Abstract
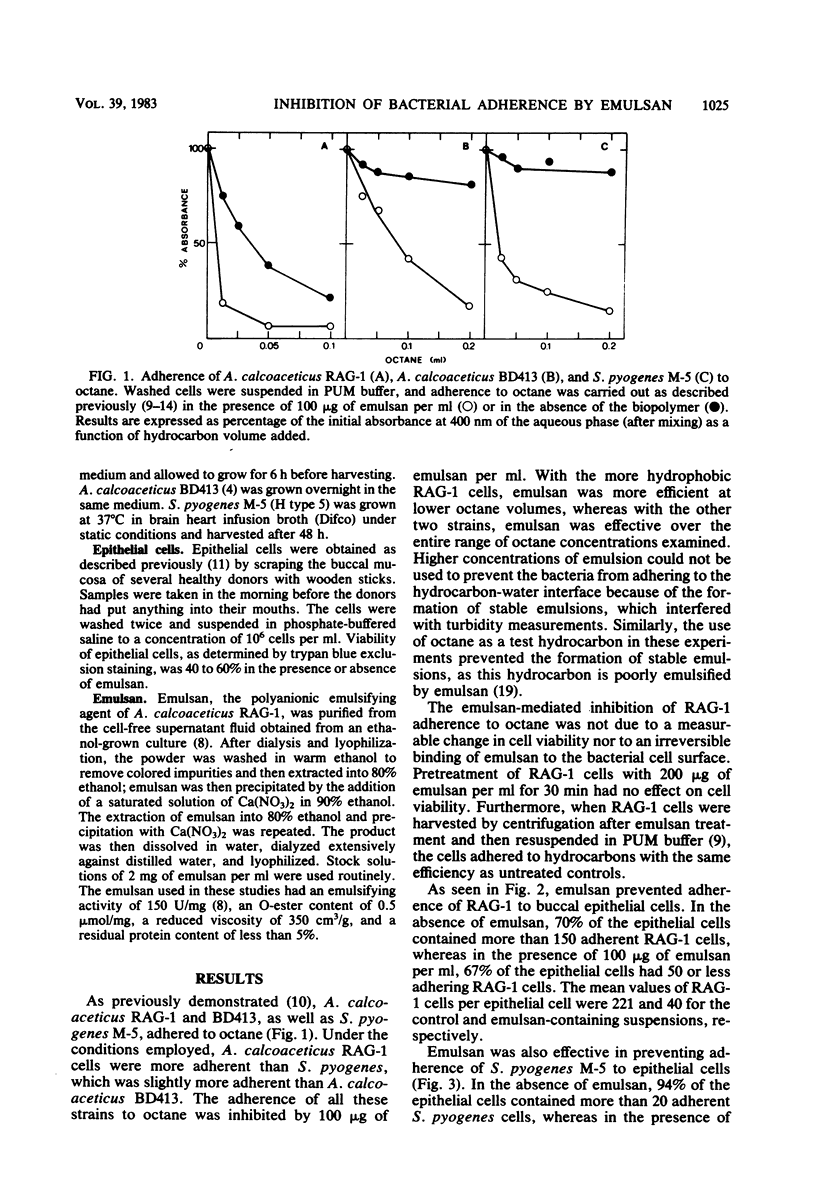
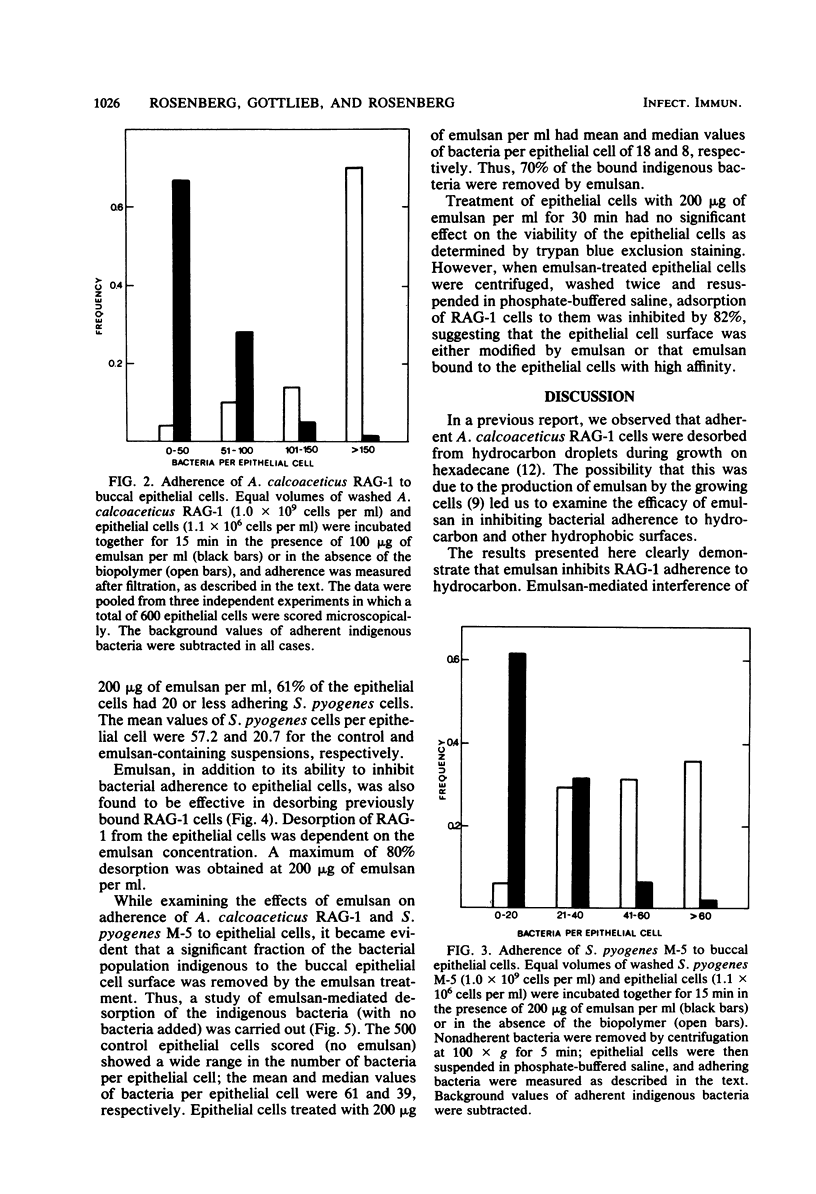
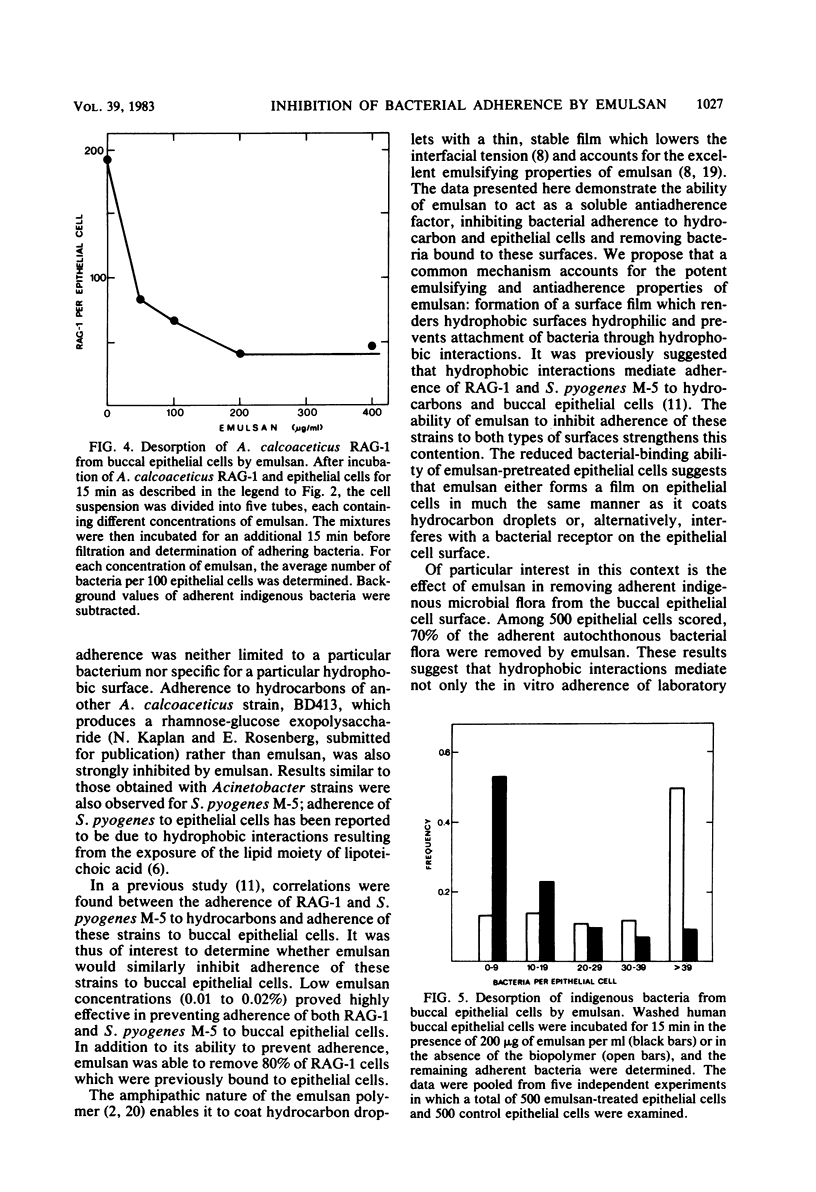
Acinetobacter calcoaceticus RAG-1 and BD413, as well as Streptococcus pyogenes M-5, adhered to octane. Adherence was inhibited by emulsan (100 micrograms/ml), the polymeric emulsifying agent produced by A. calcoaceticus RAG-1. Emulsan also inhibited adherence of S. pyogenes and RAG-1 to buccal epithelial cells. The mean values of bound S. pyogenes per epithelial cell were 57.2 and 20.7 for the control and emulsan-containing suspensions, respectively; mean values of bound RAG-1 per epithelial cell were 221 for the control and 40 for the suspension containing 100 micrograms of emulsan per ml. Desorption of previously bound RAG-1 from epithelial cells by emulsan was concentration dependent: a maximum of 80% desorption was obtained with 200 micrograms of emulsan per ml. The data showing that emulsan desorbed 70% of the indigenous bacterial flora from buccal epithelial cells suggest that hydrophobic interactions mediate not only the in vitro adherence of laboratory strains to epithelial cells, but actually govern the adherence of the majority of the bacteria that colonize this surface. The advantages of using emulsan as an antiadherence agent include its chemical purity, stability, and polymeric nature.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alkan M., Ofek I., Beachey E. H. Adherence pharyngeal and skin strains of group A streptococci to human skin and oral epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):555–557. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.555-557.