Abstract
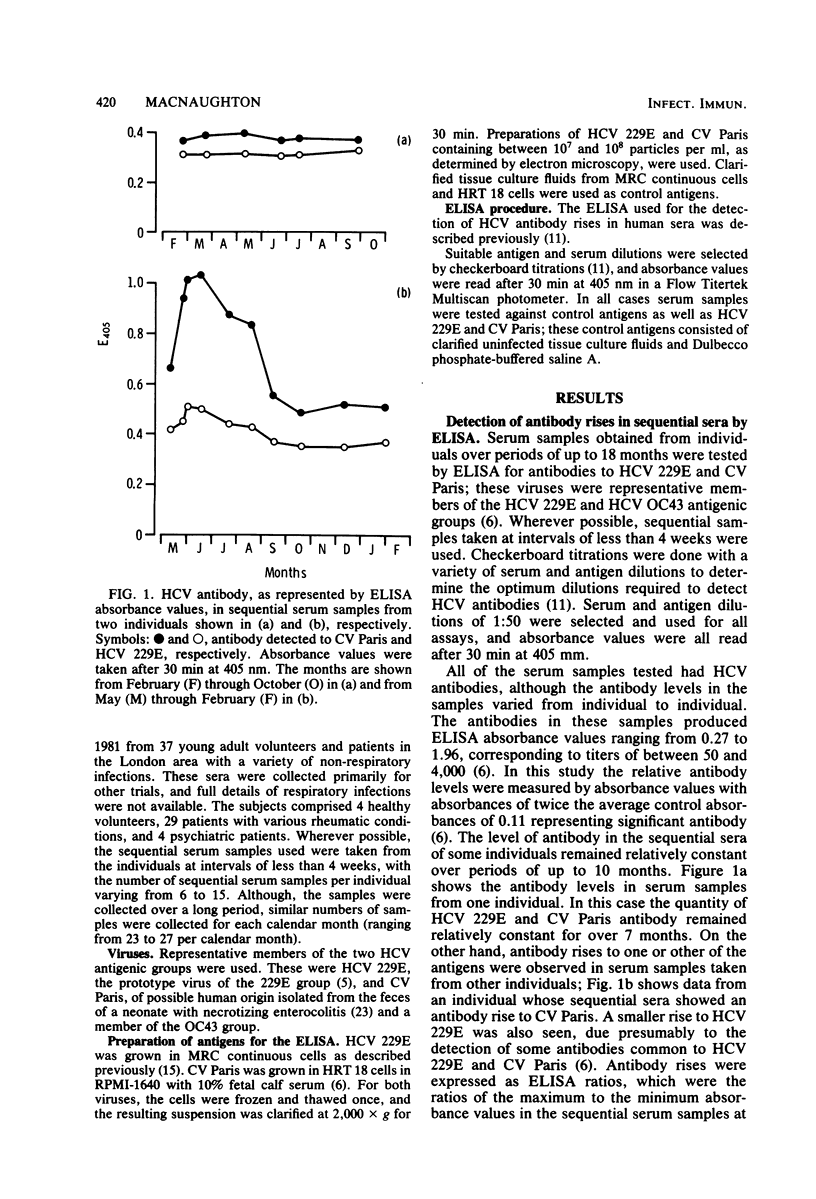
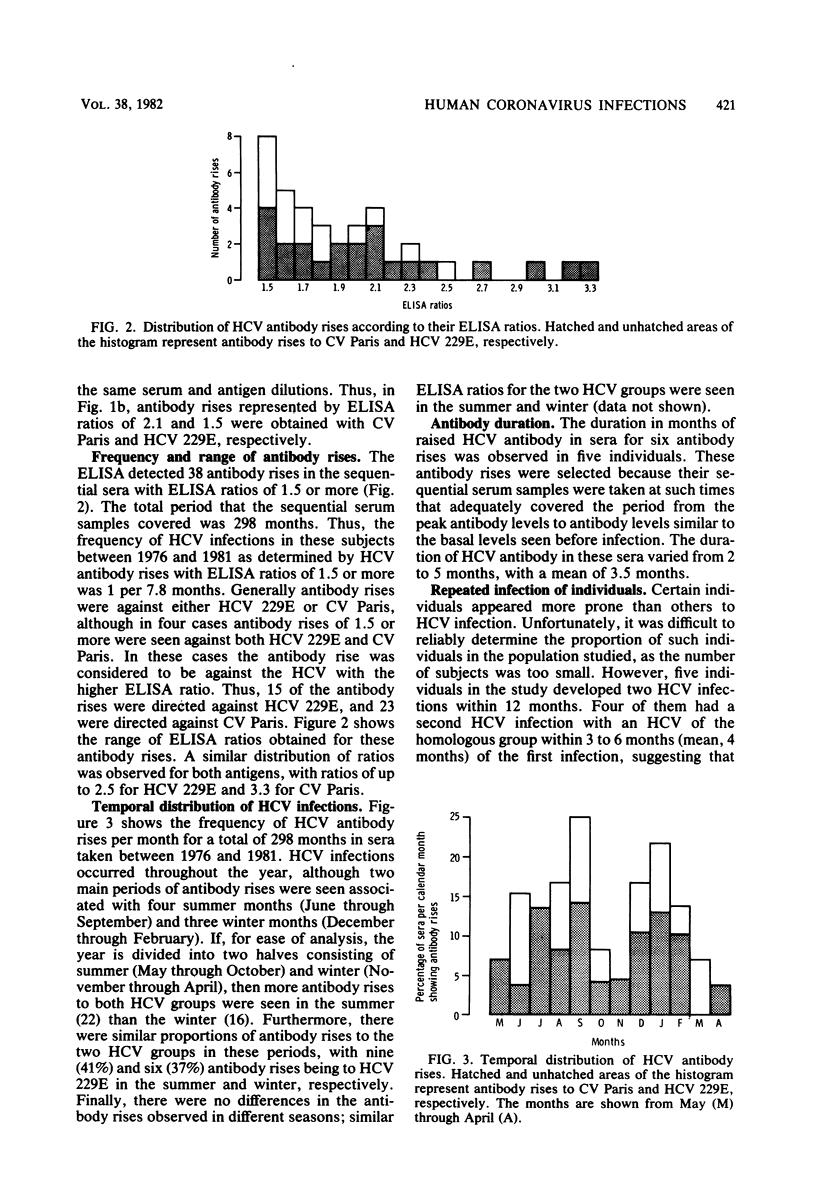
The occurrence of human coronavirus (HCV) infections was analyzed by using sequential sera taken between 1976 and 1981 from adults working in the London area. Antibody rises to HCV 229E and HCV OC43 group viruses were measured in serum samples from these subjects by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. HCV infections were found throughout the year, although most occurred during two periods, from June through September and from December through February. There were no marked seasonal differences in either the range of antibody rises obtained or in the HCV groups to which these antibody rises were directed. However, there were more HCV antibody rises during the summer than in the winter. The antibody duration varied considerably, but had a mean of 3.5 months. Finally, the frequency of HCV infection per person was calculated to be 1 per 7.8 months.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradburne A. F., Somerset B. A. Coronative antibody tires in sera of healthy adults and experimentally infected volunteers. J Hyg (Lond) 1972 Jun;70(2):235–244. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400022294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavallaro J. J., Monto A. S. Community-wide outbreak of infection with a 229E-like coronavirus in Tecumseh, Michigan. J Infect Dis. 1970 Oct;122(4):272–279. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.4.272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamre D., Beem M. Virologic studies of acute respiratory disease in young adults. V. Coronavirus 229E infections during six years of surveillance. Am J Epidemiol. 1972 Aug;96(2):94–106. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamre D., Procknow J. J. A new virus isolated from the human respiratory tract. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Jan;121(1):190–193. doi: 10.3181/00379727-121-30734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasony H. J., Macnaughton M. R. Prevalence of human coronavirus antibody in the population of southern Iraq. J Med Virol. 1982;9(3):209–216. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890090308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendley J. O., Fishburne H. B., Gwaltney J. M., Jr Coronavirus infections in working adults. Eight-year study with 229 E and OC 43. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1972 May;105(5):805–811. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1972.105.5.805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovi T., Kainulainen H., Ziola B., Salmi A. OC43 strain-related coronavirus antibodies in different age groups. J Med Virol. 1979;3(4):313–320. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890030410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., James H. D., Jr, Kelly S. J., Dees J. H., Turner H. C., McIntosh K., Kim H. W., Parrott R. H., Vincent M. M., Chanock R. M. Isolation from man of "avian infectious bronchitis virus-like" viruses (coronaviruses) similar to 229E virus, with some epidemiological observations. J Infect Dis. 1969 Mar;119(3):282–290. doi: 10.1093/infdis/119.3.282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye H. S., Marsh H. B., Dowdle W. R. Seroepidemiologic survey of coronavirus (strain OC 43) related infections in a children's population. Am J Epidemiol. 