Abstract
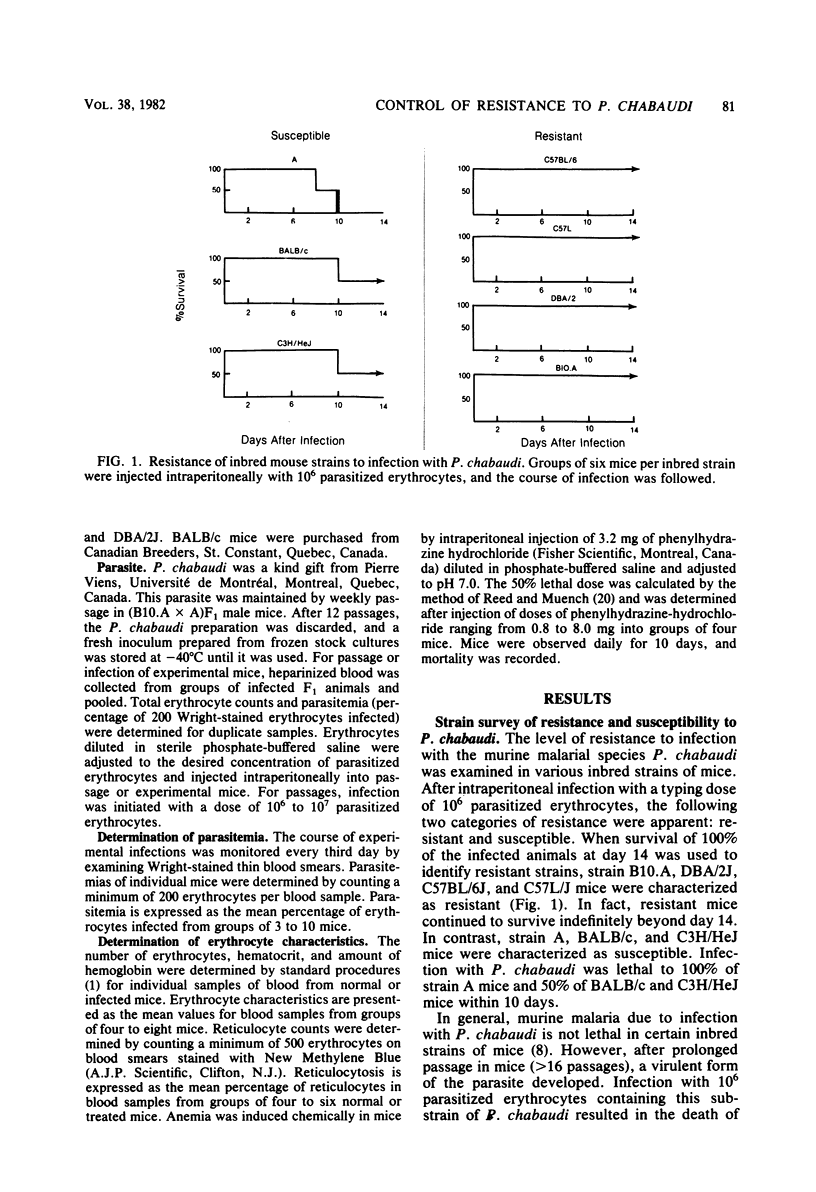
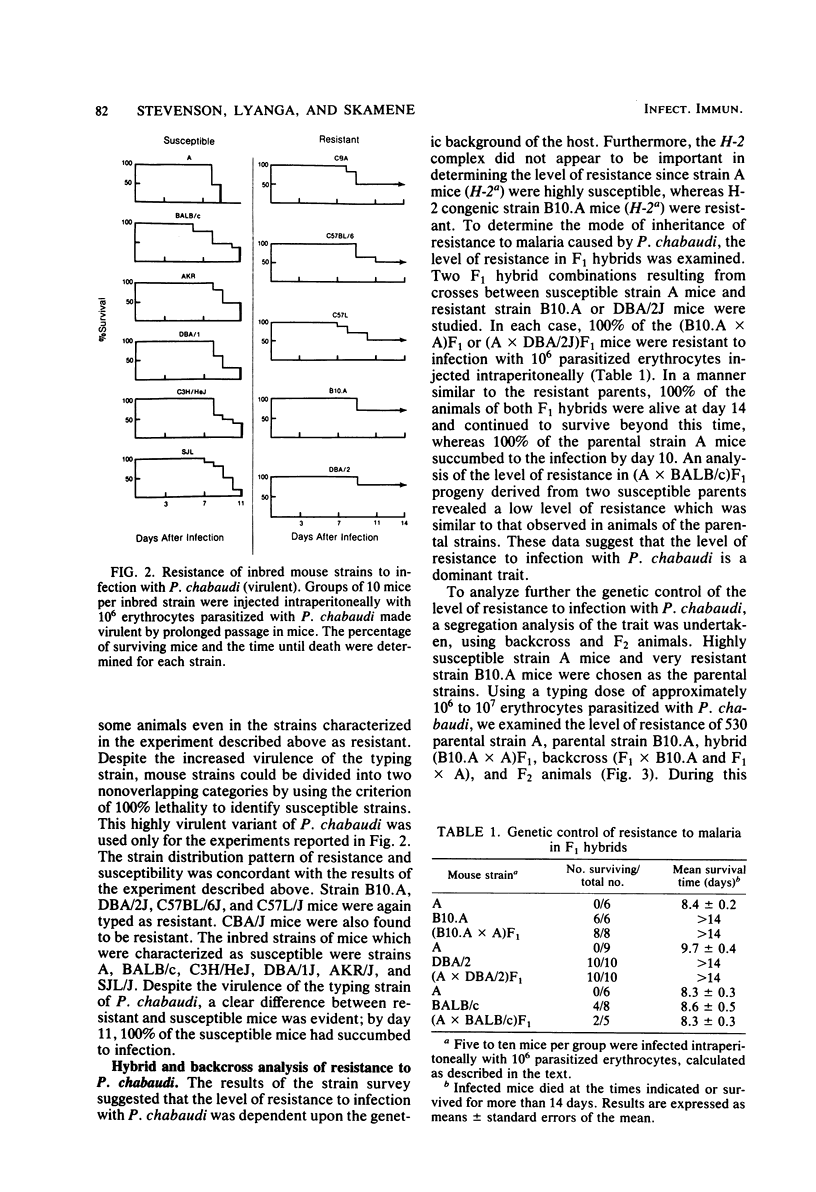
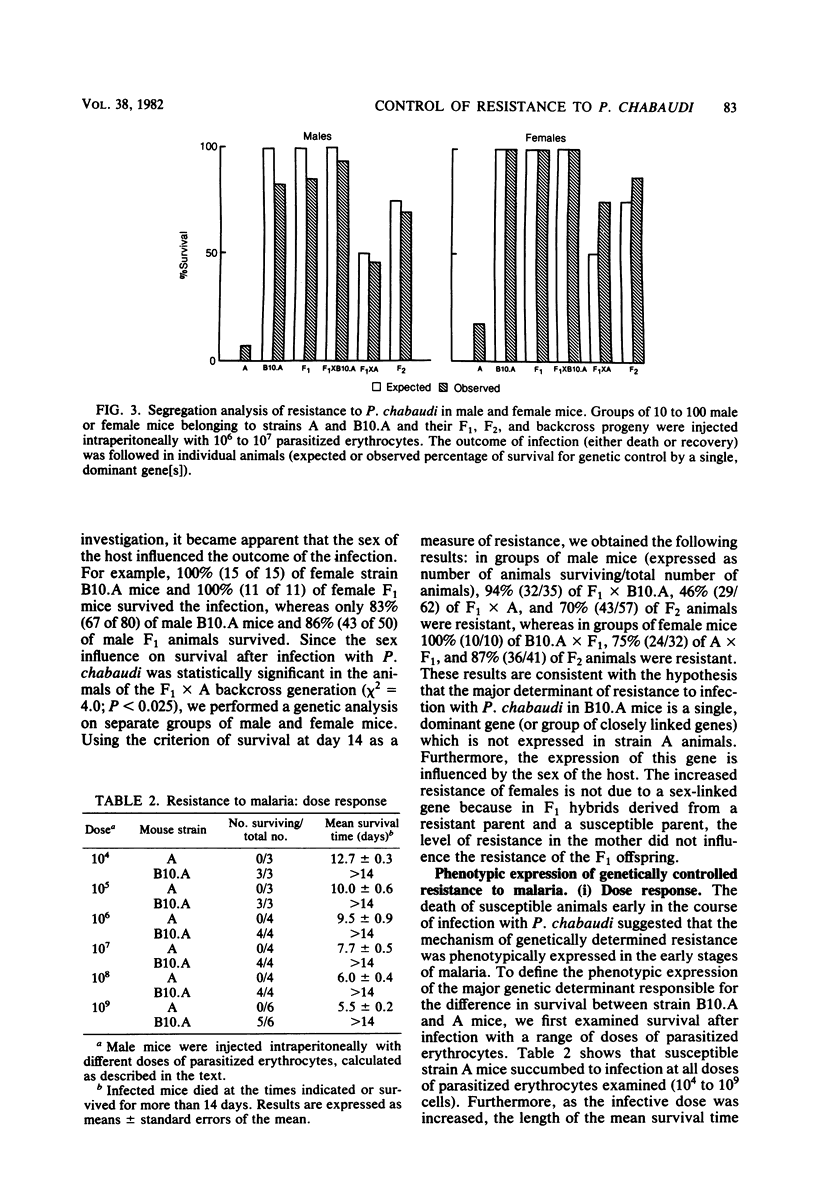
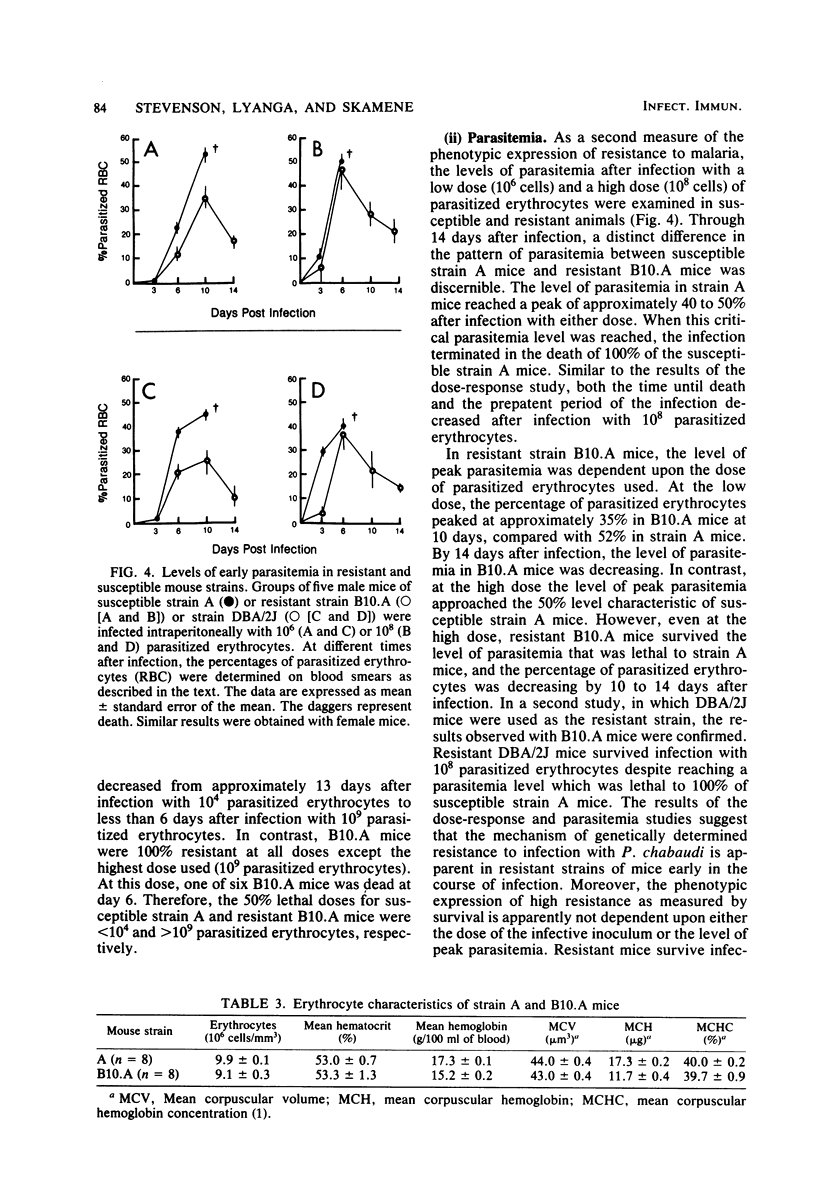
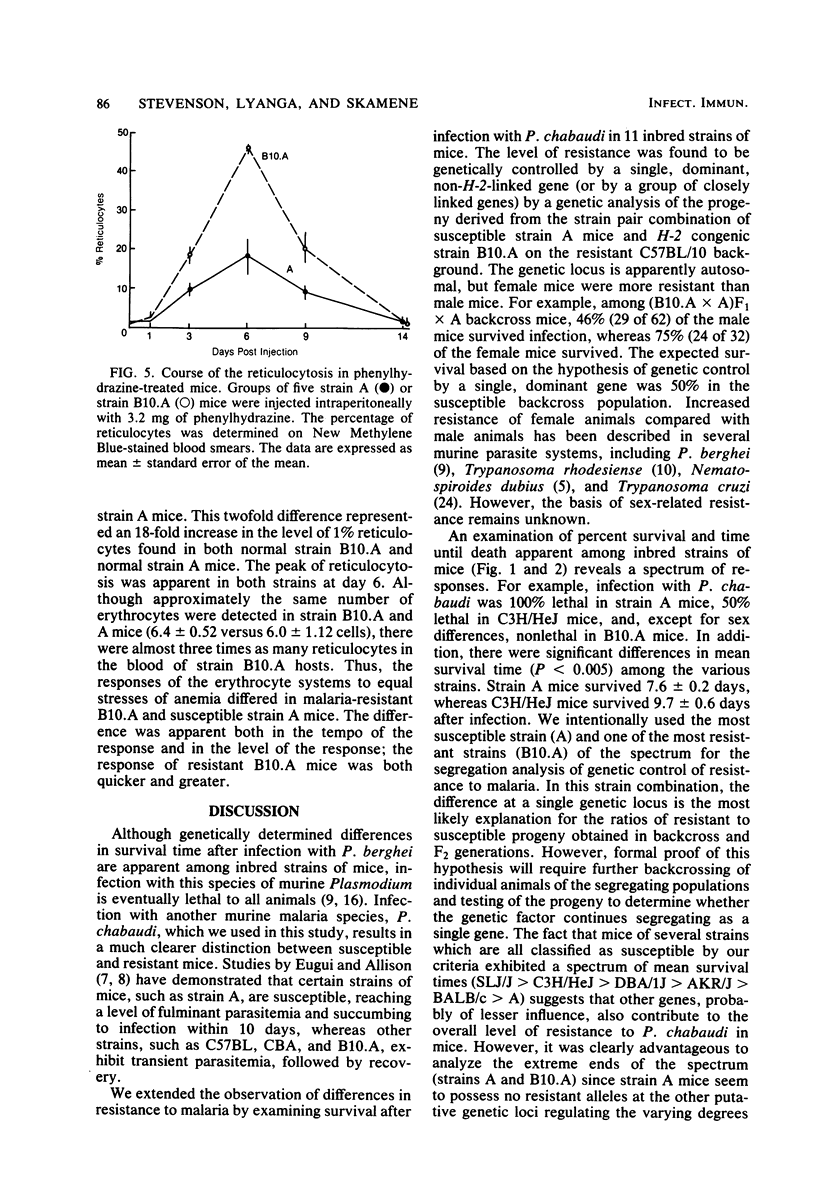
Strain variation in the level of resistance to malaria was investigated in inbred strains of mice after infection with Plasmodium chabaudi. When infected intraperitoneally with 10(6) P. chabaudi-parasitized erythrocytes, mice of 11 inbred strains could be separated into two groups by using survival time as the criterion; C57BL/6J, C57L/J, DBA/2J, CBA/J, and B10.A/SgSn mice were found to be resistant to P. chabaudi, whereas A/J, DBA/1J, BALB/c, C3H/HeJ, AKR/J, and SJL/J mice were susceptible. An examination of F1 hybrids revealed that resistance was dominant over susceptibility. A segregation analysis of backcross and F2 progeny derived from susceptible A/J and resistant B10.A/SgSn parental mice suggested that host resistance in this strain combination was genetically controlled by a single, dominant, non-H-2-linked gene. Inheritance of resistance was autosomal, but expression of the trait was influenced by the sex of the host, female mice being more resistant than male mice. Phenotypic expression of the resistance gene was apparent within 6 days of infection as a significant difference