Abstract
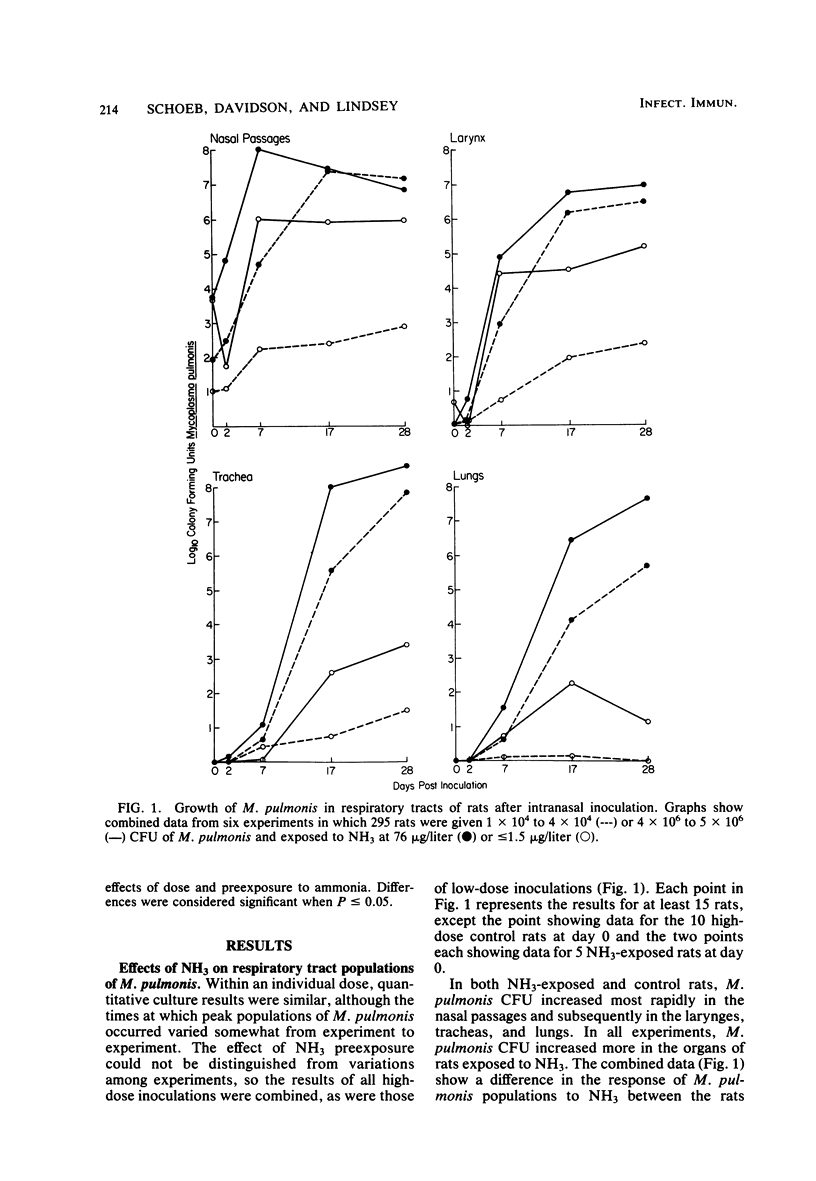
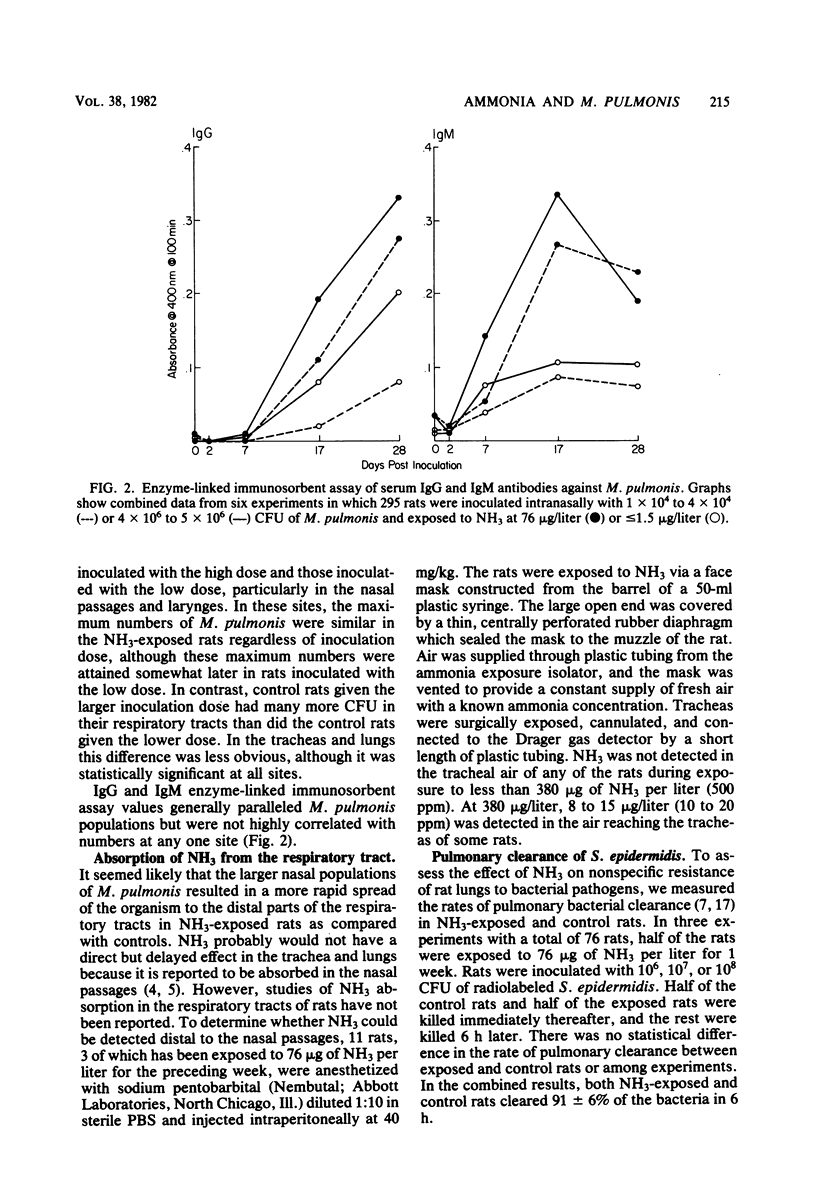
Ammonia (NH3) from soiled cage bedding is known to enhance the progression and severity of murine respiratory mycoplasmosis in rats. To test the hypothesis that NH3 directly or indirectly enhances the growth of Mycoplasma pulmonis in vivo, pathogen-free F344 rats were inoculated intranasally with 1 x 10(4) to 4 x 10(4) or 4 x 10(6) to 5 x 10(6) colony-forming units of M. pulmonis and exposed to less than or equal to 1.5 or 76 microgram of NH3 per liter (less than or equal to 2 or 100 ppm, respectively). Nasal passages, larynges, tracheas, and lungs from rats killed at intervals up to 28 days after inoculation were quantitatively cultured. Growth of M. pulmonis was much greater in NH3-exposed rats than in controls, particularly in those inoculated with the lower dose. Increases in M. pulmonis populations were more rapid in proximal airways than in distal airways. Serum immunoglobulin G and M antibody responses to M. pulmonis as measured by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay were greater in NH3-exposed rats. In other experiments, the nasal passages absorbed virtually all NH3 when the rats were exposed to less than 380 micrograms of NH3 per liter (500 ppm), indicating that NH3 induced increases in the numbers of organisms in the distal respiratory tract, probably by a secondary, rather than a direct, effect. Also, NH3 exposure did not inhibit pulmonary antibacterial activity as measured by clearance of radiolabeled Staphylococcus epidermidis. The growth of M. pulmonis in vitro was inhibited by 1 mM NH4+ added to the medium as NH4OH but not by NH4+ concentrations of 0.5, 0.1, or 0.01 mM, suggesting that NH3 increases growth indirectly through effects on the host.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Broderson J. R., Lindsey J. R., Crawford J. E. The role of environmental ammonia in respiratory mycoplasmosis of rats. Am J Pathol. 1976 Oct;85(1):115–130. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALHAMN T., SJOEHOLM J. STUDIES ON SO2, NO2 AND NH3: EFFECT ON CILIARY ACTIVITY IN RABBIT TRACHEA OF SINGLE IN VITRO EXPOSURE AND RESORPTION IN RABBIT NASAL CAVITY. Acta Physiol Scand. 1963 Aug;58:287–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1963.tb02651.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN G. M., KASS E. H. THE ROLE OF THE ALVEOLAR MACROPHAGE IN THE CLEARANCE OF BACTERIA FROM THE LUNG. J Exp Med. 1964 Jan 1;119:167–176. