Abstract
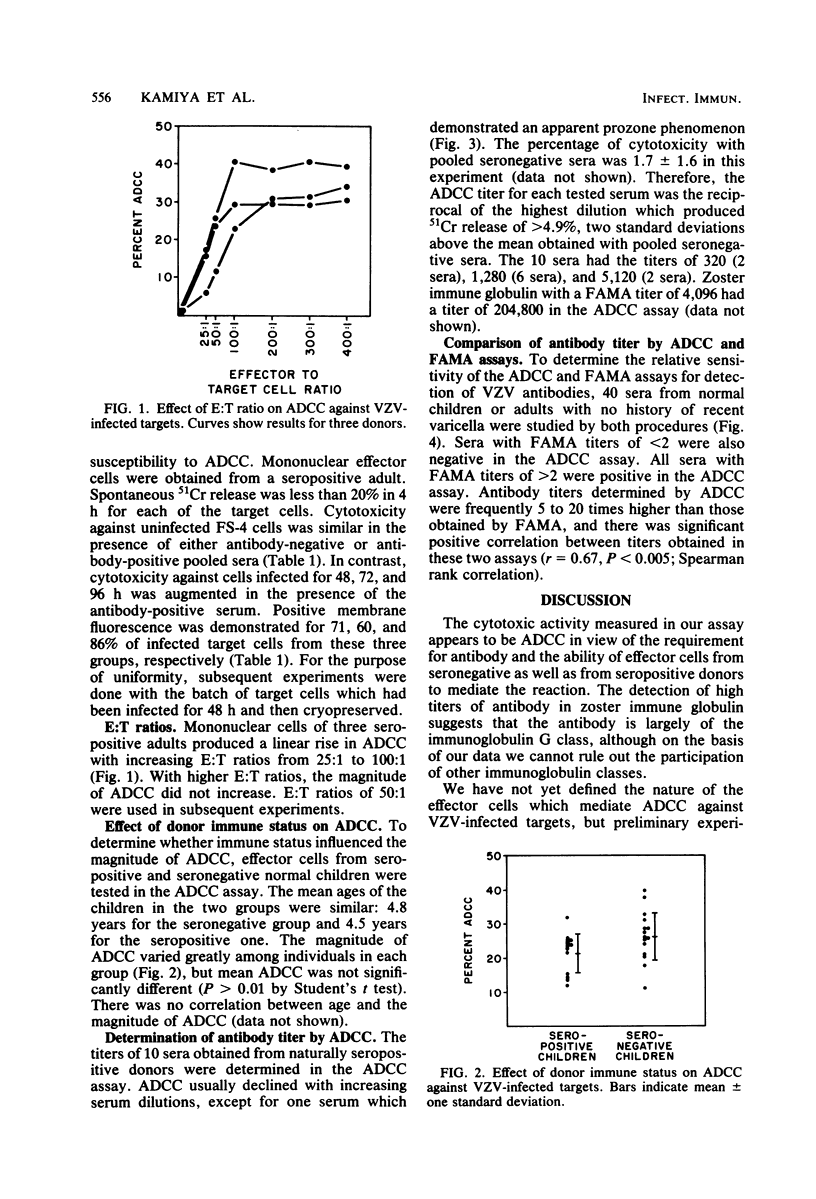
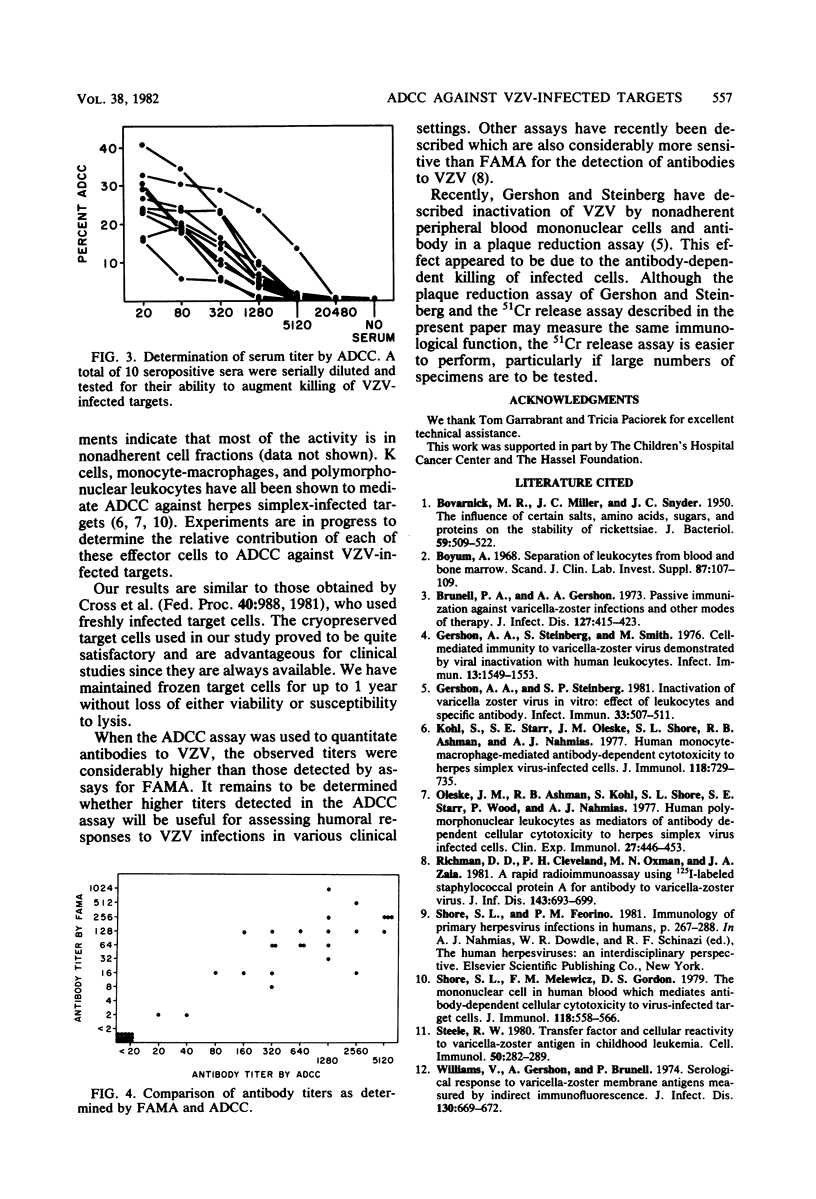
Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) against cryopreserved varicella-zoster virus-infected human foreskin fibroblasts was detected in a 51Cr release assay. Target cells, samples of seropositive or seronegative sera, and mononuclear cells obtained by Ficoll-Hypaque centrifugation of human peripheral blood were added to microtiter plate wells and allowed to incubate at 37 degrees C for 4 h. Fibroblasts infected for 48 to 96 h were susceptible to ADCC. Effector cells from seropositive and seronegative normal children were equally active in the assay. Antibody titers were determined by testing serial dilutions of sera in the ADCC assay. Zoster immune globulin had a titer of 204,800. Sera from 40 naturally seropositive individuals were compared by assays for ADCC and fluorescent antibody to membrane antigen. All sera that were negative by fluorescent antibody to membrane antigen (less than 2) were also negative by ADCC (less than 20). All sera that were positive by fluorescent antibody to membrane antigen were also positive by ADCC, but titers of individual sera were frequently 5 to 20 times higher in the ADCC assay.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOVARNICK M. R., MILLER J. C., SNYDER J. C. The influence of certain salts, amino acids, sugars, and proteins on the stability of rickettsiae. J Bacteriol. 1950 Apr;59(4):509–522. doi: 10.1128/jb.59.4.509-522.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunell P. A., Gershon A. A. Passive immunization against varicella-zoster infections and other modes of therapy. J Infect Dis. 1973 Apr;127(4):415–423. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.4.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon A. A., Steinberg S. P. Inactivation of varicella zoster virus in vitro: effect of leukocytes and specific antibody. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):507–511. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.507-511.