between resistant and susceptible mice in the level of parasitemia. A preliminary analysis of the mechanism of resistance showed that compared with susceptible A/J mice, resistant B10.A/SgSn hosts had an augmented erythropoietic response during the course of malaria, as well as phenylhydrazine-induced anemia. These results suggest that the ability to replace destroyed erythrocytes quickly and efficiently may determine host survival after infection with P. chabaudi.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clark I. A., Allison A. C. Babesia microti and Plasmodium berghei yoelii infections in nude mice. Nature. 1974 Nov 22;252(5481):328–329. doi: 10.1038/252328a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox F. E. A comparative account of the effects of betamethasone on mice infected with Plasmodium vinckei chabaudi and Plasmodium berghei yoelii. Parasitology. 1974 Feb;68(1):19–26. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000045339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson C., Owen M. E. Effect of host sex on passive immunity in mice infected with Nematospiroides dubius. Int J Parasitol. 1978 Oct;8(5):359–364. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(78)90033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eling W., van Zon A., Jerusalem C. The course of a Plasmodium berghei infection in six different mouse strains. Z Parasitenkd. 1977 Dec 13;54(1):29–45. doi: 10.1007/BF00380634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eugui E. M., Allison A. C. Differences in susceptibility of various mouse strains to haemoprotozoan infections: possible correlation with natural killer activity. Parasite Immunol. 1980 Winter;2(4):277–292. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1980.tb00059.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eugui E. M., Allison A. C. Malaria infections in different strains of mice and their correlation with natural killer activity. Bull World Health Organ. 1979;57 (Suppl 1):231–238. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENBERG J., NADEL E. M., COATNEY G. R. [The influence of strain, sex and age of mice on infection with Plasmodium berghei]. J Infect Dis. 1953 Jul-Aug;93(1):96–100. doi: 10.1093/infdis/93.1.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grun J. L., Weidanz W. P. Immunity to Plasmodium chabaudi adami in the B-cell-deficient mouse. Nature. 1981 Mar 12;290(5802):143–145. doi: 10.1038/290143a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayawardena A. N., Janeway C. A., Jr, Kemp J. D. Experimental malaria in the CBA/N mouse. