Abstract
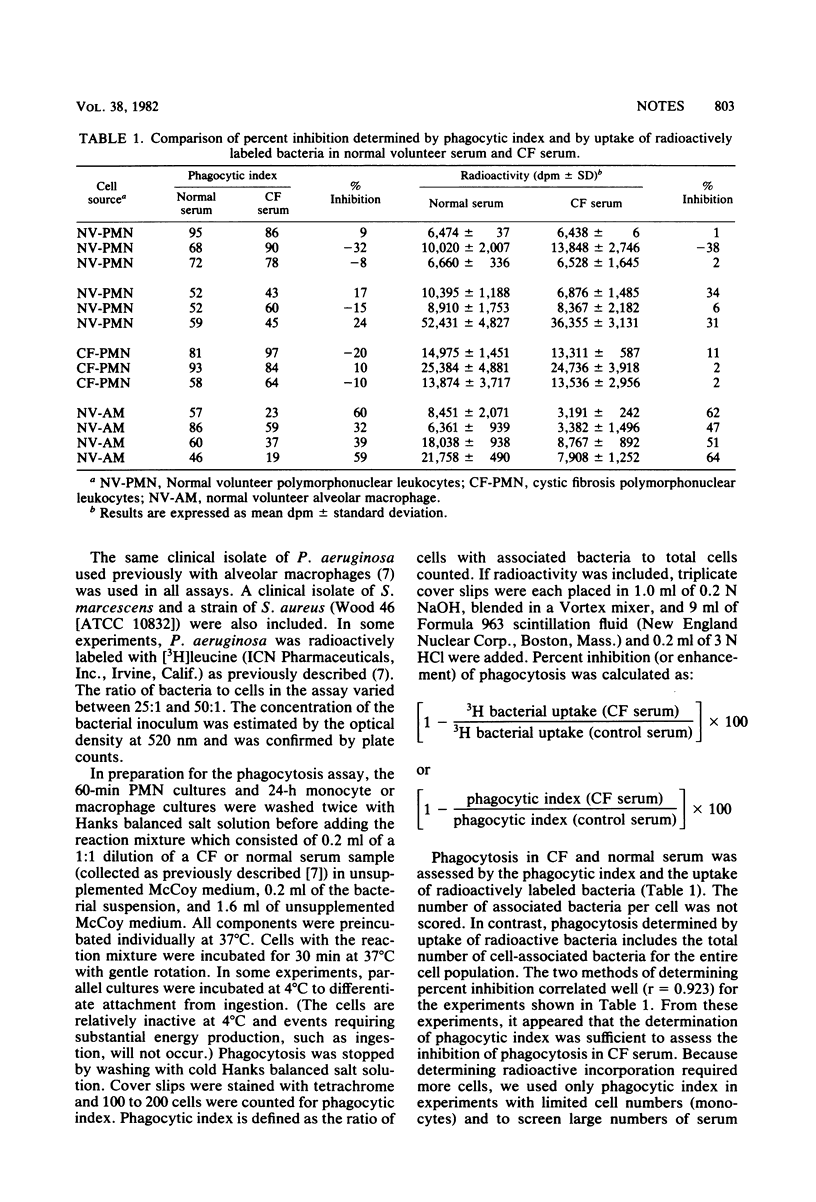
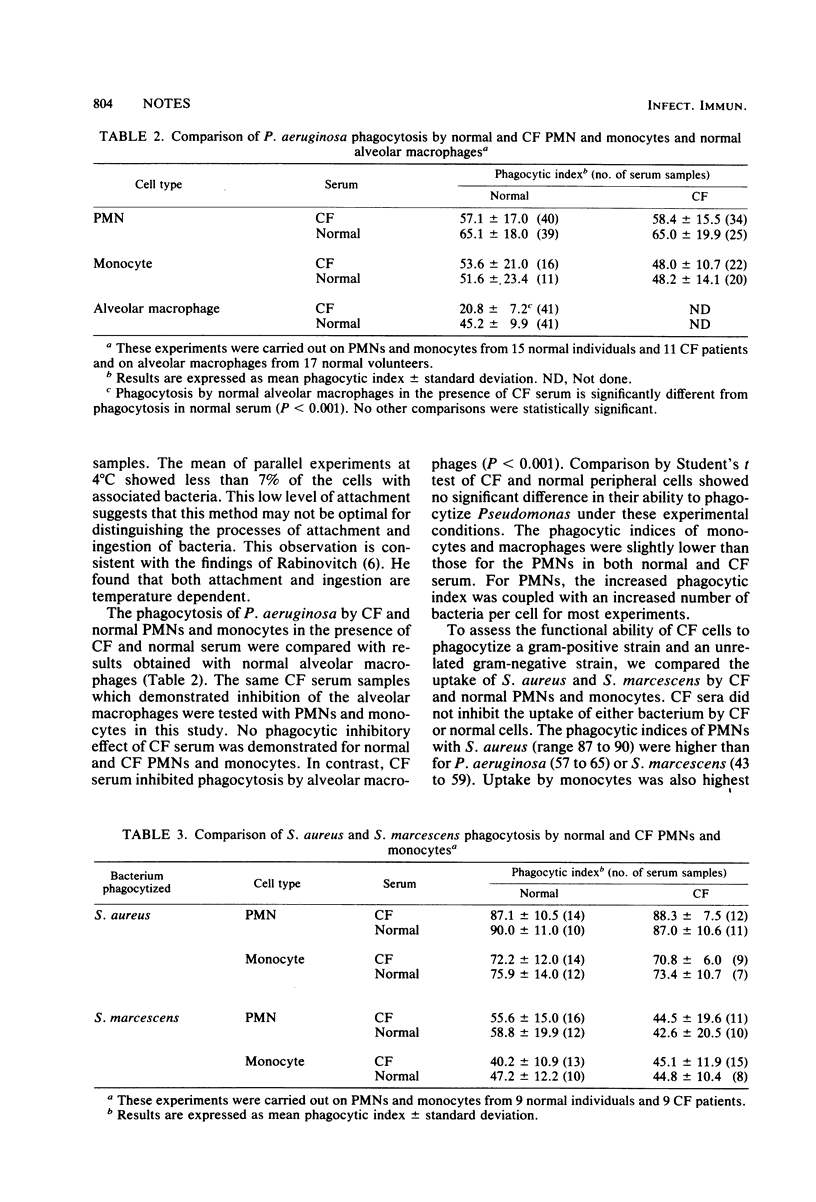
It has been shown previously that serum from chronically infected patients with cystic fibrosis inhibits the phagocytosis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by both normal and cystic fibrosis alveolar macrophages. In the present study, the ability of peripheral monocytes and polymorphonuclear leukocytes from normal volunteers and cystic fibrosis patients to phagocytize P. aeruginosa was shown not to be inhibited in the presence of serum from cystic fibrosis patients.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biggar W. D., Holmes B., Good R. A. Opsonic defect in patients with cystic fibrosis of the pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1716–1719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fick R. B., Jr, Naegel G. P., Matthay R. A., Reynolds H. Y. Cystic fibrosis pseudomonas opsonins. Inhibitory nature in an in vitro phagocytic assay. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):899–914. doi: 10.1172/JCI110345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoidal J. R., Schmeling D., Peterson P. K. Phagocytosis, bacterial killing, and metabolism by purified human lung phagocytes. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jul;144(1):61–71. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morahan P. S. Macrophage nomenclature: where are we going? J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1980 Feb;27(2):223–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch M. The dissociation of the attachment and ingestion phases of phagocytosis by macrophages. Exp Cell Res. 1967 Apr;46(1):19–28. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(67)90405-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomassen M. J., Boxerbaum B., Demko C. A., Kuchenbrod P. J., Dearborn D. G., Wood R. E. Inhibitory effect of cystic fibrosis serum on pseudomonas phagocytosis by rabbit and human alveolar macrophages. Pediatr Res. 1979 Sep;13(9):1085–1088. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197909000-00030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomassen M. J., Demko C. A., Boxerbaum B., Stern R. C., Kuchenbrod P. J. Multiple of isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa with differing antimicrobial susceptibility patterns from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Infect Dis. 1979 Dec;140(6):873–880. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.6.873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomassen M. J., Demko C. A., Wood R. E., Tandler B., Dearborn D. G., Boxerbaum B., Kuchenbrod P. J. Ultrastructure and function of alveolar macrophages from cystic fibrosis patients. Pediatr Res. 1980 May;14(5):715–721. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198005000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. E. Pseudomonas: the compromised host. Hosp Pract. 1976 Aug;11(8):91–100. doi: 10.1080/21548331.1976.11706983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


