Abstract
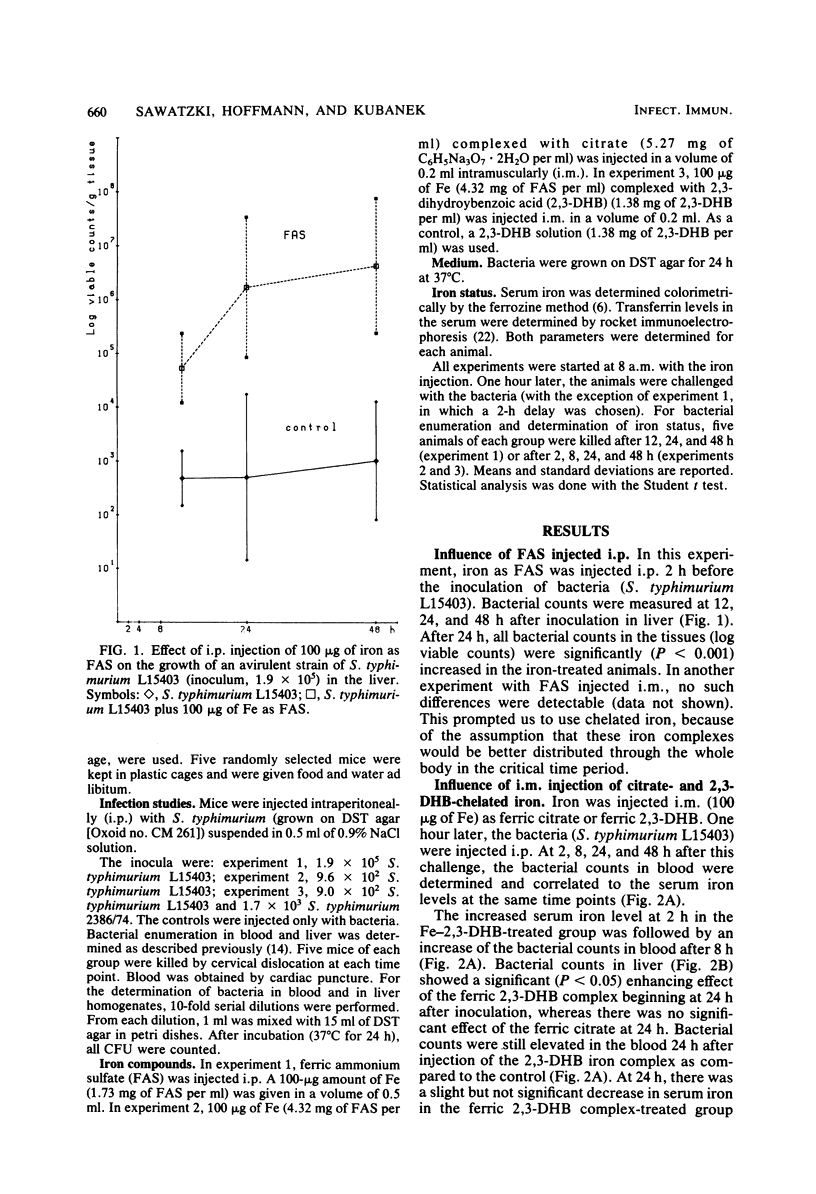
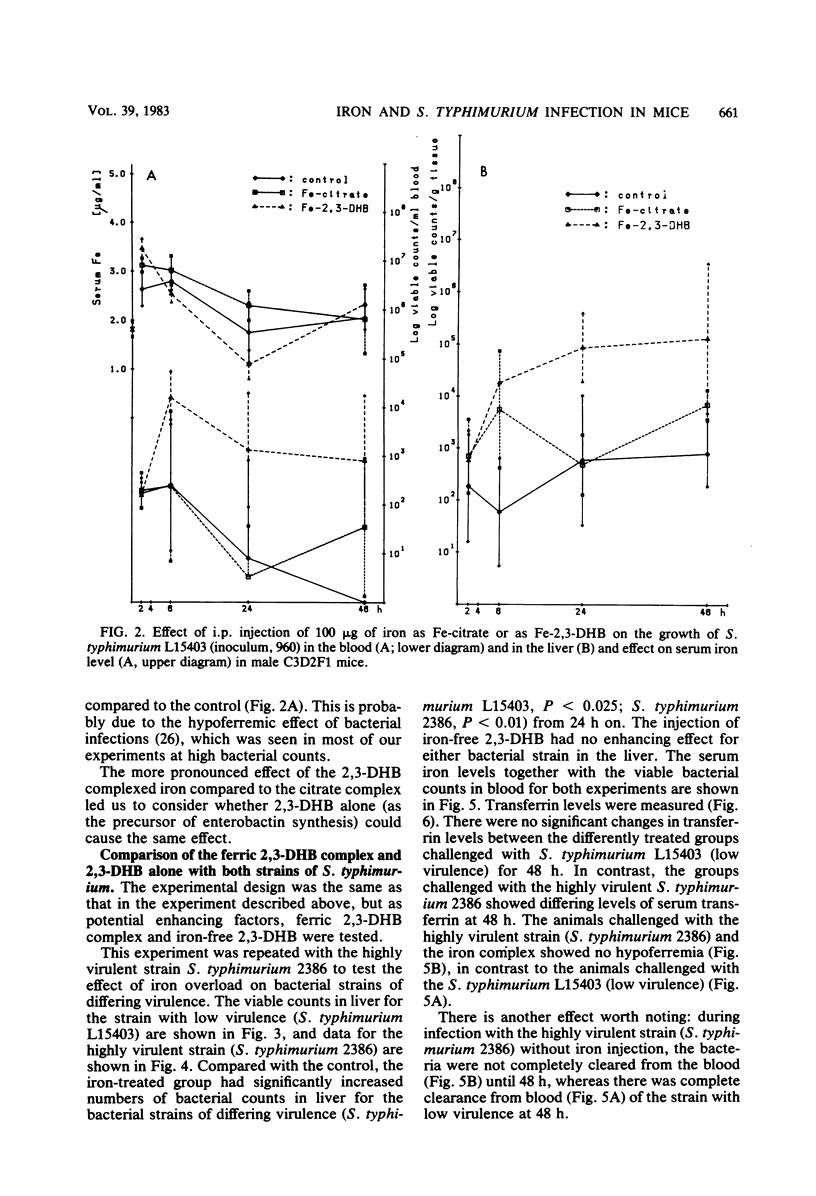
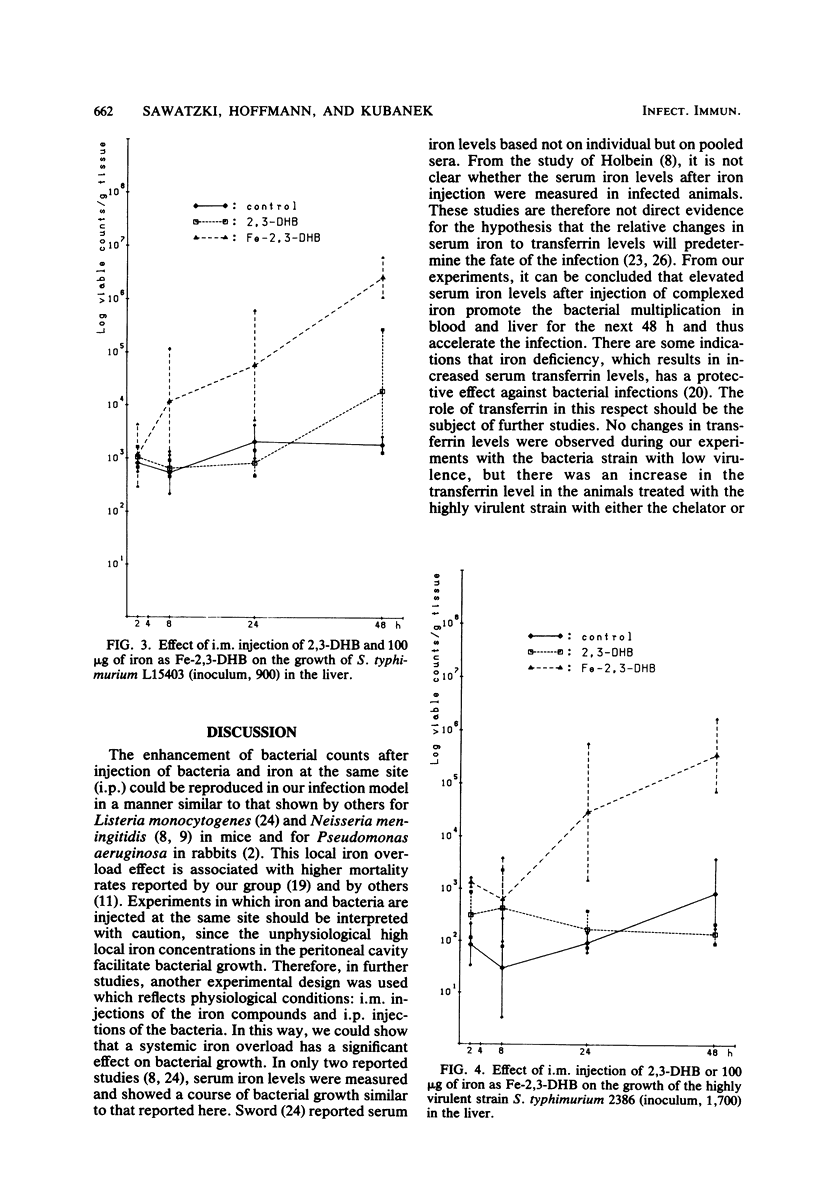
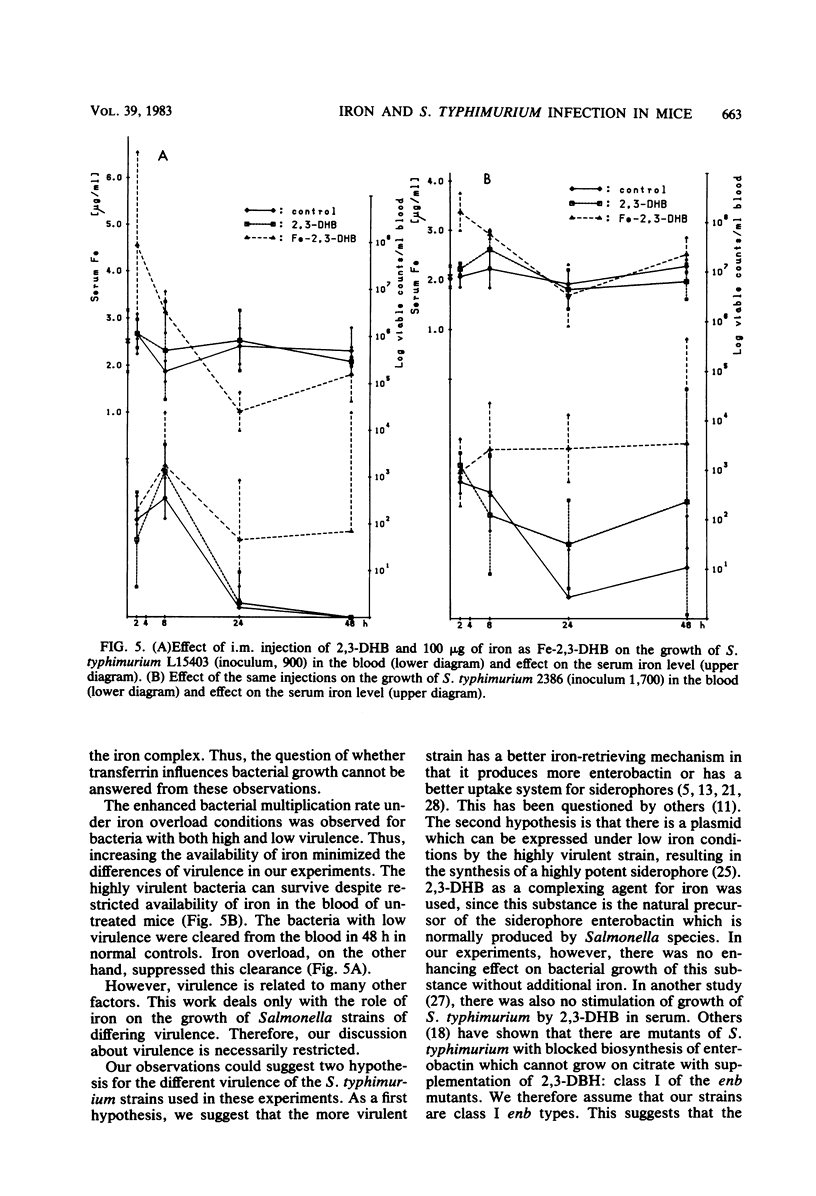
The bacterial growth in the tissues of C3D2F1 male mice was measured during an experimental infection with two Salmonella typhimurium strains (high virulence, strain 2386/74; low virulence, strain L15403). This experimental model was used for evaluation of the pathogenesis in normal and iron-overloaded animals. Acute iron overload was accomplished by intramuscular injections of chelated iron (with 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid and citrate) with a single dose of 100 micrograms of iron per mouse. Bacteria were given intraperitoneally 1 h after the iron injection. Serum iron levels, transferrin levels, and the bacteria counts in blood and liver were measured simultaneously in all animals. There was a significant increase of bacterial growth in all tissues in the iron-treated animals. Iron abolished the normal clearance of the bacteria with low virulence from the blood. This study demonstrates that a general iron overload, as determined by an increased serum iron level, resulting from preinjection of iron, enhances bacterial growth.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bullen J. J., Rogers H. J., Griffiths E. Role of iron in bacterial infection. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;80:1–35. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66956-9_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen J. J., Ward C. G., Wallis S. N. Virulence and the role of iron in Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Infect Immun. 1974 Sep;10(3):443–450. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.3.443-450.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H. A plasmid associated with virulence in the marine fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum specifies an iron-sequestering system. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):566–568. doi: 10.1038/284566a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher J., Goldstein E. The effect of parenteral iron preparations on experimental pyelonephritis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1970 Jun;51(3):280–285. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths E., Humphreys J. Isolation of enterochelin from the peritoneal washings of guinea pigs lethally infected with Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):286–289. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.286-289.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. C., Kadis S., Chapman W. L., Jr Influence of iron on Corynebacterium renale-induced pyelonephritis in a rat experimental model. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):540–545. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.540-545.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbein B. E. Enhancement of Neisseria meningitidis infection in mice by addition of iron bound to transferrin. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):120–125. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.120-125.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbein B. E. Iron-controlled infection with Neisseria meningitidis in mice. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):886–891. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.886-891.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. L., Peterson C. M., Grady R. W., Kumbaraci T., Cerami A., Graziano J. H. Effects of iron chelators and iron overload on Salmonella infection. Nature. 1977 May 5;267(5606):63–65. doi: 10.1038/267063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochan I., Wasynczuk J., McCabe M. A. Effects of injected iron and siderophores on infections in normal and immune mice. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):560–567. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.560-567.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvach J. T., Wiles T. I., Mellencamp M. W., Kochan I. Use of transferrin-iron enterobactin complexes as the source of iron by serum-exposed bacteria. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):439–445. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.439-445.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong J., Neilands J. B. Mechanisms of siderophore iron transport in enteric bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1976 May;126(2):823–830. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.2.823-830.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B., Blanden R. V., Collins F. M. Host-parasite relations in mouse typhoid. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):573–583. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles A. A., Khimji P. L., Maskell J. The variable response of bacteria to excess ferric iron in host tissues. J Med Microbiol. 1979 Feb;12(1):17–28. doi: 10.1099/00222615-12-1-17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. M., Finkelstein R. A. The critical role of iron in host-bacterial interactions. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jun;61(6):1428–1440. doi: 10.1172/JCI109062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polk H. C., Jr, Miles A. A. Enhancement of bacterial infection by ferric iron: kinetics, mechanisms, and surgical significance. Surgery. 1971 Jul;70(1):71–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack J. R., Ames B. N., Neilands J. B. Iron transport in Salmonella typhimurium: mutants blocked in the biosynthesis of enterobactin. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):635–639. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.635-639.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puschmann M., Ganzoni A. M. Eisenüberladung: Einfluss auf spezifische und unspezifische Immunität. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1977 Dec 3;107(48):1774–1776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puschmann M., Ganzoni A. M. Increased resistance of iron-deficient mice to salmonella infection. Infect Immun. 1977 Sep;17(3):663–664. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.3.663-664.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J. Iron-Binding Catechols and Virulence in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):445–456. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.445-456.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawatzki G., Anselstetter V., Kubanek B. Isolation of mouse transferrin using salting-out chromatography on Sepharose CL-6B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jan 30;667(1):132–138. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(81)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schade A. L., Caroline L. An Iron-binding Component in Human Blood Plasma. Science. 1946 Oct 11;104(2702):340–341. doi: 10.1126/science.104.2702.340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sword C. P. Mechanisms of pathogenesis in Listeria monocytogenes infection. I. Influence of iron. J Bacteriol. 1966 Sep;92(3):536–542. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.3.536-542.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner P. J., Williams P. H., Bindereif A., Neilands J. B. ColV plasmid-specific aerobactin synthesis by invasive strains of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):540–545. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.540-545.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron and infection. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):45–66. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.45-66.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins T. D., Lankford C. E. Production by Salmonella typhimurium of 2,3-dihydroxybenzoylserine, and its stimulation of growth in human serum. J Infect Dis. 1970 Feb;121(2):129–136. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.2.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancey R. J., Breeding S. A., Lankford C. E. Enterochelin (enterobactin): virulence factor for Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):174–180. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.174-180.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


