Abstract
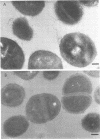
Competence for genetic transformation in an exfoliative toxin-producing strain of Staphylococcus aureus was shown to be dependent on a virion factor that was isolated from a crude bacteriophage 80 alpha lysate. This competence-conferring factor was completely separated from infectious virus particles after either centrifugation through a neutral sucrose velocity gradient or fractionation on a Sepharose 2B gel. Since the competence-conferring factor tends to aggregate, optimal separation was obtained after treatment of the phage factor with the detergent Nonidet P-40. The competence-conferring factor had a molecular weight between 3 X 10(6) and 20 X 10(6) and an approximate sedimentation coefficient of 252. The factor was neutralized after interaction with antiserum prepared against isolated infectious 80 alpha virions. Electron microscopy of transforming cells that were exposed to isolated competence-conferring factor revealed a significant number of abnormally long and aggregated phage tail-like structures attached to the surface of recipient cells. This phenomenon was only observed in the presence of donor DNA, indicating that a phage tail-DNA-surface receptor complex might be one of the early steps in DNA-mediated transformation of S. aureus.
Full text
PDF


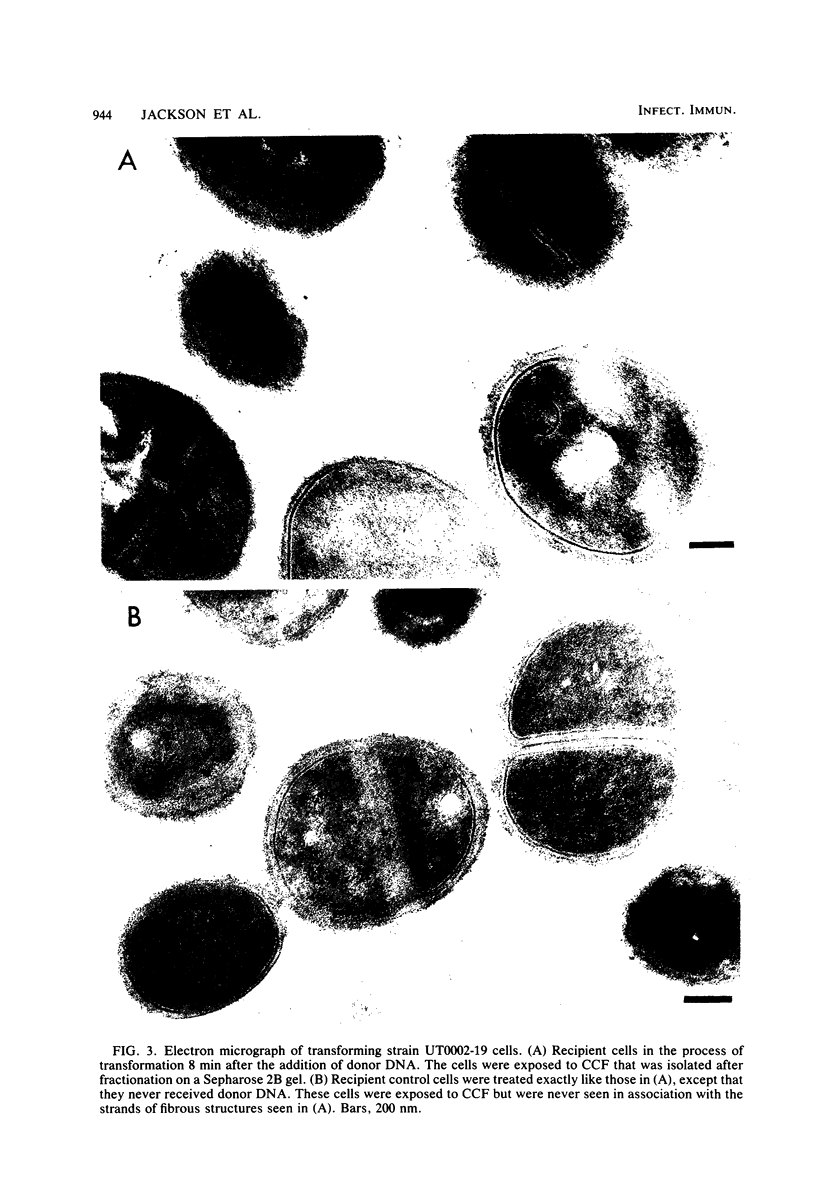



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birmingham V. A., Pattee P. A. Genetic transformation in Staphylococcus aureus: isolation and characterization of a competence-conferring factor from bacteriophage 80 alpha lysates. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):301–307. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.301-307.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. M., Rogolsky M. DNA-mediated transformation in mutants of phage group 2 Staphylococcus aureus. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Aug;26(8):938–951. doi: 10.1139/m80-161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. M., Shoham S. C., Alsup M., Rogolsky M. Genetic mapping in phage group 2 Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):532–541. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.532-541.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVICK R. P. ANALYSIS BY TRANSDUCTION OF MUTATIONS AFFECTING PENICILLINASE FORMATION IN STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Oct;33:121–136. doi: 10.1099/00221287-33-1-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogolsky M. Nonenteric toxins of Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Sep;43(3):320–360. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.3.320-360.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogolsky M., Wiley B. B., Glasgow L. A. Phage group II staphylococcal strains with chromosomal and extrachromosomal genes for exfoliative toxin production. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):44–52. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.44-52.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöström J. E., Philipson L. Role of the phi 11 phage genome in competence of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jul;119(1):19–32. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.1.19-32.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. E., Pattee P. A. Genetic transformation in Staphylococcus aureus: demonstration of a competence-conferring factor of bacteriophage origin in bacteriophage 80 alpha lysates. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):294–300. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.294-300.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. E., Pattee P. A. Transformation in Staphylococcus aureus: role of bacteriophage and incidence of competence among strains. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):778–788. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.778-788.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley B. B., Rogolsky M. Molecular and serological differentiation of staphylococcal exfoliative toxin synthesized under chromosomal and plasmid control. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):487–494. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.487-494.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]