Abstract
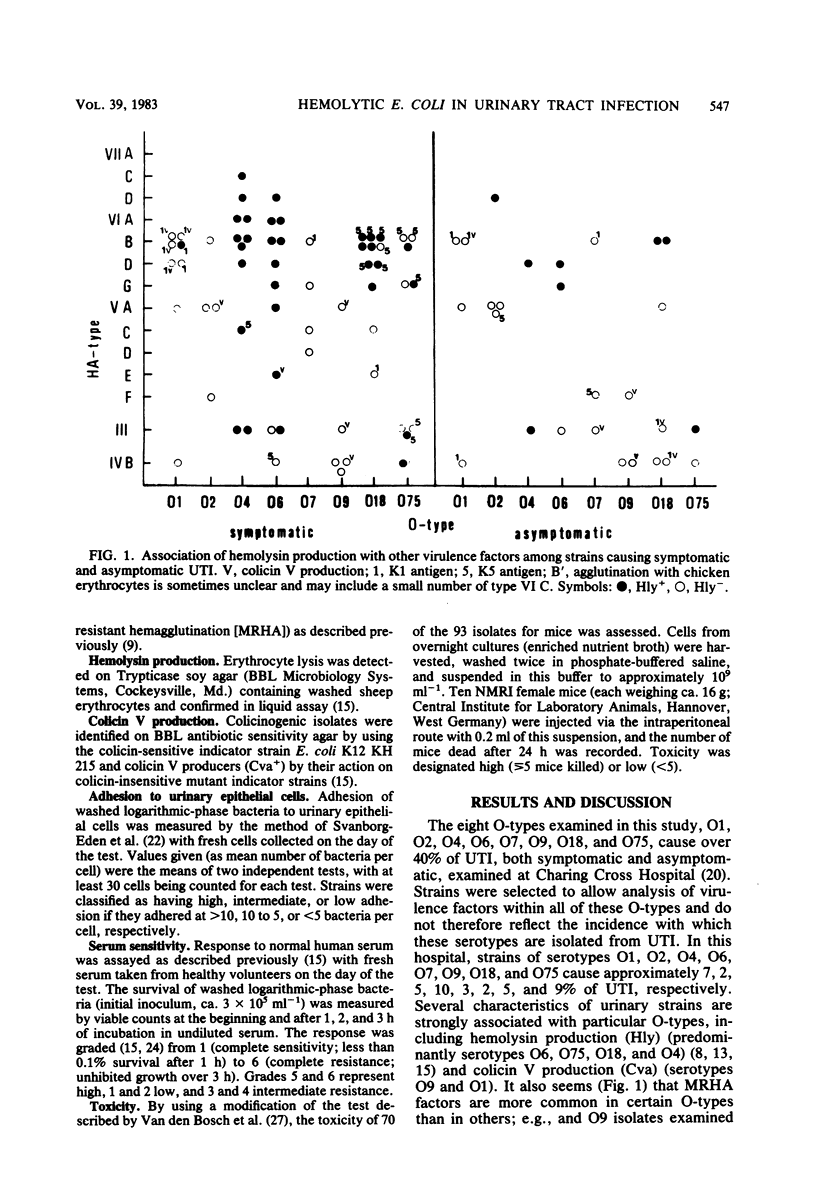
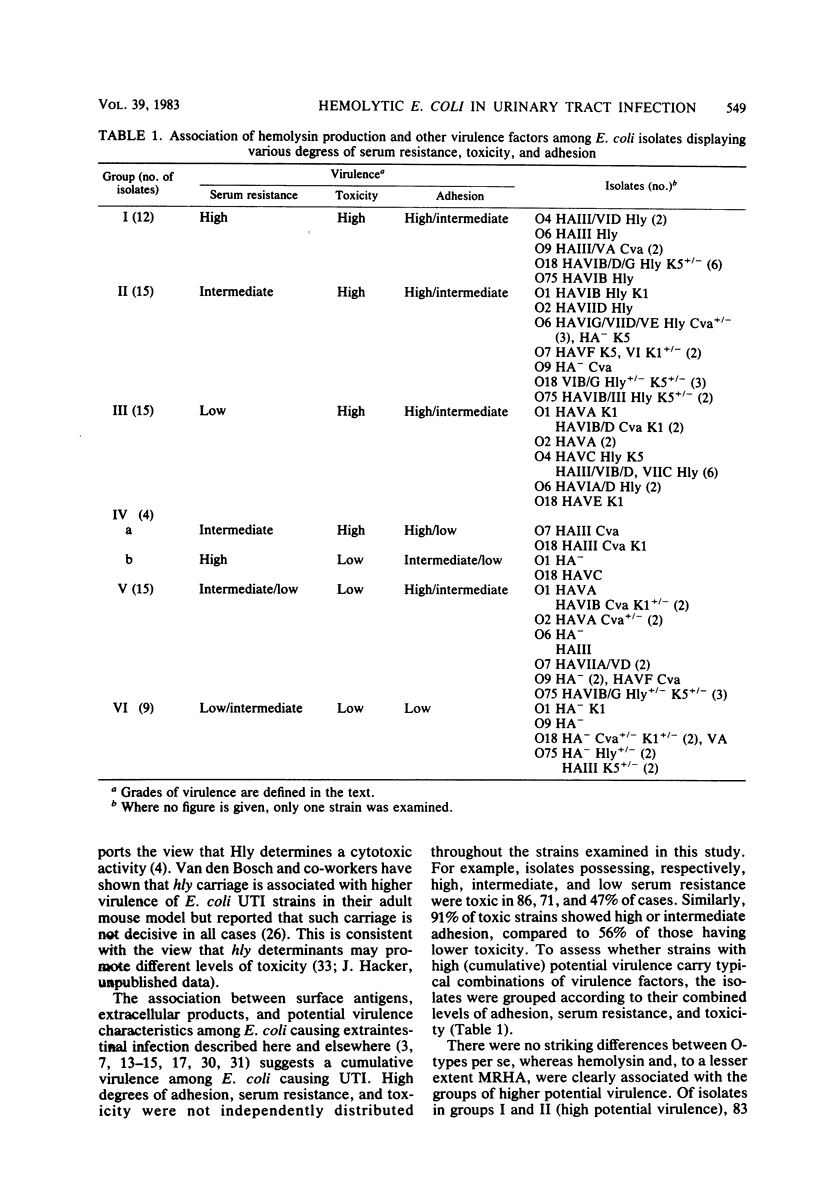
Potential virulence, as defined by combined levels of adhesion to urinary epithelial cells, serum resistance, and mouse toxicity, was assessed for Escherichia coli strains causing symptomatic and asymptomatic urinary tract infections in relation to the carriage of hemolysin and other suspected virulence determinants. Hemolysin production (Hly), associated with certain O (O4, O6, O18, and O75), K (5), and hemagglutination (VI and VII) antigenic types but not colicin V production (Cva), was evident in 83 and 60% of isolates in groups possessing high potential virulence and in only 11 and 6% of those with low virulence. Strains of particular O-types were not more virulent per se, but among the serotypes, specific combinations of virulence factors appeared decisive, e.g., O18 HAVI B/D/G Hly+ K5+/− and O18 HAIII/IVB/V Hly− Cva+/− K1+/− strains were, respectively, of high and low potential virulence. Isolates with high potential virulence were found to a similar extent in symptomatic and asymptomatic infections.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Binns M. M., Davies D. L., Hardy K. G. Cloned fragments of the plasmid ColV,I-K94 specifying virulence and serum resistance. Nature. 1979 Jun 28;279(5716):778–781. doi: 10.1038/279778a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björkstén B., Kaijser B. Interaction of human serum and neutrophils with Escherichia coli strains: differences between strains isolated from urine of patients with pyelonephritis or asymptomatic bacteriuria. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):308–311. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.308-311.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks H. J., O'Grady F., McSherry M. A., Cattell W. R. Uropathogenic properties of Escherichia coli in recurrent urinary-tract infection. J Med Microbiol. 1980 Feb;13(1):57–68. doi: 10.1099/00222615-13-1-57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalieri S. J., Snyder I. S. Cytotoxic activity of partially purified Escherichia coli alpha haemolysin. J Med Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(1):11–21. doi: 10.1099/00222615-15-1-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke E. M., Ewins S. P. Properties of strains of Escherichia coli isolated from a variety of sources. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Feb;8(1):107–111. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-1-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. L., Falkiner F. R., Hardy K. G. Colicin V production by clinical isolates of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):574–579. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.574-579.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eden C. S., Eriksson B., Hanson L. A. Adhesion of Escherichia coli to human uroepithelial cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):767–774. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.767-774.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edén C. S., Janson G. L., Lindberg U. Adhesiveness to urinary tract epithelial cells of fecal and urinary Escherichia coli isolates from patients with symptomatic urinary tract infections or asymptomatic bacteriuria of varying duration. J Urol. 1979 Aug;122(2):185–188. