Abstract
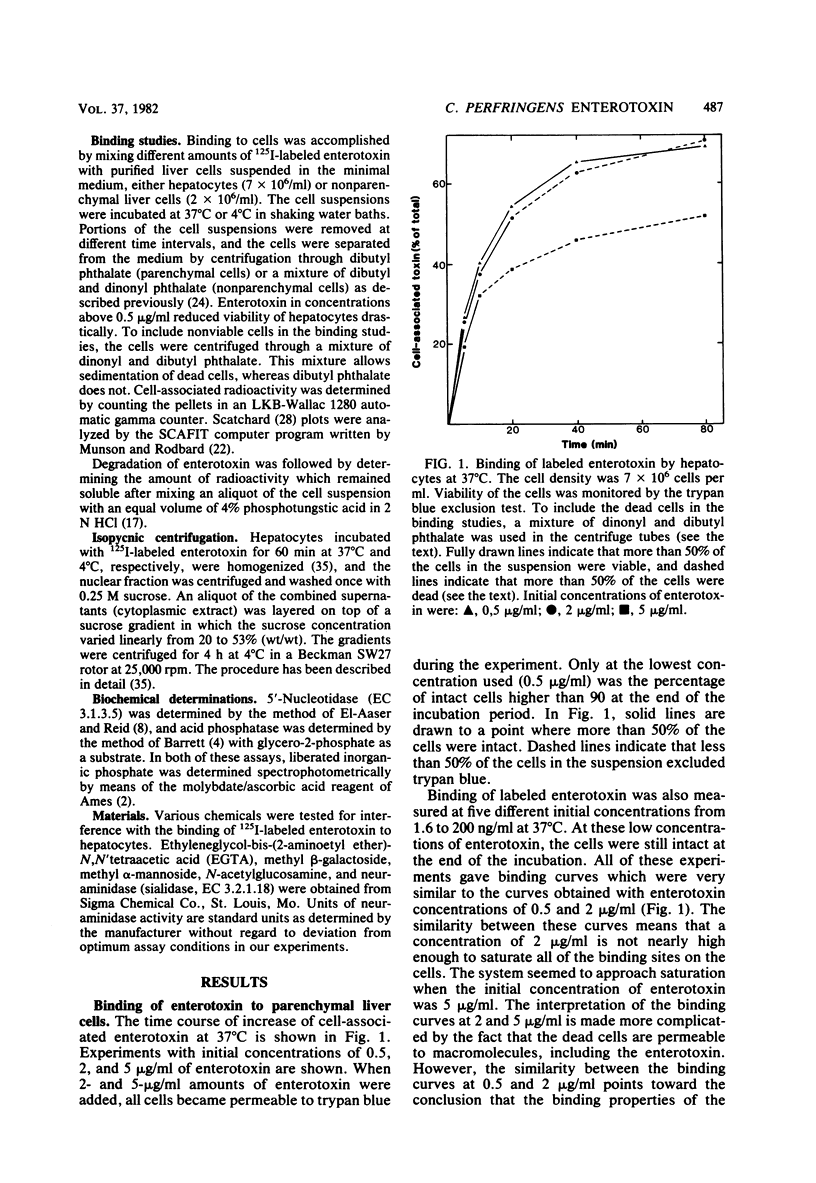
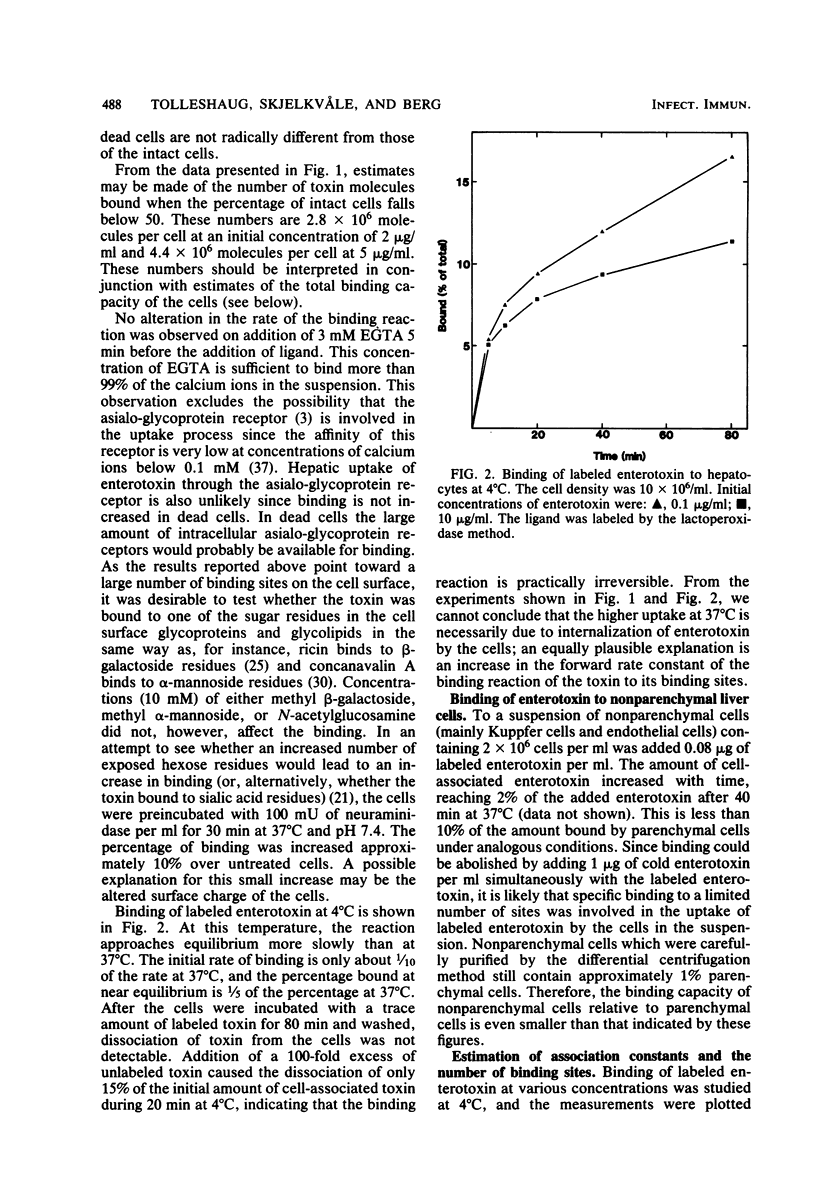
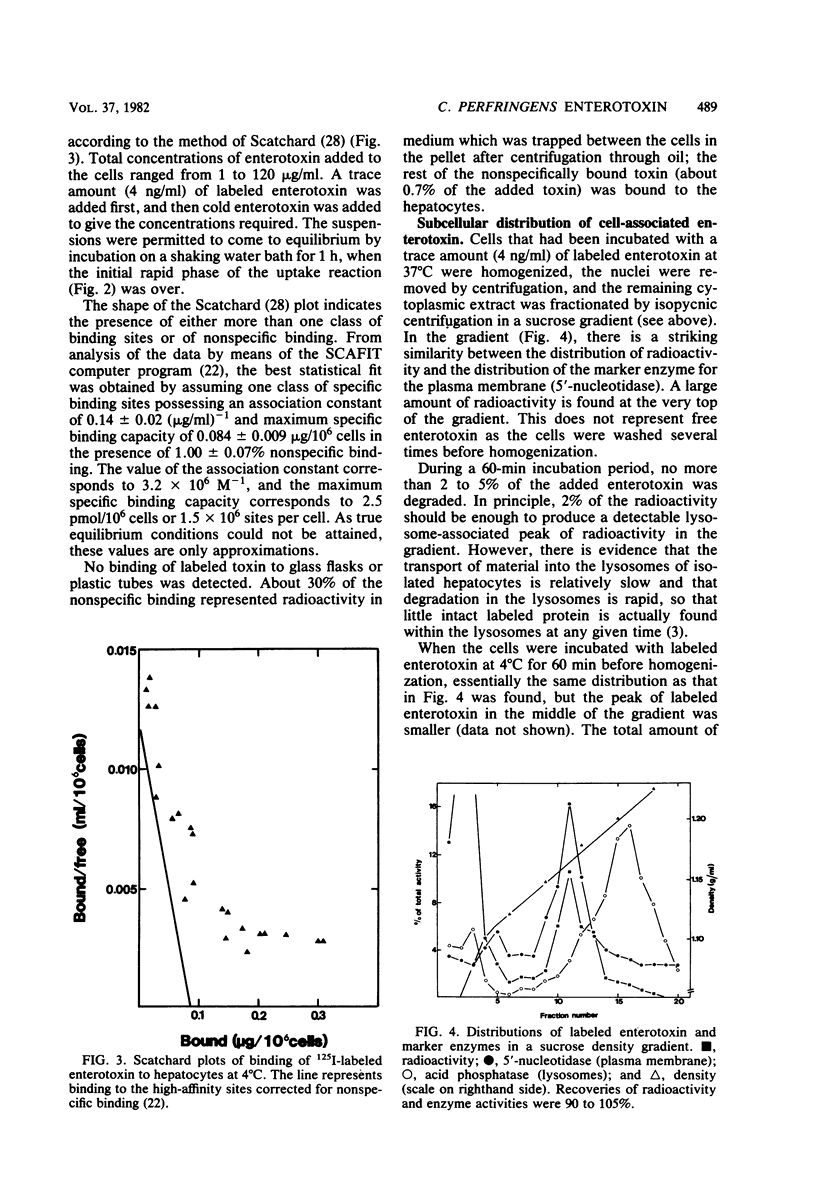
Binding of enterotoxin from Clostridium perfringens type A was studied in suspensions of parenchymal and nonparenchymal cells from rat liver. In hepatocytes, 1.5 X 10(6) specific binding sites per cell with an association constant of 3.2 X 10(6) M-1 were found. About 1% of the added toxin was nonspecifically bound to the hepatocytes. At concentrations of toxin below 0.1 micrograms/ml, 80% of the toxin density of 7 X 10(6) cells per ml. Binding did not increase after the cells became permeable to the toxin. Subcellular fractionation in a sucrose gradient produced no evidence for binding to parts of the cell other than the plasma membrane. The degree of binding to nonparenchymal cells was less than 10% of the binding to hepatocytes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amar-Costesec A., Wibo M., Thinès-Sempoux D., Beaufay H., Berthet J. Analytical study of microsomes and isolated subcellular membranes from rat liver. IV. Biochemical, physical, and morphological modifications of microsomal components induced by digitonin, EDTA, and pyrophosphate. J Cell Biol. 1974 Sep;62(3):717–745. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.3.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashwell G., Morell A. G. The role of surface carbohydrates in the hepatic recognition and transport of circulating glycoproteins. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1974;41(0):99–128. doi: 10.1002/9780470122860.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry M. N., Friend D. S. High-yield preparation of isolated rat liver parenchymal cells: a biochemical and fine structural study. J Cell Biol. 1969 Dec;43(3):506–520. doi: 10.1083/jcb.43.3.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., Lloyd J. B. Pinocytosis in the rat visceral yolk sac. Effects of temperature, metabolic inhibitors and some other modifiers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 18;544(3):647–655. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90339-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frantz W. L., Turkington R. W. Formation of biologically active 125 I-prolactin by enzymatic radioiodination. Endocrinology. 1972 Dec;91(6):1545–1548. doi: 10.1210/endo-91-6-1545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giger O., Pariza M. W. Mechanism of action of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Effects on membrane permeability and amino acid transport in primary cultures of adult rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jan 25;595(2):264–276. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90089-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon L. M., Sauerheber R. D., Esgate J. A. Spin label studies on rat liver and heart plasma membranes: effects of temperature, calcium, and lanthanum on membrane fluidity. J Supramol Struct. 1978;9(3):299–326. doi: 10.1002/jss.400090303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granum P. E., Skjelkvåle R. Chemical modification and characterization of enterotoxin from clostridium perfringens type A. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1977 Feb;85B(1):89–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb01678.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HART H. E. DETERMINATION OF EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANTS AND MAXIMUM BINDING CAPACITIES IN COMPLEX IN VITRO SYSTEMS. I. THE MAMMILLARY SYSTEM. Bull Math Biophys. 1965 Mar;27:87–98. doi: 10.1007/BF02476471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaBadie J. H., Chapman K. P., Aronson N. N., Jr Glycoprotein catabolism in rat liver: Lysosomal digestion of iodinated asialo-fetuin. Biochem J. 1975 Nov;152(2):271–279. doi: 10.1042/bj1520271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda M., Sugimoto N. Calcium-independent and dependent steps in action of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin on HeLa and Vero cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Nov 28;91(2):629–636. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91568-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonel J. L., Chang L. W., Pounds J. G., Duncan C. L. The effects of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin on rat and rabbit ileum: an electron microscopic study. Lab Invest. 1978 Sep;39(3):210–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonel J. L., McClane B. A. Binding versus biological activity of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin in Vero cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Mar 30;87(2):497–504. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91823-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekada E., Uchida T., Okada Y. Modification of the cell surface with neuraminidase increases the sensitivities of cells to diphtheria toxin and Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Oct 1;123(1):137–146. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90430-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niilo L. Mechanism of Action of the Enteropathogenic Factor of Clostridium perfringens Type A. Infect Immun. 1971 Jan;3(1):100–106. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.1.100-106.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson M., Berg T. Uptake and degradation of formaldehyde-treated 125I-labelled human serum albumin in rat liver cells in vivo and in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 29;497(1):171–182. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90150-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Refsnes K., Pihl A. Mechanism of action of the toxic lectins abrin and ricin. Nature. 1974 Jun 14;249(458):627–631. doi: 10.1038/249627a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi G., Uemura T., Riemann H. P. Simplified method for purification of Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Nov;26(5):762–767. doi: 10.1128/am.26.5.762-767.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S., Pihl A. Kinetics of binding of the toxic lectins abrin and ricin to surface receptors of human cells. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 10;251(13):3977–3984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skjelkvåle R. Radioiodination of enterotoxin from Clostridium perfringens type A using chloramine T. J Appl Bacteriol. 