1971 Jul;94(1):43–49. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraaijeveld C. A., Reed S. E., Macnaughton M. R. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of antibody in volunteers experimentally infected with human coronavirus strain 229 E. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Oct;12(4):493–497. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.4.493-497.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson H. E., Reed S. E., Tyrrell D. A. Isolation of rhinoviruses and coronaviruses from 38 colds in adults. J Med Virol. 1980;5(3):221–229. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890050306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnaughton M. R., Davies H. A. Human enteric coronaviruses. Brief review. Arch Virol. 1981;70(4):301–313. doi: 10.1007/BF01320245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnaughton M. R., Hasony H. J., Madge M. H., Reed S. E. Antibody to virus components in volunteers experimentally infected with human coronavirus 229E group viruses. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):845–849. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.845-849.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnaughton M. R., Madge M. H., Reed S. E. Two antigenic groups of human coronaviruses detected by using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):734–737. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.734-737.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnaughton M. R., Madge M. H. The genome of human coronavirus strain 229E. J Gen Virol. 1978 Jun;39(3):497–504. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-39-3-497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh K., Becker W. B., Chanock R. M. Growth in suckling-mouse brain of "IBV-like" viruses from patients with upper respiratory tract disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Dec;58(6):2268–2273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.6.2268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh K., Kapikian A. Z., Hardison K. A., Hartley J. W., Chanock R. M. Antigenic relationships among the coronaviruses of man and between human and animal coronaviruses. J Immunol. 1969 May;102(5):1109–1118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh K., Kapikian A. Z., Turner H. C., Hartley J. W., Parrott R. H., Chanock R. M. Seroepidemiologic studies of coronavirus infection in adults and children. Am J Epidemiol. 1970 Jun;91(6):585–592. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monto A. S., Lim S. K. The Tecumseh study of respiratory illness. VI. Frequency of and relationship between outbreaks of coronavirus infection. J Infect Dis. 1974 Mar;129(3):271–276. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.3.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monto A. S. Medical reviews. Coronaviruses. Yale J Biol Med. 1974 Dec;47(4):234–251. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sureau C., Amiel-Tison C., Moscovici O., Lebon P., Laporte J., Chany C. Une épidémie d'entérocolites ulcéronécrosantes en maternité. Arguments en faveur de son origine virale. Bull Acad Natl Med. 1980 Mar;164(3):286–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


