Abstract
Isolates of Staphylococcus aureus from patients with toxic shock syndrome (TSS) were compared with non-TSS strains of S. aureus with respect to their virulence in rabbits. When the organisms were injected into subcutaneous chambers (perforated polyethylene golf balls) to assess virulence, a rapid mortality was observed with TSS but not with non-TSS strains. Of 16 TSS strains, 11 caused lethal infections in 33 rabbits tested, and none of the 5 control strains caused mortality in 10 rabbits. This evidence of enhanced virulence associated with TSS strains did not appear to be associated with the size of the inoculum. In addition, strains which produced lethal infections appeared to do so despite a reduction in the size of the original inoculum during the first 24 h. All of the TSS strains and none of the non-TSS strains elaborated extracellular protein(s) with a neutral pI when grown in a dialyzed beef heart medium. No other physiological difference was noted between the TSS and non-TSS strains.
Full text
PDF

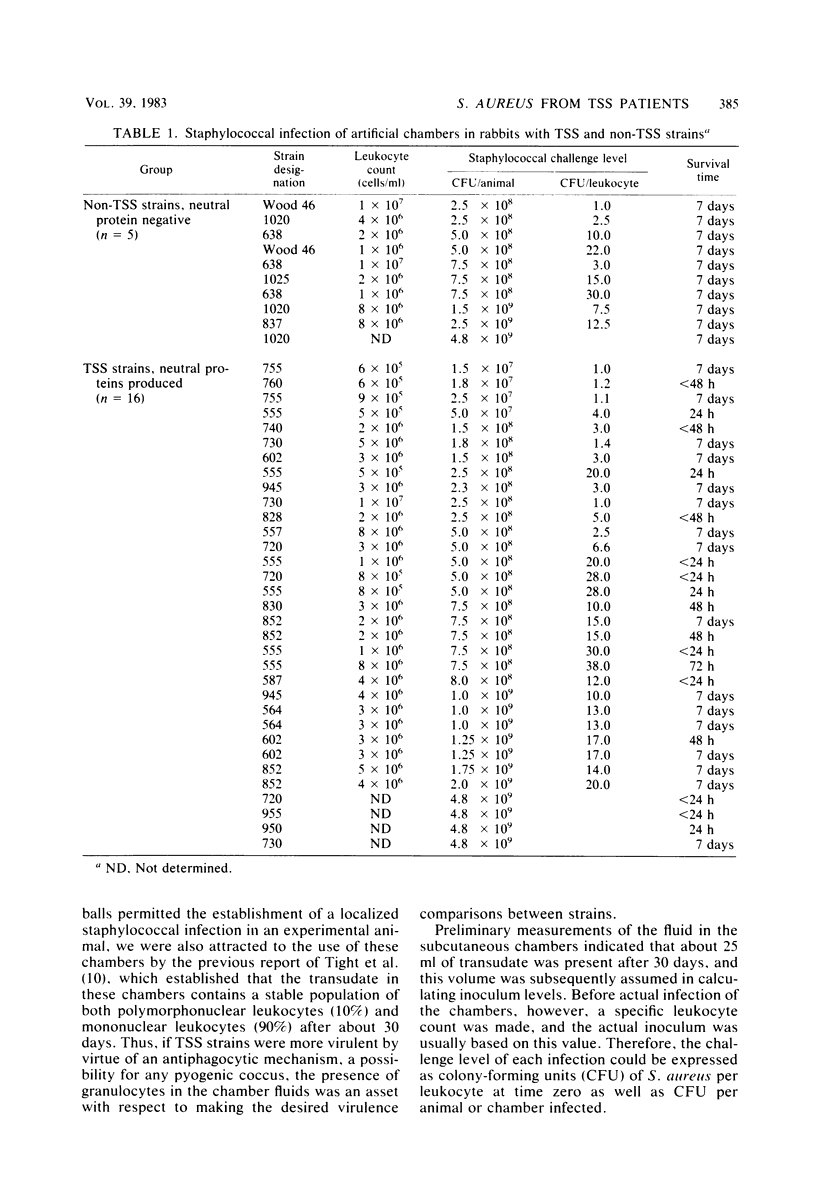
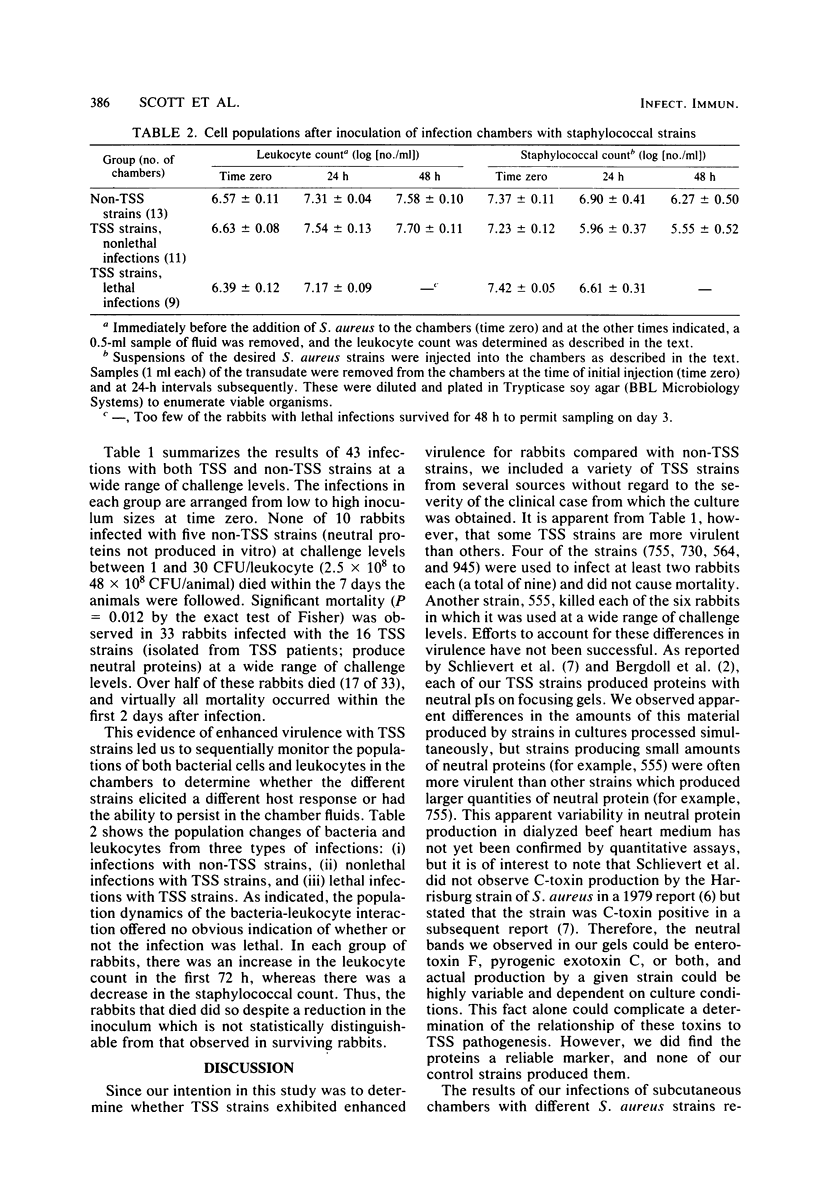

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbour A. G. Vaginal isolates of Staphylococcus aureus associated with toxic shock syndrome. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):442–449. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.442-449.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergdoll M. S., Crass B. A., Reiser R. F., Robbins R. N., Davis J. P. A new staphylococcal enterotoxin, enterotoxin F, associated with toxic-shock-syndrome Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Lancet. 1981 May 9;1(8228):1017–1021. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92186-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. P., Chesney P. J., Wand P. J., LaVenture M. Toxic-shock syndrome: epidemiologic features, recurrence, risk factors, and prevention. N Engl J Med. 1980 Dec 18;303(25):1429–1435. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198012183032501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. F., Goodpasture H. C., Peterie J. D., Voth D. W. Toxic shock syndrome in menstruating women. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Feb;94(2):156–163. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-2-156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M., Schoettle D. J., Watson D. W. Purification and physicochemical and biological characterization of a staphylococcal pyrogenic exotoxin. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):609–617. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.609-617.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M., Shands K. N., Dan B. B., Schmid G. P., Nishimura R. D. Identification and characterization of an exotoxin from Staphylococcus aureus associated with toxic-shock syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1981 Apr;143(4):509–516. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.4.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shands K. N., Schmid G. P., Dan B. B., Blum D., Guidotti R. J., Hargrett N. T., Anderson R. L., Hill D. L., Broome C. V., Band J. D. Toxic-shock syndrome in menstruating women: association with tampon use and Staphylococcus aureus and clinical features in 52 cases. N Engl J Med. 1980 Dec 18;303(25):1436–1442. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198012183032502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver M. A., Simon G. L. Toxic shock syndrome in a male postoperative patient. J Trauma. 1981 Aug;21(8):650–651. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198108000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tight R. R., Prior R. B., Perkins R. L., Rotilie C. A. Fluid and penicillin G dynamics in polyethylene chambers implanted subcutaneously in rabbits. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Oct;8(4):495–497. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.4.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J., Fishaut M., Kapral F., Welch T. Toxic-shock syndrome associated with phage-group-I Staphylococci. Lancet. 1978 Nov 25;2(8100):1116–1118. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92274-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tofte R. W., Williams D. N. Toxic shock syndrome: clinical and laboratory features in 15 patients. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Feb;94(2):149–156. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-2-149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON D. W. Host-parasite factors in group A streptococcal infections. Pyrogenic and other effects of immunologic distinct exotoxins related to scarlet fever toxins. J Exp Med. 1960 Feb 1;111:255–284. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.2.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