1980 Apr;48(2):283–295. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1980.tb01228.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skjelkvåle R., Tolleshaug H., Jarmund T. Binding of enterotoxin from Clostridium perfringens type A to liver cells in vivo and in vitro. The enterotoxin causes membrane leakage. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1980 Apr;88(2):95–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb02612.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark R. L., Duncan C. L. Transient increase in capillary permeability induced by Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1972 Jan;5(1):147–150. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.1.147-150.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolleshaug H., Abdelnour M., Berg T. Binding of concanavalin A to isolated hepatocytes and its effect on uptake and degradation of asialo-fetuin by the cells. Biochem J. 1980 Sep 15;190(3):697–703. doi: 10.1042/bj1900697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolleshaug H., Berg T., Frölich W., Norum K. R. Intracellular localization and degradation of asialofetuin in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jun 1;585(1):71–84. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90326-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolleshaug H., Berg T., Holte K. Kinetics of internalization and degradation of asialo-glycoproteins in isolated rat hepatocytes. Eur J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;23(1):104–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolleshaug H., Berg T., Nilsson M., Norum K. R. Uptake and degradation of 125I-labelled asialo-fetuin by isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 25;499(1):73–84. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90230-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Aaser A. A., Reid E. Rat liver 5'-nucleotidase. Histochem J. 1969 Aug;1(5):417–437. doi: 10.1007/BF01086983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