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juni E., Janik A. Transformation of Acinetobacter calco-aceticus (Bacterium anitratum). J Bacteriol. 1969 Apr;98(1):281–288. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.1.281-288.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Simpson W. A., Beachey E. H. Formation of molecular complexes between a structurally defined M protein and acylated or deacylated lipoteichoic acid of Streptococcus pyogenes. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):426–433. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.426-433.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perers L., Andåker L., Edebo L., Stendahl O., Tagesson C. Association of some enterobacteria with the intestinal mucosa of mouse in relation to their partition in aqueous polymer two-phase systems. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1977 Oct;85B(5):308–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb01980.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg E., Zuckerberg A., Rubinovitz C., Gutnick D. L. Emulsifier of Arthrobacter RAG-1: isolation and emulsifying properties. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):402–408. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.402-408.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Bayer E. A., Delarea J., Rosenberg E. Role of Thin Fimbriae in Adherence and Growth of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus RAG-1 on Hexadecane. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Oct;44(4):929–937. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.4.929-937.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Perry A., Bayer E. A., Gutnick D. L., Rosenberg E., Ofek I. Adherence of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus RAG-1 to human epithelial cells and to hexadecane. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):29–33. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.29-33.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Rosenberg E. Role of adherence in growth of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus RAG-1 on hexadecane. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):51–57. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.51-57.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth C. J., Jonsson P., Olsson E., Soderlind O., Rosengren J., Hjertén S., Wadström T. Differences in hydrophobic surface characteristics of porcine enteropathogenic Escherichia coli with or without K88 antigen as revealed by hydrophobic interaction chromatography. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):462–472. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.462-472.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerberg A., Diver A., Peeri Z., Gutnick D. L., Rosenberg E. Emulsifier of Arthrobacter RAG-1: chemical and physical properties. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):414–420. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.414-420.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Oss C. J. Phagocytosis as a surface phenomenon. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:19–39. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


