Abstract
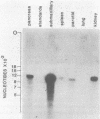
We have cloned via recombinant DNA technology the mRNA sequence for rat pancreatic preprokallikrein. Four cloned overlapping double-stranded cDNAs gave a continuous mRNA sequence of 867 nucleotides beginning within the 5'-noncoding region and extending to the poly(A) tail. The mRNA sequence reveals that pancreatic kallikrein is synthesized as a prezymogen of 265 amino acids, including a proposed secretory prepeptide of 17 amino acids and a proposed activation peptide of 11 amino acids. The activation peptide, although similar in length, is distinct from those of the other classes of pancreatic serine proteases. The amino acid sequence of the predicted active form of the enzyme is closely related to the partial sequences obtained for other kallikrein-like serine proteases including rat submaxillary gland kallikrein, pig pancreatic and submaxillary gland kallikreins, the gamma subunit of mouse nerve growth factor, and rat tonin. Key amino acid residues thought to be involved in the substrate-cleavage specificity of kallikreins are retained. Hybridization analysis showed relatively high levels of kallikrein mRNA in the rat pancreas, submaxillary and parotid glands, spleen, and kidney, indicating the active synthesis of kallikrein in these tissues.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Walter P., Chang C. N., Goldman B. M., Erickson A. H., Lingappa V. R. Translocation of proteins across membranes: the signal hypothesis and beyond. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1979;33:9–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bothwell M. A., Wilson W. H., Shooter E. M. The relationship between glandular kallikrein and growth factor-processing proteases of mouse submaxillary gland. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7287–7294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carne T., Scheele G. Amino acid sequences of transport peptides associated with canine exocrine pancreatic proteins. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4133–4140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedler F., Fritz H. Striking structural similarity of pig pancreatic kallikrein, mouse nerve growth factor gamma-subunit and rat tonin. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1981 Aug;362(8):1171–1175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedler F., Gebhard W. Isolation and characterization of native single-chain porcine pancreatic kallikrein, another possible precursor of urinary kallikrein. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1980 Nov;361(11):1661–1671. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1980.361.2.1661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman H. M., MacDonald R. J. Cloning of hormone genes from a mixture of cDNA molecules. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:75–90. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Santer M., Steitz J. A., Mans R. J. Conservation of the primary structure at the 3' end of 18S rRNA from eucaryotic cells. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):551–563. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90328-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Grez M., Hauser H., Lindenmaier W., Schütz G. 5'-Terminal sequences of eucaryotic mRNA can be cloned with high efficiency. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2251–2266. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazure C., Seidah N. G., Thibault G., Boucher R., Genest J., Chrétien M. Sequence homologies between tonin, nerve growth factor gamma-subunit, epidermal growth factor-binding protein and serine proteases. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):383–384. doi: 10.1038/292383a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon M., Fiedler F., Förg-Brey B., Hirschauer C., Leysath G., Fritz H. The isolation and properties of pig submandibular kallikrein. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 1;177(1):159–168. doi: 10.1042/bj1770159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. J., Crerar M. M., Swain W. F., Pictet R. L., Thomas G., Rutter W. J. Structure of a family of rat amylase genes. Nature. 1980 Sep 11;287(5778):117–122. doi: 10.1038/287117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. J., Stary S. J., Swift G. H. Two similar but nonallelic rat pancreatic trypsinogens. Nucleotide sequences of the cloned cDNAs. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9724–9732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. J., Swift G. H., Quinto C., Swain W., Pictet R. L., Nikovits W., Rutter W. J. Primary structure of two distinct rat pancreatic preproelastases determined by sequence analysis of the complete cloned messenger ribonucleic acid sequences. Biochemistry. 1982 Mar 16;21(6):1453–1463. doi: 10.1021/bi00535a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsas R., Proud D., Nustad K., Bailey G. S. Rapid purification of a prekallikrein from rat pancreas. Anal Biochem. 1981 May 15;113(2):264–270. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90076-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nustad K., Vaaje K., Pierce J. V. Synthesis of kallikreins by rat kidney slices. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Feb;53(2):229–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07353.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards R. I., Catanzaro D. F., Mason A. J., Morris B. J., Baxter J. D., Shine J. Mouse glandular kallikrein genes. Nucleotide sequence of cloned cDNA coding for a member of the kallikrein arginyl esteropeptidase group of serine proteases. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):2758–2761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roblero J., Croxatto H., García R., Corthorn J., De Vito E. Kallikreinlike activity in perfusates and urine of isolated rat kidneys. Am J Physiol. 1976 Nov;231(5 Pt 1):1383–1389. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.5.1383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roychoudhury R., Jay E., Wu R. Terminal labeling and addition of homopolymer tracts to duplex DNA fragments by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Jan;3(1):101–116. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stellwag E. J., Dahlberg A. E. Electrophoretic transfer of DNA, RNA and protein onto diazobenzyloxymethyl (DBM) - paper. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 25;8(2):299–317. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. A., Baglan N. C., Bradshaw R. A. The amino acid sequence of the gamma-subunit of mouse submaxillary gland 7 S nerve growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9156–9166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. A., Baglan N. C., Bradshaw R. A. The amino acid sequence of the gamma-subunit of mouse submaxillary gland 7 S nerve growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9156–9166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschesche H., Mair G., Godec G. The primary structure of porcine glandular kallikreins. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1979;120A:245–260. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-0926-1_25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson H. C., Shotton D. M., Cox J. M., Muirhead H. Three-dimensional Fourier synthesis of tosyl-elastase at 3.5 å resolution. Nature. 1970 Feb 28;225(5235):806–811. doi: 10.1038/225806a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]