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon A. A., Steinberg S., Smith M. Cell-mediated immunity to varicella-zoster virus demonstrated by viral inactivation with human leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1976 Jun;13(6):1549–1553. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.6.1549-1553.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl S., Starr S. E., oleske J. M., Shore S. L., Ashman R. B., Nahmias A. J. Human monocyte-macrophage-mediated antibody-dependent cytotoxicity to herpes simplex virus-infected cells. J Immunol. 1977 Mar;118(3):729–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oleske J. M., Ashman R. B., Kohl S., Shore S. L., Starr S. E., Wood P., Nahmias A. J. Human polymorphonuclear leucocytes as mediators of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity to herpes simplex virus-infected cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Mar;27(3):446–453. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. D., Cleveland P. H., Oxman M. N., Zaia J. A. A rapid radioimmunoassay using 125I-labeled staphylococcal protein A for antibody to varicella-zoster virus. J Infect Dis. 1981 May;143(5):693–699. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.5.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore S. L., Melewicz F. M., Gordon D. S. The mononuclear cell in human blood which mediates antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity to virus-infected target cells. I. Identification of the population of effector cells. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):558–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele R. W. Transfer factor and cellular reactivity to varicella-zoster antigen in childhood leukemia. Cell Immunol. 1980 Mar 15;50(2):282–289. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90283-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams V., Gershon A., Brunell P. A. Serologic response to varicella-zoster membrane antigens measured by direct immunofluorescence. J Infect Dis. 1974 Dec;130(6):669–672. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.6.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