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2532–2539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling R., Klein E., Wigzell H. "Natural" killer cells in the mouse. I. Cytotoxic cells with specificity for mouse Moloney leukemia cells. Specificity and distribution according to genotype. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Feb;5(2):112–117. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadel E M, Greenberg J, Jay G E, Coatney G R. Backcross Studies on the Genetics of Resistance to Malaria in Mice. Genetics. 1955 Sep;40(5):620–626. doi: 10.1093/genetics/40.5.620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojo-Amaize E. A., Salimonu L. S., Williams A. I., Akinwolere O. A., Shabo R., Alm G. V., Wigzell H. Positive correlation between degree of parasitemia, interferon titers, and natural killer cell activity in Plasmodium falciparum-infected children. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2296–2300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott K. J. Influence of reticulocytosis on the course of infection of Plasmodium chabaudi and P. berghei. J Protozool. 1968 May;15(2):365–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1968.tb02138.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rank R. G., Weidanz W. P., Bondi A. Nonsterilizing immunity in avian malaria: an antibody-independent phenomenon. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1976 Feb;151(2):257–259. doi: 10.3181/00379727-151-39186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts D. W., Weidanz W. P. T-cell immunity to malaria in the B-cell deficient mouse. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1979 Jan;28(1):1–3. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1979.28.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trischmann T. M., Bloom B. R. Genetics of murine resistance to Trypanosoma cruzi. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):546–551. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.546-551.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viens P., Chevalier J. L., Sonea S., Yoeli M. The effect of reticulocytosis on Plasmodium vinckei infection in white mice. Action of phenylhydrazine and of repeated bleedings. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Feb;17(2):257–261. doi: 10.1139/m71-043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinbaum F. I., Evans C. B., Tigelaar R. E. Immunity to Plasmodium Berghei yoelii in mice. I. The course of infection in T cell and B cell deficient mice. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 PT2):1999–2005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