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz S. A., Cassell G. H. Detection of antibodies to Mycoplasma pulmonis by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):161–170. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.161-170.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jersey G. C., Whitehair C. K., Carter G. R. Mycoplasma pulmonis as the primary cause of chronic respiratory disease in rats. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1973 Sep 15;163(6):599–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn D. F., Kirk B. E. Pathogenicity of Mycoplasma pulmonis in laboratory rats. Lab Anim Care. 1969 Jun;19(3):321–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsey J. R., Baker H. J., Overcash R. G., Cassell G. H., Hunt C. E. Murine chronic respiratory disease. Significance as a research complication and experimental production with Mycoplasma pulmonis. Am J Pathol. 1971 Sep;64(3):675–708. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mårdh P. A., Taylor-Robinson D. New approaches to the isolation of mycoplasmas. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1973;158(4):259–266. doi: 10.1007/BF02121412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. The mycoplasmas. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Jun;42(2):414–470. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.2.414-470.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruppert D., Jakab G. J., Sylwester D. L., Green G. M. Sources of variance in the measurement of intrapulmonary killing of bacteria. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Mar;87(3):544–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauraso N. M. Effect of diethylaminoethyl dextran on the growth of Mycoplasma in agar. J Bacteriol. 1967 May;93(5):1559–1564. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.5.1559-1564.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tully J. G., Rask-Nielsen R. Mycoplasma in leukemic and nonleukemic mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):345–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27674.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittlestone P., Lemcke R. M., Olds R. J. Respiratory disease in a colony of rats. II. Isolation of Mycoplasma pulmonis from the natural disease, and the experimental disease induced with a cloned culture of this organism. J Hyg (Lond) 1972 Sep;70(3):387–407. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400062975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