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)56318-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G., Höhne C., Noble M. A., Haldane E. V., Lior H., Young L. S. Hemolysin and K antigens in relation to serotype and hemagglutination type of Escherichia coli isolated from extraintestinal infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jan;13(1):171–178. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.1.171-178.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G., Young L. S., Pitt J. Hemagglutination typing of Escherichia coli: definition of seven hemagglutination types. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Aug;12(2):235–242. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.2.235-242.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried F. A., Vermeulen C. W., Ginsburg M. J., Cone C. M. Etiology of pyelonephritis: further evidence associating the production of experimental pyelonephritis with hemolysis in Escherichia coli. J Urol. 1971 Sep;106(3):351–354. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)61286-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gower P. E., Taylor P. W., Koutsaimanis K. G., Roberts A. P. Serum bactericidal activity in patients with upper and lower urinary tract infections. Clin Sci. 1972 Jul;43(1):13–22. doi: 10.1042/cs0430013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green C. P., Thomas V. L. Hemagglutination of human type O erythrocytes, hemolysin production, and serogrouping of Escherichia coli isolates from patients with acute pyelonephritis, cystitis, and asymptomatic bacteriuria. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):309–315. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.309-315.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagberg L., Jodal U., Korhonen T. K., Lidin-Janson G., Lindberg U., Svanborg Edén C. Adhesion, hemagglutination, and virulence of Escherichia coli causing urinary tract infections. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):564–570. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.564-570.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes C., Phillips R., Roberts A. P. Serum resistance among Escherichia coli strains causing urinary tract infection in relation to O type and the carriage of hemolysin, colicin, and antibiotic resistance determinants. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):270–275. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.270-275.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidin-Janson G., Hanson L. A., Kaijser B., Lincoln K., Lindberg U., Olling S., Wedel H. Comparison of Escherichia coli from bacteriuric patients with those from feces of healthy schoolchildren. J Infect Dis. 1977 Sep;136(3):346–353. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.3.346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minshew B. H., Jorgensen J., Counts G. W., Falkow S. Association of hemolysin production, hemagglutination of human erythrocytes, and virulence for chicken embryos of extraintestinal Escherichia coli isolates. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):50–54. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.50-54.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov F., Orskov I., Evans D. J., Jr, Sack R. B., Sack D. A., Wadström T. Special Escherichia coli serotypes among enterotoxigenic strains from diarrhoea in adults and children. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1976 Jun 1;162(2):73–80. doi: 10.1007/BF02121318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. P., Phillips R. Bacteria causing symptomatic urinary tract infection or asymptomatic bacteriuria. J Clin Pathol. 1979 May;32(5):492–496. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.5.492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver R. P., Aaronson W., Sutton A., Schneerson R. Comparative analysis of plasmids and some metabolic characteristics of Escherichia coli K1 from diseased and healthy individuals. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):200–206. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.200-206.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. W., Koutsaimanis K. G. Experimental Escherichia coli urinary infection in the rat. Kidney Int. 1975 Oct;8(4):233–238. doi: 10.1038/ki.1975.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. W. Sensitivity of some smooth strains of Escherichia coli to the bactericidal action of normal human serum. J Clin Pathol. 1974 Aug;27(8):626–629. doi: 10.1136/jcp.27.8.626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOSTI K. L., GOLDBERG L. M., MONTO A. S., RANTZ L. A. HOST-PARASITE INTERACTION IN PATIENTS WITH INFECTIONS DUE TO ESCHERICHIA COLI. I. THE SEROGROUPING OF E. COLI FROM INTESTINAL AND EXTRAINTESTINAL SOURCES. J Clin Invest. 1964 Dec;43:2377–2385. doi: 10.1172/JCI105112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varian S. A., Cooke E. M. Adhesive properties of Escherichia coli from urinary-tract infections. J Med Microbiol. 1980 Feb;13(1):111–119. doi: 10.1099/00222615-13-1-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vosti K. L. Relationship of hemagglutination to other biological properties of serologically classified isolates of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):507–512. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.507-512.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waalwijk C., van den Bosch J. F., MacLaren D. M., de Graaff J. Hemolysin plasmid coding for the virulence of a nephropathogenic Escherichia coli strain. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):32–37. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.32-37.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch R. A., Dellinger E. P., Minshew B., Falkow S. Haemolysin contributes to virulence of extra-intestinal E. coli infections. Nature. 1981 Dec 17;294(5842):665–667. doi: 10.1038/294665a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Bosch J. F., Postma P., de Graaff J., MacLaren D. M. Haemolysis by urinary Escherichia coli and virulence in mice. J Med Microbiol. 1981 Aug;14(3):321–331. doi: 10.1099/00222615-14-3-321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Bosch J. F., Postma P., van Brenk D., Guinée P. A., de Graaff J., MacLaren D. M. Virulence of Escherichia coli strains isolated from urine of patients with acute cystitis and from faeces of healthy women. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1981;47(2):97–106. doi: 10.1007/BF02342193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Bosch J. F., Verboom-Sohmer U., Postma P., de Graaff J., MacLaren D. M. Mannose-sensitive and mannose-resistant adherence to human uroepithelial cells and urinary virulence of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):226–233. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.226-233.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


