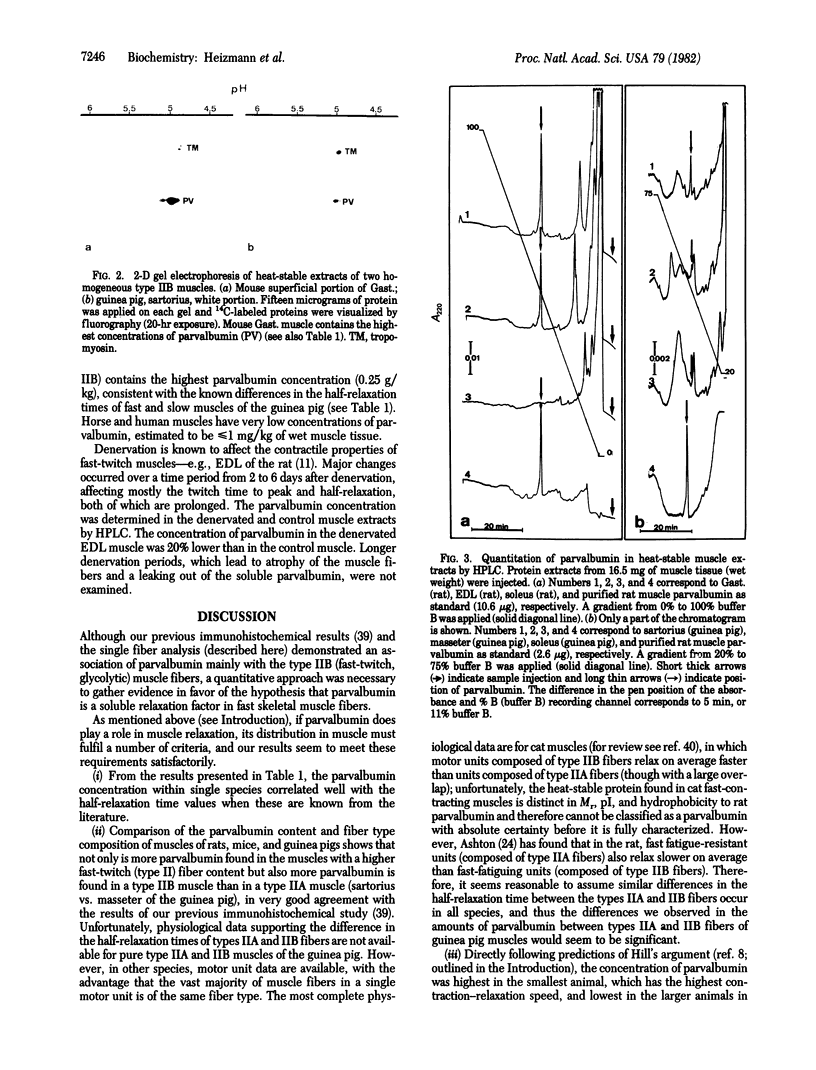
The physiological role of the Ca2+-binding protein parvalbumin in skeletal muscle has been investigated by measuring the parvalbumin content by HPLC in a variety of mammalian muscles, including man, and comparing the results with the respective muscle relaxation properties and fiber type compositions. The parvalbumin concentrations were highest in the skeletal muscles of the smallest animal investigated (mouse, gastrocnemius: 4.9 g/kg), which has the highest relaxation speed, and lowest in the larger animals (horse, deep gluteal muscle: less than or equal to 0.001 g/kg) and man (vastus, triceps: less than or equal to 0.001 g/kg), which have much lower relaxation speeds. Analysis of three type-homogeneous muscles of the guinea pig revealed highest parvalbumin concentrations (0.25 g/kg) in sartorius (type IIB) and lowest concentrations (less than or equal to 0.007 g/kg) in soleus (type I), consistent with the different half-relaxation times of fast and slow muscles. Denervation of the rat extensor digitorum longus, which increases the half-relaxation time from 9.4 to 19 msec, resulted in a 20% decrease of the parvalbumin content. Given this close correlation between parvalbumin content and relaxation speed in a variety of muscles and species, we suggest that parvalbumin is involved directly in the relaxation process in fast muscles.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrew B. L., Part N. J. Properties of fast and slow motor units in hind limb and tail muscles of the rat. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1972 Apr;57(2):213–225. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1972.sp002151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ariano M. A., Armstrong R. B., Edgerton V. R. Hindlimb muscle fiber populations of five mammals. J Histochem Cytochem. 1973 Jan;21(1):51–55. doi: 10.1177/21.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnard R. J., Edgerton V. R., Furukawa T., Peter J. B. Histochemical, biochemical, and contractile properties of red, white, and intermediate fibers. Am J Physiol. 1971 Feb;220(2):410–414. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.2.410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berchtold M. W., Heizmann C. W., Wilson K. J. Primary structure of parvalbumin from rat skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Oct;127(2):381–389. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06883.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billeter R., Heizmann C. W., Howald H., Jenny E. Analysis of myosin light and heavy chain types in single human skeletal muscle fibers. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May 15;116(2):389–395. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05347.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooke M. H., Kaiser K. K. Muscle fiber types: how many and what kind? Arch Neurol. 1970 Oct;23(4):369–379. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1970.00480280083010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchthal F., Schmalbruch H. Motor unit of mammalian muscle. Physiol Rev. 1980 Jan;60(1):90–142. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.1.90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celio M. R., Heizmann C. W. Calcium-binding protein parvalbumin as a neuronal marker. Nature. 1981 Sep 24;293(5830):300–302. doi: 10.1038/293300a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celio M. R., Heizmann C. W. Calcium-binding protein parvalbumin is associated with fast contracting muscle fibres. Nature. 1982 Jun 10;297(5866):504–506. doi: 10.1038/297504a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Close R. I., Luff A. R. Dynamic properties of inferior rectus muscle of the rat. J Physiol. 1974 Jan;236(2):259–270. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Close R. Dynamic properties of fast and slow skeletal muscles of the rat after nerve cross-union. J Physiol. 1969 Oct;204(2):331–346. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Close R. Properties of motor units in fast and slow skeletal muscles of the rat. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(1):45–55. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finol H. J., Lewis D. M., Owens R. The effects of denervation on contractile properties or rat skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1981;319:81–92. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haiech J., Derancourt J., Pechère J. F., Demaille J. G. Magnesium and calcium binding to parvalbumins: evidence for differences between parvalbumins and an explanation of their relaxing function. Biochemistry. 1979 Jun 26;18(13):2752–2758. doi: 10.1021/bi00580a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ITZHAKI R. F., GILL D. M. A MICRO-BIURET METHOD FOR ESTIMATING PROTEINS. Anal Biochem. 1964 Dec;9:401–410. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentoft N., Dearborn D. G. Labeling of proteins by reductive methylation using sodium cyanoborohydride. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4359–4365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kugelberg E. Histochemical composition, contraction speed and fatiguability of rat soleus motor units. J Neurol Sci. 1973 Oct;20(2):177–198. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(73)90029-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. M., Kean C. J., McGarrick J. D. Trophic functions of the neuron. II. Denervation and regulation of muscle. Dynamic properties of slow and fast muscle and their trophic regulation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Mar 22;228(0):105–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb20505.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. M., Parry D. J., Rowlerson A. Isometric contractions of motor units and immunohistochemistry of mouse soleus muscle. J Physiol. 1982 Apr;325:393–401. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luff A. R. Dynamic properties of the inferior rectus, extensor digitorum longus, diaphragm and soleus muscles of the mouse. J Physiol. 1981;313:161–171. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner-Brown H. S., Stein R. B., Yemm R. The orderly recruitment of human motor units during voluntary isometric contractions. J Physiol. 1973 Apr;230(2):359–370. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry D. J., Parslow H. G. Fiber type susceptibility in the dystrophic mouse. Exp Neurol. 1981 Sep;73(3):674–685. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(81)90204-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pechère J. F., Derancourt J., Haiech J. The participation of parvalbumins in the activation-relaxation cycle of vertebrate fast skeletal-muscle. FEBS Lett. 1977 Mar 15;75(1):111–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80064-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson S. P., Johnson J. D., Potter J. D. The time-course of Ca2+ exchange with calmodulin, troponin, parvalbumin, and myosin in response to transient increases in Ca2+. Biophys J. 1981 Jun;34(3):559–569. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84868-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sica R. E., McComas A. J. Fast and slow twitch units in a human muscle. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1971 Apr;34(2):113–120. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.34.2.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurway N. C. Objective characterization of cells in terms of microscopical parameters: an example from muscle histochemistry. Histochem J. 1981 Mar;13(2):269–317. doi: 10.1007/BF01006884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A., Stephens J. A. Study of human motor unit contractions by controlled intramuscular microstimulation. Brain Res. 1976 Nov 26;117(2):331–335. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90742-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan H. S., Aziz-Ullah, Goldspink G., Nowell N. W. Sex and stock differences in the histochemical myofibrillar adenosine triphosphatase reaction in the soleus muscle of the mouse. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Mar;22(3):155–159. doi: 10.1177/22.3.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]